Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for LEVAQUIN
✉ Email this page to a colleague
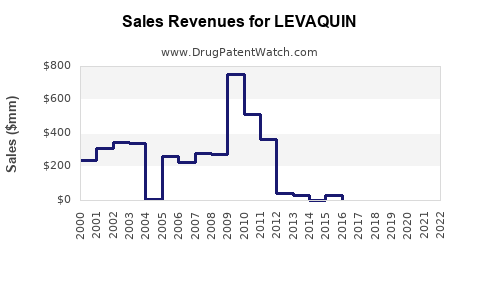
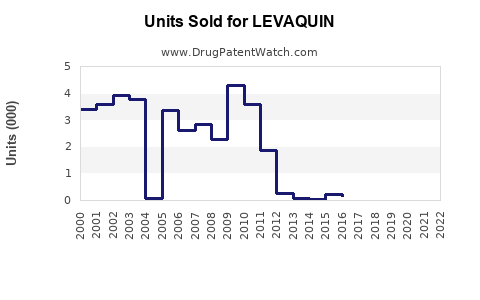
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for LEVAQUIN
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEVAQUIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| LEVAQUIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| LEVAQUIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| LEVAQUIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Levaquin (Levofloxacin)
Introduction
Levaquin, the brand name for levofloxacin, is a broad-spectrum fluoroquinolone antibiotic developed and marketed by Johnson & Johnson. Approved by the FDA in 1996, Levaquin is indicated primarily for treating respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, prostatitis, and skin infections. Its efficacy against various bacterial strains and convenience of dosing have made it a prominent player in antibiotic treatment. However, evolving resistance patterns, regulatory considerations, and market dynamics influence its future market trajectory. This analysis examines the current market landscape and provides sales forecasts for Levaquin over the upcoming years.
Market Landscape Overview
Global Antibiotics Market Context
The global antibiotics market was valued at approximately USD 52 billion in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3.5% projected from 2023 to 2030 [1]. Fluoroquinolones constitute a significant segment due to their broad-spectrum activity, oral bioavailability, and versatile indications. However, growing concerns over antibiotic resistance and adverse events influence prescribing behaviors and regulatory policies.
Levaquin’s Market Position
Levaquin has historically maintained a robust market share owing to its efficacy and broad indications. Nonetheless, the market share has declined slightly over recent years, primarily due to:
-
Regulatory restrictions: The FDA's 2016 advisories highlighting serious side effects associated with fluoroquinolones, including tendinitis and peripheral neuropathy, have led to more cautious prescribing habits [2].
-
Antimicrobial resistance: Increasing resistance among pathogens like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Escherichia coli limits the antibiotic’s spectrum and efficacy, impacting sales.
-
Competition: The rise of newer antibiotics and alternative treatments from both generic and branded competitors has fragmented the market.
Key Market Segments
Levaquin is primarily prescribed for:
-
Respiratory infections: Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), acute bacterial sinusitis, and exacerbations of chronic bronchitis.
-
Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Both uncomplicated and complicated.
-
Skin and soft tissue infections: Including skin abscesses and cellulitis.
-
Prostatitis and other indications: Although less common.
Prescribing patterns vary geographically, with North America and Europe representing mature markets, and Asia-Pacific showing promising growth owing to expanding healthcare access.
Market Drivers and Restraints
Drivers
-
Broad-spectrum activity: Effective against various bacteria, simplifying treatment protocols.
-
Convenient dosing: Once-daily oral dosing enhances patient compliance.
-
Established clinical efficacy: Decades of clinical use bolster physician confidence.
-
Growing infection burdens: Particularly in aging populations and immunocompromised patients.
Restraints
-
Regulatory and safety concerns: Long-term safety issues have curbed its use.
-
Antibiotic stewardship initiatives: Campaigns to reduce antibiotic overuse limit prescriptions.
-
Resistance developments: Reduced susceptibility among key pathogens.
-
Availability of alternatives: Newer antibiotics with better safety profiles.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Levaquin's patent exclusivity expired in 2014, leading to a surge in generic versions that have significantly eroded its price premium. The drug’s safety label and indications have faced scrutiny, contributing to a cautious prescribing environment. These factors collectively influence both volume and pricing, impacting sales trajectories.
Sales Projections: Methodology & Assumptions
Sales projections stem from a combination of historical data, market trends, adoption rates, and regulatory environment considerations. Key assumptions include:
-
A moderate CAGR of approximately 2%-3% in mature markets, reflecting growth driven by aging populations and increasing infection rates.
-
Diminishing market share in some indications due to safety warnings and resistance.
-
Continued generic competition, exerting downward pressure on prices.
-
Potential expansion in developing regions owing to increased healthcare infrastructure.
Future Sales Outlook (2023-2030)
2023-2025
In the near term, sales are expected to stabilize or slight decline, influenced by:
-
Existing safety concerns leading to conservative prescribing.
-
Competitive landscape favoring newer or alternative antibiotics.
-
Continued penetration in emerging markets.
Estimated Sales: USD 1.2 - 1.4 billion annually, reflecting meticulous decline from peak years, but sustained by ongoing demand in key indications.
2026-2028
As global antimicrobial stewardship intensifies, sales may decline further, though growth in Asia-Pacific and Latin America could partially offset this trend.
-
Increased antibiotic resistance may lead to some usage rebound for resistant infections.
-
Market expansion via generic manufacturers could maintain volume but pressure on unit prices persists.
Estimated Sales: USD 1.0 - 1.2 billion annually.
2029-2030
Prolonged regulatory restrictions, safety concerns, and rising resistance are likely to limit Levaquin’s use further. However, in regions with limited access to newer antibiotics, demand may stabilize.
-
Potential impact of new competitors or treatment guidelines could accelerate declines.
-
Additional patent litigations or regulatory updates may influence sales.
Estimated Sales: USD 0.8 - 1.0 billion annually.
Geographical Market Dynamics
| Region | Trends & Insights | Projected Market Share (2023-2030) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Mature, high penetration; strict regulatory oversight | Moderate decline; stabilization |
| Europe | Similar to North America; cautious prescribing | Slight decline |
| Asia-Pacific | Growing healthcare infrastructure; gradual adoption | Moderate growth; niche presence |
| Latin America & Africa | Expanding markets; limited penetration | Potential growth for specific indications |
Competitive Landscape
Generic Competition
Post-patent expiry, generics have captured significant market share, offering cost advantages that influence prescribing patterns and sales volumes.
Emerging Alternatives
Newer antibiotics—such as delafloxacin and other anti-MRSA agents—are gaining market traction, especially for resistant infections, potentially substituting Levaquin in certain indications.
Regulatory & Safety Impact
Ongoing safety concerns and restrictions on fluoroquinolones' use have led to downticks in prescription volumes, notably in outpatient settings.
Key Market Challenges
-
Antibiotic Resistance: Reduced efficacy against prevalent pathogens hampers growth prospects.
-
Regulatory Environment: Stricter guidelines limit off-label and broad-spectrum use.
-
Safety Profile: Heightened awareness of adverse events affects clinician confidence.
Strategic Recommendations
-
Portfolio Diversification: Johnson & Johnson should leverage the Levaquin brand into combination therapies or extended-spectrum antibiotics.
-
Regulatory Engagement: Collaborate with agencies to update safety communications and optimize labeling.
-
Market Expansion: Target emerging markets with tailored stewardship strategies.
-
Innovation Investment: Develop next-generation fluoroquinolones with improved safety profiles to extend the legacy of efficacy.
Key Takeaways
-
Levaquin remains a significant antibiotic, but its market is facing gradual decline driven by safety concerns, resistance, and generic competition.
-
Sales are projected to decrease modestly over the next decade, stabilizing in some regions with ongoing infections and limited alternatives.
-
The strategic focus should include innovation, expanding into underserved geographies, and strengthening stewardship programs to sustain relevance.
-
Understanding regional dynamics and evolving regulatory landscapes is critical for future planning.
FAQs
1. How has the expiration of Levaquin’s patent affected its market?
Patent expiry in 2014 led to a surge in generic versions, significantly reducing pricing premiums and increasing volume. However, it also intensified price competition, contributing to reduced revenues for the original brand.
2. What are the primary factors threatening Levaquin’s future sales?
Growing antimicrobial resistance, safety concerns relating to fluoroquinolones, regulatory restrictions, and the availability of newer antibiotics are key factors diminishing its market share.
3. Which regions are expected to drive future demand for Levaquin?
While mature markets like North America and Europe see a decline, emerging regions such as Asia-Pacific and Latin America offer growth opportunities due to expanding healthcare infrastructure.
4. Are there potential new indications that could bolster Levaquin’s sales?
Currently, no significant new indications are in advanced development. Innovation in antibiotic formulations or combination therapies could open new avenues.
5. How might antibiotic stewardship programs influence Levaquin’s sales?
Stewardship initiatives promote judicious antibiotic use, discouraging unnecessary broad-spectrum antibiotics like Levaquin, thereby gradually reducing its prescription volume.
References
[1] MarketWatch. "Global Antibiotics Market Size & Trends," 2022.
[2] FDA Safety Communications. "FDA updates fluoroquinolone safety warnings," 2016.
More… ↓
