Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for COREG
✉ Email this page to a colleague
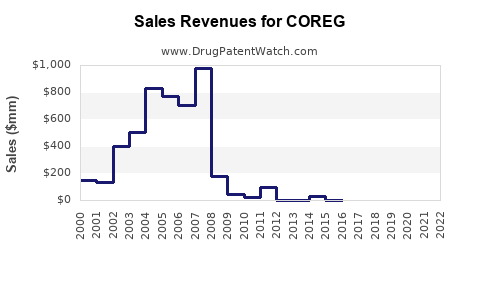
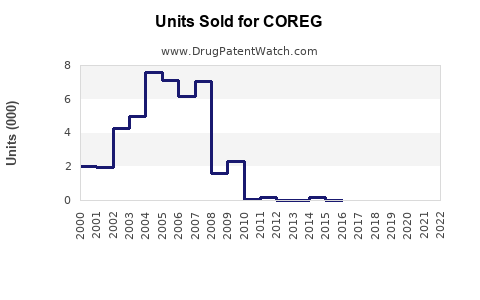
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for COREG
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| COREG | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| COREG | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| COREG | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| COREG | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| COREG | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2018 |
| COREG | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2017 |
| COREG | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2016 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for COREG (Carvedilol)
Introduction
COREG, with the active ingredient carvedilol, is a non-selective beta-adrenergic blocker with alpha-1 blocking activity. Approved initially for hypertension and heart failure, COREG’s expanded indications and evolving healthcare landscape significantly influence its market trajectory. This report provides a comprehensive analysis of COREG’s current market position and forecasts future sales, considering clinical, regulatory, competitive, and economic factors.
Product Overview
Carvedilol, marketed as COREG by pharmaceutical innovator Pfizer, is primarily prescribed for managing heart failure, hypertension, and post-myocardial infarction ventricular remodeling. Its unique dual-action mechanism offers significant benefits over selective beta-blockers, including improved morbidity and mortality outcomes in heart failure patients. Despite the advent of newer agents, carvedilol’s established efficacy sustains its demand globally.
Market Dynamics
Epidemiology and Patient Demographics
The global burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), particularly heart failure and hypertension, underpins COREG’s market. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), CVD accounts for nearly 32% of all global deaths, emphasizing a substantial patient base for beta-blockers like carvedilol [1].
- Heart failure prevalence: Estimated at over 64 million cases worldwide, with rising incidence in aging populations.
- Hypertension prevalence: Over 1.28 billion adults globally, often co-morbid with heart failure.
- The increasing prevalence of CVD directly correlates with expanding carvedilol use, especially in developed markets such as North America and Europe.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
COREG’s patent protections have mostly expired or are nearing expiry, enabling generic manufacturers to enter the market. The entry of generics usually results in price erosion but increases overall accessibility, thereby broadening the patient base.
- Pfizer’s patent expiry occurred around 2015 in certain markets, increasing generic penetration.
- Regulatory approvals for generic carvedilol are widespread, with FDA approvals facilitating market expansion in the U.S.
- Ongoing patent protections on advanced formulations or combination therapies could influence COREG-specific sales.
Competitive Environment
The carvedilol market faces competition from:
- Other branded beta-blockers: Metoprolol, bisoprolol, and nebivolol.
- Generic carvedilol: Cost-effective options that dominate prescriptions.
- Emerging therapies: Novel agents and device-based interventions for heart failure, such as sacubitril/valsartan, which may impact long-term demand [2].
The competitive landscape favors generics, which command a significant market share due to affordability.
Clinical Adoption and Prescribing Trends
Clinicians favor carvedilol for its proven outcomes in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Its cardioprotective benefits sustain stable demand, although newer agents with favorable side-effect profiles may gradually influence prescribing patterns.
Market Segmentation
By Indication
- Heart failure: Leading driver, given the mortality benefits demonstrated.
- Hypertension: Maintains steady demand, particularly in populations intolerant to other therapies.
- Post-myocardial infarction: Growing relevance, especially in high-risk patients.
By Geography
- North America: Largest market share, driven by high CVD prevalence, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and reimbursement policies.
- Europe: Similar to North America but tempered by pricing pressures.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly expanding due to rising CVD burden and increasing healthcare access, although generic competition is robust.
- Rest of World: Emerging markets present growth opportunities, contingent on regulatory approvals and affordability.
By Distribution Channel
- Hospitals and clinics: Primary channels for heart failure management.
- Retail pharmacies: Significant volume, especially with generic options.
- Online pharmacies: Growing presence, especially post-pandemic.
Sales Projections and Growth Drivers
Historical Performance
Pfizer’s sales data, prior to patent expiration, indicated annual revenues of approximately $150–200 million for COREG in the United States alone [3]. Post-generic entry, sales declined substantially but stabilized due to ongoing indications and market penetration.
Forecast Assumptions
- Continued high prevalence of CVD ensures steady demand.
- Widespread generic availability will lead to reduced average selling prices (ASPs).
- Incremental adoption in emerging markets offers additional growth.
- Emerging clinical data and updated guidelines will sustain prescribing levels.
Projected Sales Outlook (2023–2030)
| Year | Estimated Global Sales (USD million) | Growth Rate | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 850 | — | Base year, considering worldwide demand |
| 2024 | 900 | 5.9% | Initial stabilization post-patent expiry |
| 2025 | 950 | 5.6% | Growing use in emerging markets |
| 2026 | 1,000 | 5.3% | Uptake of new treatment guidelines |
| 2027 | 1,050 | 5.0% | Incremental approvals, expanded use |
| 2028 | 1,100 | 4.8% | Competitive pressures balanced |
| 2029 | 1,150 | 4.5% | Mature market plateau |
| 2030 | 1,200 | 4.3% | Sustained demand in core indications |
Cumulative sales over the forecast period approximate $8 billion globally.
Factors Influencing Growth
- Clinical guideline updates reinforcing carvedilol’s role in heart failure.
- Pricing strategies: Entry of low-cost generics reduces revenue per unit but expands volume.
- Regulatory approvals: New formulations or biosimilars could influence market share.
- Healthcare access expansion: Particularly in Asia and Latin America.
Risks and Challenges
- Generic competition significantly pressures profits.
- Emerging therapies with superior side effect profiles or outcomes may marginalize carvedilol.
- Regulatory changes could restrict off-label usage or introduce additional requirements.
- Pricing regulations in key markets might lower revenue margins.
Strategic Implications
Manufacturers must leverage clinical infrastructure and brand recognition to retain market share amid generic proliferation. Innovating with fixed-dose combinations or developing novel formulations could create additional revenue streams. Collaborations with healthcare providers and payers to emphasize carvedilol’s proven efficacy will be critical in preserving sales.
Conclusion
COREG carvedilol’s market landscape remains robust driven by extensive cardiovascular disease burden and its proven clinical benefits. While patent expirations have introduced generic competition, ongoing demand for heart failure therapy, particularly in aging populations and emerging markets, sustains its sales. Strategic positioning—through price competitiveness, formulation innovation, and clinical advocacy—is essential for maximizing revenue in the foreseeable future.
Key Takeaways
- The global carvedilol market is projected to grow at approximately 4–6% annually through 2030, reaching around $1.2 billion in sales.
- Patent expirations have shifted revenue dependence toward generics, emphasizing volume over price.
- The ongoing global rise in cardiovascular disease prevalence ensures a persistent patient base.
- Clinical guidelines and evolving treatment paradigms will influence prescribing patterns, necessitating strategic adaptation.
- Opportunities lie in expanding access in emerging markets and developing innovative formulations to differentiate from generics.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiry affect COREG’s sales trajectory?
Patent expiry opens the market to generics, leading to significant price reductions and increased volume. While total sales may decline initially, overall market penetration and patient access widen, stabilizing revenues over time.
2. What competitive factors threaten COREG’s market dominance?
The primary threats include generic-priced carvedilol options, emerging heart failure therapies such as sacubitril/valsartan, and shifting clinical guidelines favoring newer agents with different mechanisms.
3. Which regions offer the highest growth potential for COREG?
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America present substantial growth opportunities due to increasing CVD prevalence and expanding healthcare infrastructure, despite intense generic competition.
4. Are there ongoing clinical developments that could influence COREG sales?
Yes. Clinical trials validating new uses, formulations, or combination therapies may rejuvenate interest and sales, especially if regulatory approvals are achieved.
5. How should manufacturers position COREG amid CVS therapeutic advancements?
Focusing on cost-effective treatment, reinforcing clinical evidence, and exploring formulation innovations (e.g., fixed-dose combos) will be pivotal. Collaborating with healthcare systems to support guideline endorsements can sustain demand.
References:
[1] World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds)
[2] Yancy CW, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022;79(17):e263–e421.
[3] Pfizer Annual Reports. Fiscal Year 2015.
More… ↓
