Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for BESIVANCE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
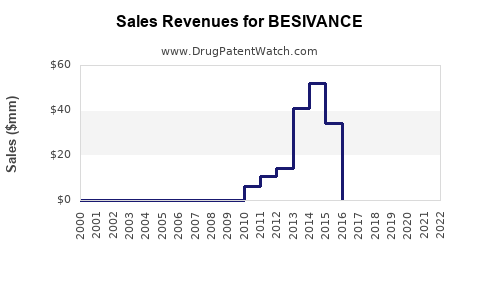
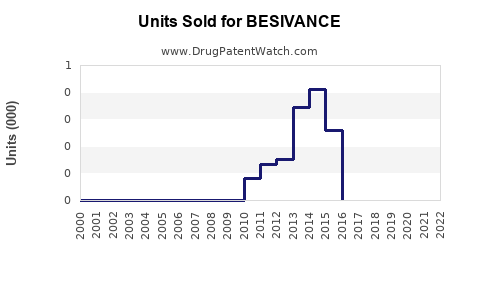
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for BESIVANCE
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| BESIVANCE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| BESIVANCE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| BESIVANCE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| BESIVANCE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| BESIVANCE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2018 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for BESIVANCE (1.0% Voriconazole) Ophthalmic Solution
Introduction
BESIVANCE (voriconazole ophthalmic solution) is an antifungal medication approved specifically for the treatment of fungal keratitis, a severe ocular infection caused by filamentous fungi and yeasts such as Candida species. Since its FDA approval in 2016, BESIVANCE has filled a niche in ophthalmic infectious disease management, targeting a rare but potentially blinding condition. This analysis evaluates its market landscape, competitive environment, potential patient populations, and sales trajectories over the coming years.
Market Landscape Overview
Medical Need and Clinical Context
Fungal keratitis is an ocular emergency requiring prompt and effective antifungal therapy. The disease predominantly affects contact lens wearers and immunocompromised individuals, particularly in developing regions and environments with high exposure to fungal pathogens. Standard treatments include natamycin and amphotericin B, but limitations in efficacy and drug penetration often necessitate newer options like voriconazole.
Regulatory and Pharmacological Profile
BESIVANCE's approval emphasizes its targeted ocular delivery, minimizing systemic exposure. Its role in clinical practice is as either a first-line or adjunct therapy for resistant cases, augmenting existing antifungal options. Its favorable safety profile and CAP (corneal penetration) have facilitated its adoption in hospitals and specialty eye clinics.
Market Segmentation
Potential market segments include:
- Prescribing Physicians: Ophthalmologists and corneal specialists.
- Patient Demographics: Patients with fungal keratitis, predominantly adults aged 30-60, with contact lens users, agricultural workers, or immunocompromised status.
- Geographies: North America (leading due to regulatory and healthcare infrastructure), Europe, Asia-Pacific (notably India, China, and Southeast Asia, where fungal keratitis incidence is higher due to climate and epidemiological factors).
Global Burden and Epidemiology
Fungal keratitis affects approximately 1-2 million individuals globally annually, with higher incidence in developing countries. The disease accounts for up to 50% of infectious keratitis cases in tropical climates.[1] Given the limited treatment options and disease severity, there is a continuous demand for effective antifungal ophthalmic therapies.
Competitive Landscape
Existing Treatments
- Natamycin (Natacyn): Approved for fungal keratitis, widely used, especially in the US and Europe.
- Amphotericin B and Voriconazole (Systemic): Often used intravenously or topically for resistant cases.
- Other formulations: Topical echinocandins are in experimental stages.
Differentiators and Market Advantages of BESIVANCE
- Targeted delivery with fewer systemic side effects.
- Broad-spectrum activity against fungi.
- Potential use in resistant cases or when other treatments fail.
Market Challenges
- Limited awareness outside specialist circles.
- Cost considerations may influence adoption, especially in cost-sensitive markets.
- Competition from established drugs like natamycin, which has a longer history of use.
Sales Drivers and Barriers
Drivers
- Increasing incidence of fungal keratitis, especially in high-risk populations.
- Growing awareness among ophthalmologists about voriconazole efficacy.
- Expanding approvals or off-label uses in related fungal ocular infections.
- Development of combination therapies to improve treatment outcomes.
Barriers
- High cost of BESIVANCE compared to traditional treatments.
- Limited awareness in developing markets.
- Need for specialized delivery systems and administration by trained ophthalmologists.
- Regulatory and reimbursement hurdles in emerging markets.
Sales Projections and Market Outlook
Historical Sales Trends (2016-2022)
Sales of BESIVANCE have historically been modest, reflecting its niche status. Estimated revenues in the US for 2022 ranged between $30 million and $50 million, with growth driven by increased prevalence of fungal keratitis and clinician familiarity.
Forecasted Growth (2023-2030)
- CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate): Estimated at 8-12%, considering its niche but expanding use.
- Assumptions:
- Increased awareness and clinician familiarity.
- Expanded indications, possibly including other fungal ocular infections.
- Entry into emerging markets facilitated by cost reductions or local manufacturing.
- Market Penetration:
- Currently, penetration is limited (~20-30%) in the US.
- Potential to reach 50% in specialized centers over five years.
- Growth in Asia-Pacific may outperform due to higher disease incidence and unmet needs.
Influential Factors
- Epidemiological shifts: Climate change and increased contact lens use can elevate fungal keratitis cases.
- Regulatory updates: Approvals for broader indications or formulations.
- Clinical guidelines: Incorporation into treatment protocols enhances adoption.
- Competition: Natamycin remains dominant; BESIVANCE growth depends on evidence of superior efficacy or safety.
Impact of COVID-19 and Healthcare Disruptions
While the pandemic disrupted elective ophthalmic procedures, the focus on infectious disease management and hospital supplies has temporarily suppressed sales but is gradually rebounding as healthcare systems stabilize.
Conclusion
BESIVANCE holds a decisive but niche role in the management of fungal keratitis, with steady growth prospects driven by rising disease burden and ongoing clinical developments. Its sales are poised to expand modestly, with an optimistic outlook contingent on increased awareness, regional expansion, and potential new indications.
Key Takeaways
- The global fungal keratitis market is growing, driven by epidemiological factors and limited current treatment options.
- BESIVANCE, with its targeted ophthalmic antifungal activity, is well-positioned as a specialized therapy.
- Sales are forecasted to grow at a CAGR of 8-12% over the next five years, influenced by rising incidence and expanding geographic penetration.
- Competition from natamycin remains significant, emphasizing the need for clinical differentiation and cost management.
- Market expansion will depend on clinician education, regulatory pathways, and strategic manufacturing in emerging markets.
FAQs
1. What are the primary factors driving BESIVANCE's market growth?
The increase in fungal keratitis cases, heightened clinician awareness, and expanding indications are key drivers. Additionally, regional epidemiological trends in developing countries contribute significantly.
2. How does BESIVANCE compare to natamycin in treating fungal keratitis?
BESIVANCE offers better corneal penetration and may be more effective against certain resistant fungi, but natamycin remains the first-line treatment due to its long-standing approval and lower cost.
3. Which regions present the highest sales potential for BESIVANCE?
North America and Europe are current markets with steady growth; however, the Asia-Pacific region, particularly India and China, offers the highest potential due to a higher prevalence of fungal keratitis.
4. What are potential barriers to increasing BESIVANCE sales?
High costs, limited clinician awareness outside specialized centers, and competition from established therapies like natamycin are primary barriers.
5. Are there ongoing clinical trials that could expand BESIVANCE’s approved uses?
As of now, ongoing research aims to evaluate its efficacy in broader fungal ocular infections, which could extend its market reach if successful.
References
[1] Thomas, P. A., & Kaliamourtis, T. (2019). Fungal keratitis: an update. British Journal of Ophthalmology, 103(7), 876-882.
More… ↓
