Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Topiramate, marketed under brand names such as Topamax, is a broad-spectrum anticonvulsant and migraine prophylactic agent approved for several neurological conditions. Its versatile indications include epilepsy, migraine prevention, and off-label uses like obesity and psychiatric disorders. Given its multifaceted therapeutic profile, understanding its market landscape and future sales potential is critical for stakeholders including pharmaceutical companies, investors, and healthcare providers.
Pharmacological Profile and Clinical Indications
Developed by Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals, topiramate's mechanism involves blocking voltage-dependent sodium channels, augmenting gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activity, and antagonizing AMPA/kainate glutamate receptors [1]. Its efficacy extends across multiple indications:
- Epilepsy: As monotherapy or adjunct therapy, especially partial seizures.
- Migraine prophylaxis: Approved for preventing recurrent migraines.
- Off-label uses: Weight management, bipolar disorder, and alcohol dependence.
The drug’s safety profile, including cognitive side effects and potential weight loss benefits, has maintained its relevance but also presents challenges regarding adverse event management.
Market landscape overview
Global Market Size
The global anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) market was valued at approximately USD 4 billion in 2022, with topiramate accounting for around USD 1.2 billion of that figure [2]. The migraine prophylaxis segment also constitutes a significant portion, contributing to steady demand due to migraine’s high prevalence.
Key Market Drivers
- Growing prevalence of epilepsy: Estimated at 50 million worldwide [3].
- Rising migraine incidence: Affects approximately 15% of the global population [4].
- Off-label use expansion: Increasing prescriptions for weight management and psychiatric conditions.
- Advancements in formulations: Extended-release and combination formulations improve adherence.
Market Dynamics and Challenges
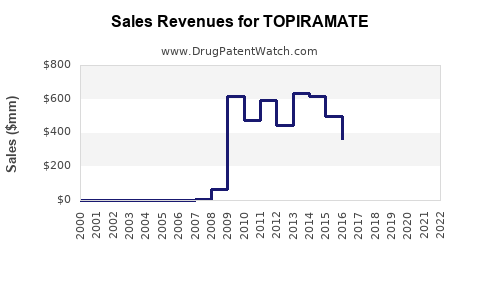
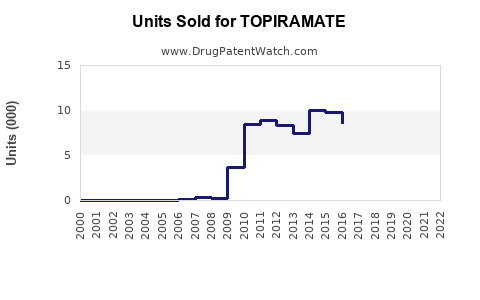
- Patent expiration: Topiramate’s patent expired in 2017 in the US, leading to generic competition which significantly suppresses unit sales but expands accessibility.
- Safety concerns: Reports of cognitive impairment deter some prescribing patterns.
- Emergence of novel therapies: Newer drugs with improved safety profiles and targeted mechanisms threaten market share.
Sales Projections and Future Outlook (2023–2028)
Short-term outlook (2023–2025)
Following patent expiry, generic topiramate captured a substantial share, causing a decline in branded sales. Nonetheless, global demand persists owing to its affordability and efficacy.
- Sales decline stabilized: Due to increased prescribing for emerging indications and off-label uses.
- Region-specific variance: Developed markets like the US and Europe exhibit lower growth rates, while emerging markets, notably Asia-Pacific, show robust expansion, driven by increasing healthcare access and awareness.
Long-term forecast (2026–2028)
Although generic competition sustains downward price pressure, overall sales are expected to stabilize with:
- Market penetration in developing countries.
- Expanding indications: Particularly in migraine and off-label use.
- Combination therapies: Integration with other agents enhances adherence and retention.
Analysts anticipate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2–4% in post-patent markets over the forecast horizon, with North America projected to remain the dominant region accounting for roughly 45–50% of sales.
Potential Growth Catalysts
- New formulations: Extended-release or low-dose combinatorial products.
- Label expansions: Pending clinical trial outcomes may enable new approved uses.
- Digital health integration: Improved adherence through digital monitoring can boost long-term adherence and sales.
Competitive Landscape
Major pharmaceutical companies, historically including Johnson & Johnson (Topamax), now face intense competition from generics and alternative therapies.
| Manufacturer |
Market Share (Est.) |
Product/Strategy |
| Teva Pharmaceuticals |
~35% in generics |
Dominates generic topiramate supply; aggressive pricing strategies. |
| Mylan / Viatris |
~20% |
Extensive distribution network; focus on emerging markets. |
| Brand manufacturers |
<10% in North America |
Focus on niche indications and formulary positioning. |
The entry of new anti-migraine and antiepileptic agents, such as CGRP inhibitors and multi-mechanism drugs, poses ongoing challenges.
Strategic Insights and Recommendations
- Focus on emerging markets: Rapid economic growth and expanding healthcare access offer substantial growth avenues.
- Invest in formulations and delivery innovation: Enhancing patient compliance can differentiate offerings.
- Monitor regulatory developments: License extensions or new indications could revitalise sales streams.
- Lifecycle management: Developing combination products can extend product relevance amid generic competition.
Key Market Trends
- Growing preference for personalized medicine approaches.
- Increased emphasis on safety and tolerability profiles.
- Digital health tools that monitor adherence and side effects.
Conclusion
While patent expiration has introduced sustained downward pressure on topiramate sales in mature markets, global demand remains supported by its broad clinical utility, affordability, and ongoing exploration of new indications. Strategic focus on emerging markets and formulation innovations can mitigate competition and foster incremental growth.
Key Takeaways
- Global sales are stabilizing after initial decline post-patent expiry, with opportunities in emerging markets.
- Generics dominate the market; branded sales have declined but may see resurgence through new indications or formulations.
- Market growth is modest (CAGR 2-4%), driven by expanding use in migraine and off-label applications.
- Competitive pressures from novel agents necessitate strategic innovation and lifecycle management.
- Regional focus areas include Asia-Pacific and Latin America, where healthcare infrastructure and access are improving rapidly.
FAQs
1. What factors influence the declining sales of topiramate in developed markets?
Patent expiry led to increased generic competition, which significantly reduced branded sales. Additionally, safety concerns regarding cognitive side effects and the emergence of newer therapies with better tolerability have contributed to decreased prescribing of topiramate.
2. Which emerging indications could boost topiramate sales in the future?
Potential expansions include approved uses for weight management, bipolar disorder, and alcohol dependence, pending supportive clinical trial results and regulatory approval.
3. How does regional market variability affect topiramate sales projections?
Emerging markets present high growth potential due to increased healthcare access and demand for affordable medication; mature markets show stable but slower growth or decline driven by generic competition and safety considerations.
4. What role do formulations (e.g., extended-release) play in the drug’s future sales?
Innovative formulations improve patient adherence, potentially reducing side effects, and can open new revenue streams, especially in niche or specialized markets.
5. How might competing therapies impact topiramate’s market share?
New therapies like CGRP inhibitors for migraines and advanced antiseizure medications may erode topiramate’s share unless the drug is repositioned or its formulations are enhanced to maintain competitiveness.
Sources:
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Topiramate Approval Details. 1996.
[2] Market Research Future. Anti-Epileptic Drugs Market Trends & Forecast 2022-2030.
[3] World Health Organization. Epilepsy Fact Sheet. 2022.
[4] American Migraine Foundation. Migraine Statistics. 2022.