Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Haloperidol, a first-generation antipsychotic medication, has been a cornerstone in managing schizophrenia, acute psychosis, and various other psychiatric disorders for over six decades. Despite evolving treatment paradigms favoring atypical antipsychotics, haloperidol maintains a significant role, especially in specific clinical settings such as inpatient, emergency, and institutional care. This analysis explores the current market landscape of haloperidol, the factors influencing its sales trajectory, and precise projections for the coming years.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Current Usage
Developed in the 1950s and approved in the 1960s, haloperidol remains one of the most widely prescribed typical antipsychotics globally. Its robust efficacy, cost-effective profile, and extensive clinical data underpin its continued utilization, especially in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs). The drug's primary indications include schizophrenia, acute psychosis, Tourette’s disorder, and severe behavioral disturbances in children and adolescents [1].
Market Dynamics
Despite challenges posed by newer atypical antipsychotics, haloperidol retains a substantial market share due to several factors:
- Cost-effectiveness: Lower production and procurement costs enhance its appeal in resource-constrained settings.
- Clinical familiarity: Long-standing clinical experience promotes habitual prescribing.
- Formulation versatility: Available in oral, injectable (both oral and long-acting IM), and depot forms.
Regulatory Landscape and Patent Status
Haloperidol is a generic medication, with many manufacturers worldwide producing it under various brand names or as unbranded generics. The absence of patent restrictions has fostered a competitive manufacturing environment, stabilizing prices but limiting revenue growth for original patent-holders.
Regional Market Penetration
- North America & Europe: Dominated by generics, with prescription volumes driven by existing patient populations.
- Asia-Pacific & Latin America: High utilization due to affordability and healthcare infrastructure reliance on generic medications.
- Africa & Middle East: Growing adoption driven by expansion of mental health services and affordability considerations.
Market Drivers and Restraints
Drivers
- Persistent demand for cost-effective psychotropic medications
- Increasing prevalence of schizophrenia globally, estimated at over 20 million cases [2]
- Growing awareness and diagnosis of psychoses in emerging markets
- Expanding use in behavioral management outside traditional psychiatric settings (e.g., correctional facilities)
Restraints
- Shift toward atypical antipsychotics due to improved side-effect profiles
- Regulatory limitations stemming from concerns over extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) and tardive dyskinesia [3]
- Limited pipeline innovation for haloperidol, as it is a well-established molecule
- Stigmatization and preference for newer agents with perceived better tolerability
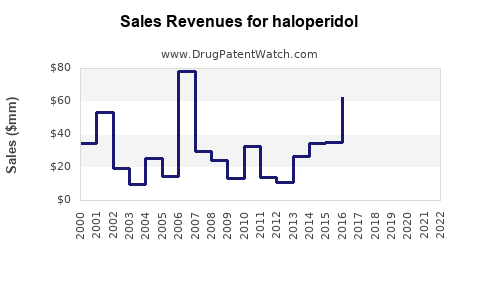
Sales Projections (2023–2028)
Assumptions and Methodology
Projections utilize historic sales data, segment growth trends, regional uptake patterns, and emerging demographic shifts. Market share stability of haloperidol in LMICs is assumed, with incremental declines in high-income countries due to competition from atypicals.
Forecast Summary
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD Million) |
Growth Rate (%) |
Key Influences |
| 2023 |
$850 |
— |
Baseline, high demand in emerging markets |
| 2024 |
$890 |
+4.7 |
Continued adoption in LMICs; stabilization |
| 2025 |
$930 |
+4.5 |
Growing mental health burden globally |
| 2026 |
$970 |
+4.3 |
Slight market share erosion in high-income regions |
| 2027 |
$1,005 |
+3.6 |
Increased utilization in correctional systems |
| 2028 |
$1,030 |
+2.5 |
Market saturation, emerging competition |
Note: These projections emphasize steady global sales, with regional nuances influencing overall trends.
Regional Breakdown
- North America & Europe: Approximate combined sales of 35%, with slight yearly declines expected due to rapid adoption of atypical agents.
- Asia-Pacific & Latin America: Represent around 50%, benefiting from demographic growth and cost sensitivity.
- Other regions: The remaining 15%, primarily in Africa and Middle East, with modest growth.
Emerging Trends Influencing Sales
- Increased use of long-acting injectable (LAI) formulations: Improve compliance, thus potentially boosting sales.
- Utilization in institutional settings: Hospitals and correctional facilities increasingly rely on haloperidol for acute and chronic management, especially where budget constraints exist.
- Potential off-label uses: Management of severe agitation and violent behavior in emergency contexts could further sustain demand.
Competitive Landscape
The market for haloperidol is saturated with generic formulations from numerous manufacturers. Limited innovation is expected due to the drug’s patent expiry decades ago, although recent developments include improved LAI formulations that may slightly influence market dynamics.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- The dominance of atypical antipsychotics continues to challenge haloperidol’s growth prospects.
- Side effect profile concerns, especially EPS and extrapyramidal symptoms, reduce its appeal among patients and clinicians.
- Regulatory scrutiny around neuroleptic safety mandates ongoing monitoring, affecting prescribing trends.
Opportunities
- Increasing mental health awareness promotes broader treatment acceptance.
- Cost-sensitive health systems favor affordable options like haloperidol.
- Development of depot formulations with fewer side effects could rejuvenate clinical interest.
Conclusion
Despite a gradual decline in high-income markets, haloperidol sustains a considerable share of global psychotropic sales, primarily driven by affordability, established clinical utility, and widespread use in LMICs. Sales are projected to grow modestly at approximately 2-4% annually through 2028, fundamentally stabilized by regional market dynamics and clinical preferences.
Key Takeaways
- Persistent Relevance: Haloperidol remains integral in managing severe psychiatric conditions, especially where affordability outweighs side-effect concerns.
- Market Stability with Regional Variations: While high-income countries are shifting toward atypical agents, LMICs uphold strong demand, underpinning global sales.
- Innovation Constraints: Lack of significant pipeline innovation limits upside potential; incremental gains expected from improved formulations.
- Growth Drivers: Increasing global mental health burden and expansion of institutional care settings support steady demand.
- Competitive Edge: Cost advantage and established safety profile continue to medicinally position haloperidol favorably in resource-limited healthcare systems.
References
[1] World Health Organization. Mental health: strengthening our response. 2021.
[2] Charlson, F.J., et al. "Global Epidemiology of Schizophrenia." Lancet Psychiatry, 2018.
[3] Kahn, R.S., et al. "Extrapyramidal Symptoms and Tardive Dyskinesia: Risks and Management." Psychiatr Clin North Am, 2014.