Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for zoloft
✉ Email this page to a colleague
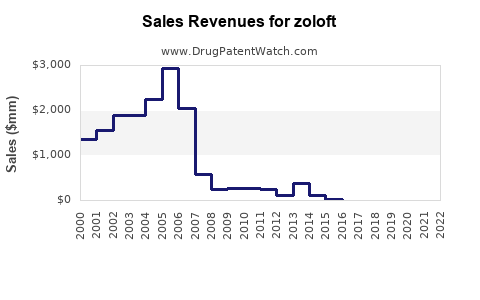
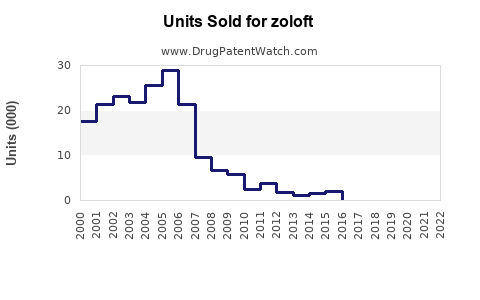
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for zoloft
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZOLOFT | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| ZOLOFT | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| ZOLOFT | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| ZOLOFT | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| ZOLOFT | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2018 |
| ZOLOFT | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2017 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Zoloft (Sertraline)
Introduction
Zoloft (sertraline) remains one of the most widely prescribed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) for treating depression, anxiety disorders, and a range of psychiatric conditions. Since its FDA approval in 1991, Zoloft has established a dominant position within the antidepressant market, bolstered by its favorable efficacy profile and safety record. This comprehensive analysis explores the current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory influences, and future sales projections, providing insights that are crucial for pharmaceutical stakeholders, investors, and healthcare professionals.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Growth
The global antidepressant market was valued at approximately USD 18.9 billion in 2021, with expectations to reach USD 26.8 billion by 2028, growing at a CAGR of around 6%. Zoloft, as a leading SSRI, historically commanded significant market share, particularly in North America and Europe, driven by the high prevalence of depression and anxiety disorders.
Prevalence of Indications
Depressive disorders affect over 264 million people worldwide, with depression ranking as a leading cause of disability (WHO, 2020). Anxiety disorders impact an estimated 284 million globally, often co-occurring with depression, further expanding the treatment market for SSRIs like Zoloft.
Prescription Trends
In the U.S., Zoloft held a dominant position in the SSRI class for decades — though it has faced patent expirations and increased generic competition since 2006. Prescription volumes have seen fluctuations, often reflecting shifting clinician preferences, emerging evidence, and regulatory changes.
Competitive Landscape
Patents and Generics
Zoloft's primary patent expired in 2006, prompting a surge of generic formulations that significantly eroded brand sales. Currently, multiple generic sertraline products are available, reducing cost barriers and expanding access but intensifying price competition.
Emerging Therapies and Alternatives
- Newer antidepressants (e.g., vortioxetine, vilazodone) offer alternative mechanisms and potentially better side effect profiles, impacting Zoloft’s market share.
- Non-pharmacological treatments, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and psychotherapy, influence prescription patterns.
Market Share Dynamics
Despite generic competition, Zoloft maintains a presence due to physician familiarity, brand trust, and determined marketing efforts. However, its market share has decreased from over 80% pre-patent expiration to an estimated 20-30% among SSRIs in North America.
Sales Data and Historical Trends
Pre-Patent Expiry Performance
At peak, Zoloft generated over USD 3 billion annually in global sales, with North America comprising approximately 70% of revenues. The drug was among the top-selling antidepressants worldwide during the 2000s.
Post-Patent Expiry Decline
Following patent expiry, sales declined precipitously. For instance, Pfizer’s (original manufacturer) reported sales fell by approximately 80% by 2010 due to generic penetration.
Current Sales Figures
Recent data indicate that Zoloft generates annual revenues in the vicinity of USD 300-500 million globally, primarily from North America. This decline reflects generic substitution, with prescriptions shifting toward newer agents.
Regulatory and Market Influences
Regulatory Environment
FDA and EMA approvals continue to facilitate access. However, increased scrutiny around SSRIs' safety profiles, especially concerning pediatric populations and long-term use, influences prescribing trends.
Pricing and Reimbursement Dynamics
Cost-effectiveness concerns, insurance formularies, and increased use of generics have pressured prices downward, reducing profit margins but expanding patient access.
Pandemic Impact
COVID-19 has increased mental health disorders, potentially expanding the market for antidepressants. While overall prescriptions have risen, the impact on Zoloft specifically depends on prescriber preferences and formulary policies.
Future Sales Projections
Optimistic Scenario (Stable or Growing Market Share)
Assuming continued awareness of Zoloft’s efficacy and safety, coupled with expanding mental health needs, sales could stabilize around USD 500 million annually over the next five years. The growth of telepsychiatry and increased diagnosis rates may favor established medications.
Moderate Scenario (Market Share Decline Continues)
If newer agents or non-drug treatments increasingly replace Zoloft, sales may decline further to approximately USD 200-300 million annually within five years, mainly driven by generic competition and prescriber shifts.
Downside Risks
- Regulatory restrictions on SSRI use for specific populations.
- Market saturation with generics and new therapies.
- Emerging safety concerns impacting clinician preference.
Upside Opportunities
- Branding or differentiation strategies focusing on niche populations.
- Expansion into emerging markets, where antidepressant access is increasing.
- Development of novel formulations (e.g., sustained-release) to enhance compliance.
Key Factors Influencing Future Market Performance
| Factor | Impact | Strategic Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Patent status | No current patent exclusivity | Focus on brand loyalty & education |
| Competition | Intensified from generics & new drugs | Differentiation & targeted marketing |
| Market needs | Rising mental health awareness | Expand indications & markets |
| Pricing policies | Favor generics & cost-effective solutions | Optimize pricing & reimbursement strategies |
| Regulatory trends | Possible new safety regulations | Proactive compliance & safety profiling |
Key Takeaways
- Declined but Stable Presence: Since patent expiration, Zoloft's global sales have declined significantly, but it maintains a presence through established clinical trust and global distribution networks.
- Growth Opportunities in Emerging Markets: Increasing mental health awareness in Asia, Latin America, and Africa presents avenues for market expansion, especially using generics.
- Competitive Challenges: Intense price competition from generics and rising preferences for newer antidepressants necessitate strategic branding and differentiation efforts.
- Market Dynamics are Shifting: Behavioral health services, telemedicine, and non-pharmacological therapies influence prescribing trends, potentially limiting future sales.
- Data-Driven Strategy Essential: Stakeholders should leverage detailed prescription data and epidemiological trends to refine sales strategies, emphasizing patient access, safety, and formulary positioning.
Conclusion
Zoloft's market remains vital but has transitioned from a blockbuster to a mature product heavily impacted by generic erosion and evolving treatment paradigms. Strategic positioning within the context of expanding mental health awareness and emerging therapeutic options will determine its future trajectory. Pharmaceutical companies should focus on optimizing access, extending indications, and differentiating through safety and efficacy to sustain relevance and revenue.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How has patent expiration affected Zoloft’s market sales?
Patent expiration in 2006 led to an influx of generic formulations, causing a substantial decline in brand sales—over 80% within a few years—and a significant shift towards lower-cost generics in prescribing patterns.
2. What are the main competitors to Zoloft in the SSRI market?
Main rivals include Prozac (fluoxetine), Lexapro (escitalopram), and newer agents like vortioxetine and vilazodone. Non-SSRI antidepressants and non-pharmacological treatments also compete for patient and clinician preference.
3. Can Zoloft’s sales recover or grow in the future?
While unlikely to reach previous peak levels, sales could stabilize or moderately grow through expansion into emerging markets, targeted indications, or formulations, especially amid rising mental health awareness.
4. How do regulatory trends impact Zoloft’s continued marketability?
Regulatory agencies increasingly scrutinize SSRI safety profiles; however, current approvals support ongoing use. New safety data or guidelines could influence prescribing behavior negatively or positively.
5. What strategic moves should stakeholders consider to maximize Zoloft’s market potential?
Focus on geographic expansion, product differentiation, patient adherence strategies, safety profile communication, and leveraging digital health platforms can help maintain relevance and revenue.
References
[1] WHO. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders. World Health Organization, 2020.
[2] MarketWatch. Antidepressant Market Size & Forecast (2021–2028).
[3] Pfizer. Annual Reports & Press Releases on Zoloft Sales.
[4] EvaluatePharma. Top-selling Generic Drugs and Market Trends.
[5] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Approvals and Safety Information.
More… ↓
