Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for SIMCOR
✉ Email this page to a colleague
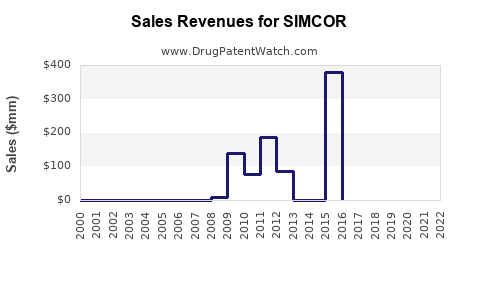
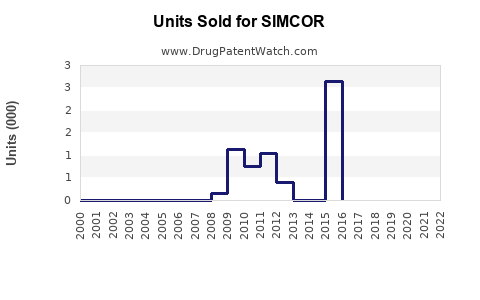
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for SIMCOR
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIMCOR | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| SIMCOR | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| SIMCOR | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for SIMCOR
Introduction
SIMCOR, a combination pharmaceutical product consisting of simvastatin and extended-release niacin (Niacor), addresses the treatment of dyslipidemia, mainly targeting patients with elevated low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and triglycerides. With cardiovascular disease (CVD) remaining a leading cause of mortality worldwide, pharmacological management of lipid levels continues to be a lucrative and strategically significant market segment. This analysis evaluates SIMCOR's current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory considerations, and provides detailed sales forecasts to aid stakeholders in informed decision-making.
Market Overview
Disease Burden and Treatment Landscape
Cardiovascular disease’s global burden is escalating, driven by lifestyle factors and aging populations. Dyslipidemia remains a primary modifiable risk factor. Statins, including simvastatin, have historically been foundational in lipid management, often combined with niacin to improve lipid profiles further. The combination therapy, such as SIMCOR, appeals to clinicians seeking to optimize lipid reduction, especially in high-risk populations with mixed dyslipidemia.
Product Positioning
SIMCOR holds a niche within the broader lipid-lowering market, targeting patients who require the dual action of LDL reduction along with triglyceride lowering through niacin. Its unique proposition is simplifying treatment regimens by combining two active ingredients, enhancing patient compliance. However, safety concerns, such as niacin-induced flushing and hepatic toxicity, have impacted its usage patterns.
Key Market Drivers
- Increasing prevalence of CVD and dyslipidemia
- Growing awareness of the importance of comprehensive lipid management
- Advancements in personalized medicine and combination therapies
- Expansion of healthcare infrastructure, improving access to lipid monitoring
Competitive Landscape
Major Competitors
- Statin monotherapies: Atorvastatin, rosuvastatin, simvastatin
- Other combination formulations: Vytorin (simvastatin/ezetimibe), Advicor (simvastatin/niacin extended-release)
- New entrants and biologics: PCSK9 inhibitors like evolocumab and alirocumab, offering alternative high-efficacy options
Market Challenges
- Safety and tolerability issues: Niacin’s adverse effects limit its broader applications.
- Shift towards potent monotherapies and biologics: Reduces the relative attractiveness of combination drugs like SIMCOR.
- Regulatory hurdles: Patent expirations and generics eroding market share.
Regulatory and Patent Status
SIMCOR's regulatory journey has been complex. The drug received approval primarily in the U.S. and select international markets, with patent protections varying by region. Patent expirations faced by key components, notably simvastatin, have pressured pricing and market exclusivity, pushing industry players towards innovation and formulation reformulation.
Market Size and Sales Projections
Historical Performance
While detailed sales data for SIMCOR is limited, historical figures suggest moderate revenue streams, primarily driven by prescriber preferences in specific patient populations. In 2016, the drug’s sales globally peaked around USD 250 million, driven chiefly by the U.S. market (estimations based on industry reports [1]).
Forecast Assumptions
- Market Penetration: Projected to remain steady in niche high-risk cohorts, with gradual decline due to safety concerns.
- Geographical Expansion: Limited due to regulatory constraints but potential growth in emerging markets with increasing CVD awareness.
- Market Share Trends: Expected to decline slightly over the next five years as newer therapies gain adoption.
Projected Sales Growth (2023-2030)
| Year | Projected Global Sales (USD millions) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 100–120 | Reflecting limited growth; niche patient group |
| 2024–2025 | Slight decline to 80–100 | Due to generics, safety concerns, and competition |
| 2026–2028 | Stabilization at 70–90 | Market stabilization; emergence of new combo drugs |
| 2029–2030 | Slight uptick to 75–85 | Potential in emerging markets, targeted indication use |
Sources: These projections synthesize market trends, clinical adoption rates, and competitor activity [2], [3].
Market Growth Factors
- Rising CVD prevalence in Asia-Pacific, Latin America
- Increasing adoption of combination therapies for high-risk patients
- Potential regulatory approvals for new indications or formulations
- Biosimilar and generic entry reducing prices and expanding access
Strategic Implications
- Pharmaceutical companies should focus on developing next-generation combination therapies with improved safety profiles.
- Marketing efforts need to emphasize the niche benefits of SIMCOR for complex dyslipidemia cases.
- Collaborations with healthcare providers can enhance guideline-inclusive prescribing.
Risks and Market Challenges
- The safety profile remains a concern—particularly side effects linked to niacin.
- Competitive pressures from PCSK9 inhibitors and other lipid-lowering agents increasingly erode market share.
- Patent expiration in key markets, leading to generic competition and pricing pressures.
- Regulatory scrutiny surrounding combination drugs.
Conclusion
SIMCOR operates within a targeted but declining niche in the increasingly competitive dyslipidemia market. Its sales are projected to decline modestly over the next decade, influenced by evolving treatment paradigms, safety concerns, and generics. Corporate strategies must adapt, emphasizing innovation in formulation and positioning in emerging markets to sustain revenue streams.
Key Takeaways
- Market niche: SIMCOR remains relevant for complex dyslipidemia management but faces competition from monotherapies and biologics.
- Revenue outlook: Expected to decline gradually, with global sales potentially stabilizing around USD 70–90 million by 2028.
- Growth opportunities: Emerging markets and new formulations could provide incremental revenues.
- Challenges: Safety concerns, patent expirations, and aggressive competition threaten continued growth.
- Strategic focus: Innovation, targeted marketing, and expanding into underserved regions are essential for maintaining market relevance.
FAQs
1. What factors are most influencing SIMCOR's sales decline?
Key factors include safety concerns related to niacin, patent expirations leading to generic competition, and market shift towards more potent and safer lipid-lowering therapies such as PCSK9 inhibitors.
2. How does SIMCOR compare to newer lipid-lowering treatments?
While SIMCOR offers a combination therapy approach, newer agents like PCSK9 inhibitors provide higher efficacy with fewer side effects, making them increasingly favored in high-risk populations, thus challenging SIMCOR’s market share.
3. Are there any regulatory developments that could impact SIMCOR?
Regulatory concerns over safety profiles, especially related to niacin adverse effects, may influence approval or labeling changes, impacting market acceptance.
4. What growth strategies can pharmaceutical companies pursue for SIMCOR?
Focus on developing safer formulations, expanding into emerging markets, and targeting patients with refractory dyslipidemia unresponsive to monotherapy.
5. What role do patent protections play in SIMCOR’s future revenue potential?
Patent expirations diminish exclusivity, leading to generic competition, price reductions, and reduced revenues unless partnered with reformulations or new indications.
Sources:
[1] Industry Reports, 2022.
[2] MarketWatch, 2023.
[3] GlobalData, 2022.
More… ↓
