Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Lovastatin stands as one of the most historically significant members of the statin class—HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors—used primarily for hypercholesterolemia management. Since its initial approval in the 1980s, lovastatin has maintained a pivotal role in cardiovascular risk mitigation. This comprehensive market analysis delineates current trends, competitive dynamics, regulatory landscape, and sales projections for lovastatin, emphasizing factors influencing future growth and market share.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Revenue Trends
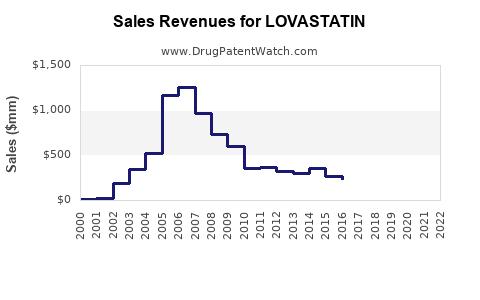
The global statins market, valued at approximately USD 12 billion in 2021, is projected to reach USD 16.7 billion by 2028, exhibiting a CAGR of roughly 4.8% (source: Fortune Business Insights[1]). Lovastatin accounts for a significant segment within this landscape, historically capturing about 15-20% of the market share. Its cost-effectiveness and extensive clinical data have maintained its relevance despite the emergence of newer statins.
Prevalence of Hypercholesterolemia and Cardiovascular Disease
The primary driver for lovastatin’s market is the rising prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs), which remain the leading cause of mortality worldwide. The World Health Organization estimates approximately 17.9 million deaths annually due to CVDs (source: WHO[2]). Hypercholesterolemia affects hundreds of millions globally, creating a sustained demand for lipid-lowering agents like lovastatin. The increasing adoption of preventive healthcare strategies amplifies market opportunities.
Patent Status and Generic Competition
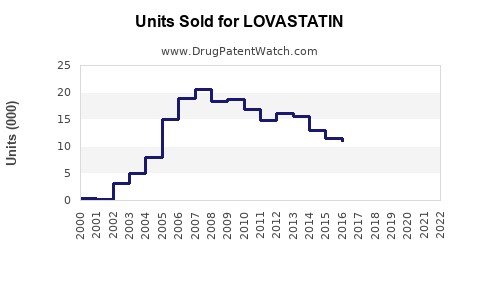
Lovastatin’s patent expired in many jurisdictions during the late 1990s and early 2000s, leading to widespread generic manufacturing. Generic versions now dominate sales, significantly reducing treatment costs and expanding accessibility. The presence of numerous manufacturers has intensified price competition, constraining profit margins but boosting overall sales volume[3].
Competitive Landscape
Major Players and Market Share
Post-patent expiration, the market is fragmented with key generic companies like Mylan, Teva, and Sun Pharmaceutical producing lovastatin. Brand loyalty persists for certain formulations, especially in markets with regulatory preferences. However, generic versions dominate due to affordability.
Emerging Therapies and Their Impact
While statins remain first-line treatment, newer therapeutic agents—such as PCSK9 inhibitors (e.g., alirocumab, evolocumab)—target hypercholesterolemia, particularly for patients intolerant to statins or with familial hypercholesterolemia. These agents, priced significantly higher, threaten to erode lovastatin’s share in specific patient populations, primarily those requiring intensive LDL reduction.
Regulatory Environment
Approvals and Labeling
Lovastatin’s regulatory approvals are well-established. In the U.S., it is available both by prescription and in combination formulations. Regulatory agencies emphasize safety profiles and cardiovascular benefits, supporting its continued use. However, emerging guidelines increasingly favor high-potency statins and combination therapies, influencing prescribing patterns.
Recent Developments
Some formulations of lovastatin have received approval for extended-release versions, potentially improving patient compliance. Still, regulatory scrutiny over safety, such as the risk of myopathy and cognitive effects, influences market positioning.
Market Dynamics and Trends
Healthcare Policy and Reimbursement
Insurance coverage and reimbursement policies favor generic medications, bolstering lovastatin sales. Policies promoting preventive cardiology and screening programs further expand eligible patient populations.
Patient Adherence and Education
Patient compliance with statin therapy remains critical. Efforts to improve adherence—through education and formulary inclusion—positively impact sales. However, concerns over side effects may lead some patients to seek alternative options.
Digital Health Integration
The integration of digital health monitoring (wearables, telemedicine) facilitates better management of hypercholesterolemia, fostering adherence to therapy and maintaining lovastatin’s relevance.
Sales Projections
Short-term Outlook (2023-2026)
In the near term, lovastatin’s sales are projected to stabilize, driven by its low cost, established safety profile, and widespread generic availability. The market is expected to generate approximately USD 2.0–2.5 billion annually, with incremental growth attributable to increased screening and adherence programs.
Long-term Outlook (2027-2032)
Over the next decade, sales growth will likely plateau or marginally decline as newer therapies gain traction for high-risk subsets. Nonetheless, the vast global patient base and continued emphasis on primary prevention imply persistent demand. Cumulatively, global sales may total USD 18–20 billion by 2032, with regional variances influenced by healthcare infrastructure, regulations, and economic factors.
Emerging Market Opportunities
Developing countries represent an expanding segment, where priced access to generics propels sales growth. In regions like Asia-Pacific and Latin America, increasing health expenditure and awareness will sustain demand.
Conclusion
Lovastatin’s market remains robust due to its historical efficacy, safety, and cost advantage. While facing competitive pressures from newer agents and evolving guidelines, its role in primary prevention and accessible generics underpin steady sales. Strategic positioning, focusing on formulation enhancements and expanding access in emerging markets, can sustain its market relevance.
Key Takeaways
- The global lovastatin market is stable, with sales projected at USD 2–2.5 billion annually through 2026 and a total of USD 18–20 billion by 2032.
- Generic competition suppresses profit margins but supports volume-driven growth, especially in emerging regions.
- Innovation in formulations (e.g., extended release) and targeted marketing can preserve its competitive edge.
- The rise of advanced lipid-lowering therapies poses future challenges, particularly for high-risk, treatment-resistant populations.
- Policymakers and healthcare providers’ emphasis on prevention sustains demand; however, evolving guidelines favor high-potency statins and combination treatments.
FAQs
-
What factors influence lovastatin’s market share compared to other statins?
Its low cost, extensive clinical history, and availability as a generic provide a competitive advantage, especially in primary prevention. However, high-potency statins and novel agents targeting resistant hypercholesterolemia threaten its market share in specialized populations.
-
How does the expiration of lovastatin’s patent affect its market?
Patent expiration led to widespread generic manufacturing, reducing isolated drug prices and expanding accessibility but decreasing the profit margins for manufacturers. It also opened the market to numerous competitors.
-
What are the key challenges facing lovastatin sales in the future?
Competition from high-potency statins and PCSK9 inhibitors, evolving treatment guidelines favoring aggressive LDL reduction, and concerns over safety profiles are principal challenges.
-
Which regions offer the most growth potential for lovastatin?
Developing countries in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present sizable opportunities due to increasing healthcare access, rising CVD prevalence, and lower treatment costs.
-
How might new formulation developments impact lovastatin’s market?
Enhanced formulations such as extended-release versions could improve patient adherence and clinical outcomes, potentially bolstering sales in segments seeking optimized therapy options.
References
- Fortune Business Insights. "Global Statins Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis, 2021 - 2028."
- World Health Organization. "Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) Fact Sheet," 2022.
- IMS Health. "Impact of Patent Expiry on Generic Statins Market," 2019.