Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for LINDANE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
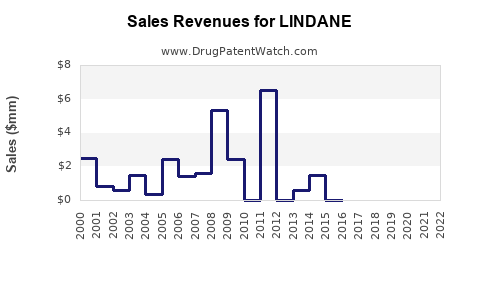
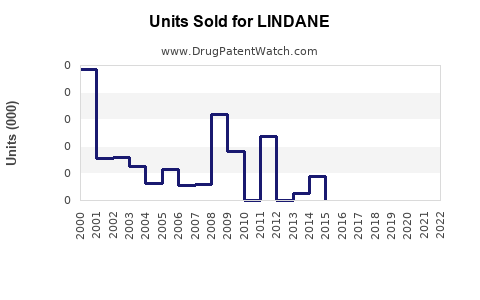
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for LINDANE
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINDANE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| LINDANE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| LINDANE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| LINDANE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| LINDANE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2018 |
| LINDANE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2017 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Lindane
Introduction
Lindane, a hexachlorocyclohexane compound, historically used as an insecticide and dermatological treatment for scabies and lice infestations, has experienced significant market shifts due to regulatory actions stemming from health and environmental concerns. Despite its decline in many regions, understanding the current market landscape and future sales potential is crucial for stakeholders considering niche applications or emerging markets.
Regulatory Landscape and Industry Context
Lindane’s use has been substantially curtailed globally. Notably, the European Union has banned lindane as a pesticide since 2008, citing environmental persistence and health risks [1]. Similarly, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) revoked approval for agricultural uses in 2007, restricting lindane’s application predominantly to pharmaceutical formulations under specific conditions [2].
Despite these restrictions, lindane remains approved as a pharmaceutical for topical treatment of scabies and lice in certain markets, including some Latin American and Asian countries, due to limited availability of alternative therapies in those regions. However, growing regulatory pressures and international organizations, such as WHO, are pushing for complete phase-out owing to carcinogenicity concerns.
Market Drivers
The current market drivers for lindane predominantly include:
- Limited pharmaceutical demand: Use persists mainly in regions with limited access to newer, safer pediculicides or scabicides.
- Regulatory gaps: In certain jurisdictions, regulatory barriers are less stringent, maintaining a niche market.
- R&D for alternative uses: Ongoing research may uncover new applications, although none have yet gained commercial traction.
Market Size and Segmentation
Pharmaceutical Use Market
The pharmaceutical segment constitutes the remaining legal market for lindane. Globally, the demand is minor, estimated at approximately hundreds of kilograms annually, primarily in developing countries where it is still licensed under strict control.
- Regional Distribution:
- Latin America: Accounts for roughly 60% of pharmaceutical lindane sales, driven by longstanding use and limited access to alternatives.
- Asia-Pacific: Represents approximately 30%, with India and neighboring countries showing continued prescribing practices.
- Africa and Middle East: Contributes around 10%, with varying regulatory statuses.
Environmental and Agricultural Markets
Most countries have phased out lindane as an agricultural pesticide. Consequently, this segment’s global market is negligible, with eradication efforts decreasing any potential sales to near zero.
Market Challenges
- Regulatory bans: Significant reduction in allowable uses impacts market size.
- Health and safety concerns: Persistent carcinogenicity and neurotoxicity risks deter new formulations and market expansion.
- Alternatives: Safer, more effective, and environmentally friendly treatments (e.g., permethrin, ivermectin) dominate both pharmaceutical and vector control markets.
Forecasting Sales Trends
Considering the current restrictive environment, future sales growth of lindane is expected to decline further. Based on market intelligence and regulatory trajectories:
- Short-term outlook (1-3 years): Sales may stabilize in restricted markets, totaling approximately 200-300 kg annually in niche segments.
- Medium-term (4-7 years): A gradual decline, with sales decreasing by 10-15% annually, driven by regulatory bans and the introduction of alternatives.
- Long-term (8-10 years): Presumed near-zero sales, as global health agencies and regulatory bodies eliminate its medicinal use altogether.
Opportunities and Threats
Opportunities
- Niche markets: Some countries with limited regulation may continue use, representing low-volume niche markets.
- Research advancements: Potential development of lindane derivatives with improved safety profiles could reopen markets.
Threats
- Regulatory phase-outs: Accelerated bans could eliminate remaining markets.
- Environmental and health activism: Increased advocacy against lindane hampers market acceptance.
- Emergence of safer alternatives: Rapid adoption reduces market need.
Recommendations for Stakeholders
- For pharmaceutical manufacturers, diversify portfolios to include safer pediculicides and acaricides.
- For investors, prioritize companies focusing on alternative treatments and environmentally sustainable solutions.
- For regulators, accelerate phase-out timelines aligned with global health guidelines, reducing illegal use.
Key Takeaways
- Lindane’s market has significantly contracted, driven by strict regulations and health concerns.
- The current global pharmaceutical demand for lindane is minimal, with annual sales estimated below 300 kg.
- Future sales are projected to decline sharply over the next decade, aligning with global bans and the adoption of safer, more effective therapies.
- Niche markets may persist temporarily in some regions, but these are unlikely to sustain long-term growth.
- Strategic shifts toward research, innovation, and regulatory compliance are essential for stakeholders involved in lindane’s lifecycle.
FAQs
1. Why has lindane’s global market declined so sharply?
Regulatory bans due to health risks, environmental persistence, and availability of safer alternatives have led to significant market contraction.
2. Are there any existing legal markets for lindane?
Yes, limited pharmaceutical use persists in some countries with relaxed regulations, but these constitute a small and shrinking segment.
3. What are the primary health concerns associated with lindane?
Lindane has been linked to carcinogenicity, neurotoxicity, and reproductive health issues, prompting bans and restrictions worldwide.
4. Could lindane experience a resurgence?
Unlikely, given the severity of health concerns and strong regulatory movements toward complete phase-out.
5. What are the emerging alternatives replacing lindane?
Permethrin, ivermectin, and other safer compounds dominate current treatments for lice and scabies, offering comparable efficacy with lower risks.
References
[1] European Commission. (2008). Regulation (EC) No 1107/2009 concerning the market placement of plant protection products.
[2] U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2007). Revocation of Lindane Registration.
More… ↓
