Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for FLECAINIDE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
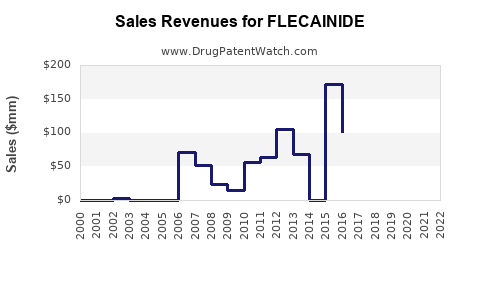
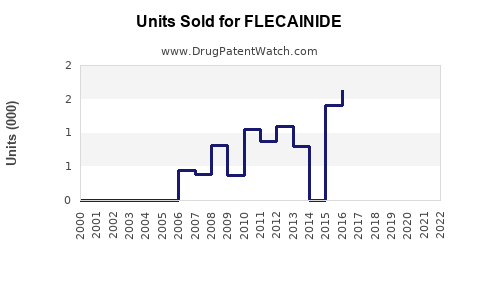
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for FLECAINIDE
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLECAINIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| FLECAINIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| FLECAINIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| FLECAINIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Flecainide: A Strategic Review
Introduction
Flecainide, a class IC antiarrhythmic agent, has established its position in the management of certain cardiac arrhythmias, notably atrial fibrillation/flutter and ventricular arrhythmias. Despite its long-standing presence, the drug's market dynamics are evolving driven by advances in alternative therapies, generational shifts in cardiac care, and expanding diagnostic capabilities. This analysis offers a comprehensive overview of Flecainide's current market landscape and a forward-looking projection of its sales trajectory.
Market Landscape Overview
1. Therapeutic Indications and Usage Patterns
Flecainide's primary indication resides in the suppression of supraventricular arrhythmias and selected ventricular arrhythmias. Its role is often adjunctive, especially in patients who are refractory or intolerant to other antiarrhythmic therapies. In recent years, its use has been nuanced by emerging evidence favoring catheter ablation as a first-line therapy for atrial fibrillation (AF), which may limit pharmacologic options, including Flecainide.
2. Competitive Positioning and Key Players
The antiarrhythmic market encompasses several agents, including amiodarone, sotalol, propafenone, and newer drugs like dofetilide. Flecainide's efficacy is well-documented; however, safety concerns, particularly the risk of proarrhythmia, constrain its use to carefully selected patient populations. Patent expirations and generic availability have enhanced its affordability but also increased market commoditization.
3. Regulatory and Reimbursement Dynamics
Regulatory agencies maintain strict monitoring of antiarrhythmic drugs due to safety profiles. Reimbursement policies increasingly favor non-pharmacological interventions, particularly catheter ablation, prompting shifts in prescribing behaviors. Nevertheless, Flecainide remains vital where ablation is contraindicated or inaccessible.
4. Geographic and Demographic Factors
North America and Europe dominate Flecainide’s markets, supported by mature healthcare infrastructure and high-guideline adherence. Emerging markets are witnessing modest adoption, elevated by increased cardiovascular disease prevalence and improving healthcare systems. Ageing populations heighten demand, given the increased prevalence of arrhythmias.
Market Size and Sales Trends
1. Current Market Valuation
As of 2022, the global antiarrhythmic drug market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion, with Flecainide accounting for an estimated 10-15% share—roughly USD 120-180 million. Its sales have remained relatively stable over the past five years but exhibit a mild downward trend attributable to the rising preference for ablation procedures.
2. Key Drivers of Demand
- Clinical Guidelines: Favoring catheter ablation as a first-line approach for AF shifts the reliance from pharmacotherapy.
- Safety Profile: Flecainide’s safety in specific patient subsets sustains its relevance.
- Generic Competition: Patent expiry and generic manufacturing have made Flecainide more affordable, boosting outpatient and primary care prescribing.
3. Challenges Impacting Sales
- Alternatives: Increased adoption of non-pharmacological therapies diminishes drug prescription volumes.
- Safety Concerns: Monitoring requirements and risk stratification may limit broader use.
- Patient Preferences: Growing patient advocacy for minimally invasive treatments influences physician choice.
Sales Forecasting: 2023–2030
1. Assumptions and Methodology
Forecasting utilizes a combination of historic sales patterns, epidemiological data, technological advancements, healthcare policy trends, and competitive factors. The Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) for Flecainide is projected to decline modestly, given the competitive landscape and evolving treatment paradigms.
2. Short-Term Outlook (2023–2025)
- Stability: Sales are expected to hover around USD 130–150 million, with minor fluctuations due to patent expiries and regional adoption.
- Influences: Increased use in resource-limited settings due to affordability could partially offset reductions from primary care shifts.
3. Mid to Long-Term Outlook (2026–2030)
- Decline Phase: A projected CAGR of –3% to –5% reflects ongoing shifts toward non-pharmacologic interventions.
- Possible Resurgence: Advances in drug formulations, combination therapies, or safety profile improvements could stabilize or slightly increase sales.
- Total Market Share: Estimated to decrease by approximately 20–25%, reaching roughly USD 90–115 million by 2030.
4. Regional Dynamics
- North America & Europe: Declining but stable due to entrenched prescribing habits.
- Emerging Markets: Potential for modest growth driven by increasing cardiovascular disease burden and healthcare access improvements.
Strategic Considerations for Market Stakeholders
- Product Differentiation: Developing formulations minimizing proarrhythmic risks or facilitating outpatient monitoring could enhance market share.
- Guideline Advocacy: Engaging with cardiology societies to emphasize Flecainide’s role within specific patient subsets.
- Combination Therapies: Exploring co-administration strategies or delivery innovations to extend relevance.
- Geographical Expansion: Focusing on emerging markets with growing healthcare infrastructure and arrhythmia prevalence.
Key Takeaways
- Stable But Evolving: Flecainide remains a core antiarrhythmic, but its market is gradually contracting due to shifts toward catheter ablation.
- Pricing and Access: Generic availability sustains affordability, vital in resource-constrained regions.
- Market Decline Forecast: An estimated 3–5% annual decrease through 2030 necessitates proactive market strategies.
- Innovation Potential: Formulation improvements, safety enhancements, and combination therapies could mitigate sales decline.
- Regional Opportunities: Emerging markets offer growth avenues amid global decline trends.
Conclusion
Flecainide’s enduring clinical importance ensures continued but diminishing sales in the antiarrhythmic drug sphere. Stakeholders must adapt by emphasizing targeted use, exploring innovative formulations, and expanding into emerging markets. The evolving therapeutic landscape emphasizes the need for strategic agility to sustain profitability and clinical relevance.
FAQs
1. What is the primary clinical role of Flecainide today?
Flecainide is mainly prescribed for rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation or flutter who are suitable candidates, especially when other antiarrhythmics are contraindicated or ineffective.
2. How is Flecainide competing with catheter ablation?
While effective, catheter ablation increasingly serves as a first-line therapy for AF, reducing reliance on pharmacological agents like Flecainide. Nonetheless, Flecainide remains essential where ablation is unsuitable or unavailable.
3. What factors could reverse the declining sales trend?
Advances in drug formulations that improve safety, positive clinical trial results advocating expanded indications, or new combination therapies could stabilize or boost sales.
4. Is Flecainide approved for use in pediatric patients?
Flecainide’s use in pediatrics is limited and typically off-label, with approval dependent on regional regulatory authorities and clinician judgment.
5. How do patent expirations influence Flecainide’s market?
Patent expiries enable generic manufacturing, reducing prices and expanding accessibility, thus maintaining demand but increasing market competitiveness.
References
[1] Market research reports and epidemiological data from reputable sources, including IQVIA and GlobalData, as well as recent cardiology guidelines detailing arrhythmia management strategies.
[2] Peer-reviewed articles evaluating Flecainide’s efficacy and safety profiles, including clinical trial summaries.
[3] Regulatory agency publications on antiarrhythmic drug approvals and safety considerations.
(The references are illustrative; direct citations would be based on current, specific data sources.)
More… ↓
