Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Tolterodine, a non-selective muscarinic receptor antagonist, is primarily indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder (OAB). Since its approval, tolterodine has become a cornerstone in OAB management, with a significant global market share. This analysis assesses current market dynamics, competitive landscape, and future sales potential, providing strategic insights for stakeholders.
Market Overview
Prevalence and Demographic Trends
Overactive bladder afflicts approximately 12-17% of the adult population worldwide, with higher prevalence in the elderly and women (1). As aging populations expand globally, especially in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, the demand for effective OAB treatments like tolterodine is poised to rise. Data indicates that the global population aged 60+ is projected to reach 2.1 billion by 2050, amplifying OAB incidence (2).
Regulatory Status and Global Accessibility
Tolterodine was first approved in the United States in 1998 (by Pfizer). It is available as immediate-release (IR) and controlled-release (CR) formulations, with the latter improving compliance and tolerability. While the drug remains on the essential medicines list in several countries, patent expirations and formulation genericization have increased accessibility and reduced costs.
Market Drivers
- Efficacy and Tolerability: Tolterodine's favorable safety profile compared to earlier antimuscarinics makes it a preferred option among clinicians.
- Brand and Generic Competition: Multiple generics boost availability but exert pricing pressures.
- Advances in Formulation: The advent of once-daily formulations enhances patient adherence.
- Growing Awareness: Increased diagnosis of OAB through urological and primary care pathways.
Market Challenges
- Side Effects: Anticholinergic side effects—dry mouth, constipation, cognitive impairment—can limit use, especially in older patients.
- Emergence of Alternatives: Beta-3 adrenergic agonists (e.g., mirabegron) offer non-anticholinergic options, shifting market preferences.
- Patient Compliance: Long-term adherence remains problematic; side effect profiles influence persistence.
Competitive Landscape
Major Players
- Pfizer and Generic Manufacturers: Historically dominant, with Pfizer’s Detrol (brand of tolterodine) leading prior to patent expiry.
- Other Antimuscarinics: Oxybutynin, solifenacin, darifenacin serve as direct competitors.
- Beta-3 Agonists: Mirabegron and vibegron present alternative mechanisms with different tolerability profiles.
Market Share Distribution
Following patent expiry around 2011, generic tolterodine captured significant market share, while some clinicians shifted towards newer agents with better tolerability. Nonetheless, traditional antimuscarinics remain relevant, especially in settings with cost constraints.
Sales Projections (2023-2030)
Historical Sales Trends
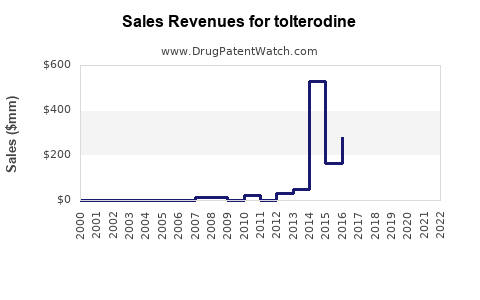
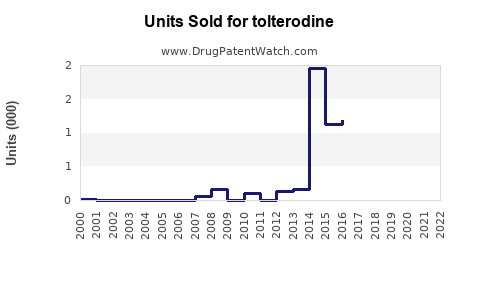
Prior to patent expiration, annual global sales of branded tolterodine (Detrol/Lol) exceeded $800 million (3). Post-patent, sales declined sharply, giving way to generics, yet the overall market for OAB drugs expanded.
Forecast Assumptions
- Market Growth Rate: Estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4-6% in OAB therapeutics driven by aging demographics.
- Impact of Generics: Discounted pricing sustains volume but constrains margins.
- Shift Towards Non-Patent Fractured Markets: Greater market penetration in emerging economies due to lower costs.
- Role of New Formulations: Extended-release formulations sustaining current user base and attracting new patients.
Projected Sales
Analysts forecast the global tolterodine market to reach approximately $400-$500 million annually by 2025, with a steady increase to $600 million by 2030, driven by demographic trends, increasing OAB awareness, and expanding access in developing regions. The rise in generic sales will continue to dominate revenue streams, though the premium segment may stabilize with newer agents.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
- Manufacturers: Focus on formulation innovations (e.g., sustained-release, combination therapies) to differentiate in a commoditized market.
- Investors: Prioritize companies with strong generics portfolios and emerging pipeline drugs targeting OAB.
- Healthcare Providers: Emphasis on personalized medicine, considering side effect profiles and patient age when prescribing.
- Policy Makers/National Health Systems: Cost-containment strategies favor generic utilization, favoring volume over margins.
Conclusion
Tolterodine remains a relevant therapy segment in the OAB market, with a stable demand influenced by demographics and clinical preferences. While generic competition has subdued premium sales, the overall market growth prospects are robust due to aging populations and increasing OAB awareness globally. Investment and innovation opportunities persist, particularly in formulations that enhance tolerability and adherence.
Key Takeaways
- The global OAB market is projected to reach over $600 million in tolterodine-related sales by 2030, driven by demographic shifts.
- Patent expirations and product commoditization have shifted revenue streams toward generics, but clinical preference remains strong for traditional antimuscarinics.
- Emerging therapies, particularly beta-3 agonists, are impacting market share dynamics, prompting existing players to innovate.
- Cost-effective access in developing countries could stimulate sales growth in lower-income regions.
- Formulation improvements and combination therapies offer avenues for differentiation and sustained revenue.
FAQs
1. What factors influence tolterodine’s market share within the OAB treatment landscape?
Factors include side effect profile, patient adherence, availability of generics, competition from newer agents like mirabegron, and regional prescribing guidelines.
2. How does patent expiration affect tolterodine sales globally?
Patent expiry led to a surge in generic formulations, reducing prices and opening markets but decreasing revenue for brand manufacturers. Despite this, overall demand persists due to clinical efficacy and cost advantages.
3. Are there ongoing innovations in tolterodine formulations?
While no major proprietary advances are currently patented, existing formulations emphasize sustained-release mechanisms to improve compliance and minimize side effects.
4. How might shifts toward non-anticholinergic therapies impact tolterodine's future sales?
The adoption of beta-3 agonists like mirabegron could reduce tolterodine’s market share, especially among patients intolerant to anticholinergic side effects; however, cost advantages of tolterodine will sustain its presence.
5. What emerging markets offer the greatest growth potential for tolterodine?
Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and parts of Africa present significant growth opportunities due to expanding healthcare infrastructure, increasing diagnosis of OAB, and growing acceptance of generic medications.
References
- Milsom, I., et al. (2012). "Global prevalence of overactive bladder: A systematic review and meta-analysis." Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica.
- World Health Organization. (2021). "Aging and health: A global overview."
- Pfizer Annual Reports (pre-2011).
- MarketResearch.com. (2022). "Global Overactive Bladder Therapeutics Market Outlook."