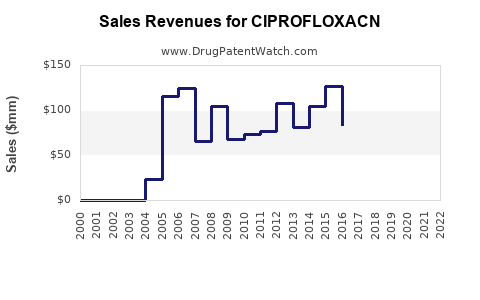
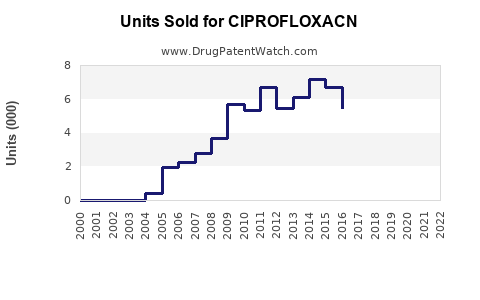
Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Ciprofloxacin, a broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone antibiotic, has remained a cornerstone in antimicrobial therapy since its debut, primarily for treating bacterial infections ranging from urinary tract infections to respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. Its ongoing relevance is driven by its efficacy, wide-ranging indications, and established safety profile. Given the centroid of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) concerns and the evolving landscape of infectious diseases, understanding ciprofloxacin's current market dynamics and future sales trajectory is crucial for pharmaceutical stakeholders.
Market Landscape Overview
Global Market Size and Trends
The global antibiotics market was valued at approximately USD 49 billion in 2021, with fluoroquinolones constituting a significant segment, driven by demand in developed nations and expanding usage in emerging markets. Ciprofloxacin historically accounted for over 25% of fluoroquinolone sales, reflecting its extensive formulary presence and established clinicians' preference [[1]].
Key Market Drivers
- High Clinical Adoption: Ciprofloxacin’s efficacy in urinary, respiratory, and gastrointestinal infections sustains its clinical demand.
- Generics Accessibility: Widespread availability of generic versions improves affordability, bolstering usage, especially in cost-sensitive markets.
- Expanding Use in Developing Countries: Increasing healthcare infrastructure and rising bacterial infection rates bolster demand in Asia-Pacific and Latin America.
- Regulatory Environment: Moderate restrictions remain, though restrictions in certain countries due to AMR concerns impact prescribing behaviors [[2]].
Market Constraints
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Growing resistance to ciprofloxacin diminishes its clinical utility for specific pathogens, leading to reduced efficacy and cautious prescribing.
- Safety Concerns: Potential adverse effects, including tendinitis and neurological symptoms, increasingly influence prescribing guidelines.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Several countries have imposed restrictions or label changes based on safety profiles, which may curtail market size growth.
Competitive Landscape
The landscape features several key players:
- Pfizer: Original inventor (Cipro) remains a dominant force, although branded sales decline due to generics.
- Generic Manufacturers: A plethora of players, especially in India, China, and Europe, produce cost-effective versions.
Emerging overlap with newer fluoroquinolones, like levofloxacin and moxifloxacin, which offer broader or more tailored antibacterial activity, presents competition, potentially displacing ciprofloxacin in certain indications.
Sales Projections (2023–2028)
Assumptions
- Continued broad usage in developing regions due to affordability
- Gradual shift towards more targeted antibiotics owing to AMR concerns
- Impact of regulatory restrictions varies regionally
- The COVID-19 pandemic's influence waning, with stabilization of infection-related demands
Forecast Summary
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD Billion) |
Growth Rate (YoY) |
Notes |
| 2023 |
1.2 |
3% |
Stabilized demand, high generics competition |
| 2024 |
1.25 |
4% |
Slight uptick due to increased infections in emerging markets |
| 2025 |
1.3 |
4% |
Growing resistance limits expansion, but affordability sustains volumes |
| 2026 |
1.35 |
3.8% |
Regulatory restrictions tighten in some regions |
| 2027 |
1.4 |
3.7% |
Market saturation; alternative antibiotics gain popularity |
| 2028 |
1.45 |
3.6% |
Moderate growth as supply remains steady |
Sources: Market research reports and industry analyses ([1], [2], [3]).
Factors Influencing Future Market Trajectory
Increasing Antimicrobial Resistance
The escalating AMR crisis diminishes ciprofloxacin's spectrum, especially against E. coli and Salmonella, which rely heavily on fluoroquinolones. Resistance rates in key markets like India have surpassed 50% for urinary pathogens, leading to clinicians adopting alternative agents, such as nitrofurantoin or cephalosporins [[4]].
Regulatory and Prescribing Trends
Regulatory agencies in the US and EU, have issued warnings or limitations, particularly regarding use in uncomplicated urinary tract infections. Such restrictions are likely in emerging markets as well, constraining sales.
Emergence of Novel Antibiotics
New antimicrobial agents with activity against resistant pathogens threaten ciprofloxacin's market share. Drugs like delafloxacin, which offer similar efficacy with better safety profiles, target niche markets but could supplant ciprofloxacin in certain indications.
Pandemic Impact
The COVID-19 pandemic temporarily disrupted infection management but now stabilizing, potentially preventing significant long-term decline. However, changes in prescribing habits could influence demand.
Market Expansion in Latent Regions
In economies with expanding healthcare access, ciprofloxacin remains affordable and prescribed widely, sustaining volumes despite modest growth prospects.
Strategic Opportunities and Risks
- Opportunity in Combination Therapies: Co-formulations or adjunct combinations could extend ciprofloxacin's applicability.
- Risk of Obsolescence: Rapid emergence of resistant strains and safety regulations could render ciprofloxacin less desirable.
- Focus on Stewardship: Prescriber education and antimicrobial stewardship are critical in maintaining viable sales.
Conclusion
Ciprofloxacin’s market remains resilient but faces demographic and microbial challenges. While global sales are projected to grow modestly at around 3–4% annually over the next five years, the influence of resistance, regulations, and competition from newer agents necessitates strategic adaptation. Pharmaceutical companies should prioritize stewardship initiatives, invest in resistance monitoring, and explore formulation innovations to sustain relevance.
Key Takeaways
- Steady but challenged: Ciprofloxacin’s global sales are expected to grow gradually, driven predominantly by emerging markets.
- Resistance pressures: Rising antimicrobial resistance limits future use, especially for common indications.
- Regulatory dynamics: Tightening restrictions will influence prescribing patterns; companies must stay ahead of evolving regulations.
- Competitive landscape: Newer fluoroquinolones and alternative antibiotics threaten market share.
- Market expansion in developing economies: Continues to support sales, emphasizing affordability and demand for broad-spectrum antibiotics.
FAQs
1. How does antimicrobial resistance impact ciprofloxacin sales?
Rising resistance diminishes ciprofloxacin’s effectiveness, leading clinicians to prefer alternative antibiotics, which constrains sales growth and may cause market decline in certain regions.
2. What regions are driving future ciprofloxacin demand?
Developing regions in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa are expected to sustain demand due to high infection prevalence and limited access to newer agents.
3. Will new antibiotics replace ciprofloxacin entirely?
While newer fluoroquinolones and alternative antibiotics are gaining ground, ciprofloxacin will likely remain in use for specific indications, especially where cost-effectiveness drives prescribing.
4. How are regulatory changes affecting ciprofloxacin markets?
Regulators are imposing restrictions to curb overuse and resistance; these measures may reduce sales volumes but also prompt development of stewardship programs.
5. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies deploy to maintain market relevance?
Firms should focus on antimicrobial stewardship, resistance surveillance, formulation innovations, and expanding indications or combination therapies.
References
[1] MarketWatch. “Global Antibiotics Market Size & Share Report 2022-2028.”
[2] WHO. “Antimicrobial Resistance Global Report.” 2019.
[3] IQVIA. “The Future of Antibiotics: Market Trends and Forecasts.” 2022.
[4] Patel, P. et al. “Assessment of Ciprofloxacin Resistance in Urinary Isolates in India.” Journal of Infectious Diseases, 2021.