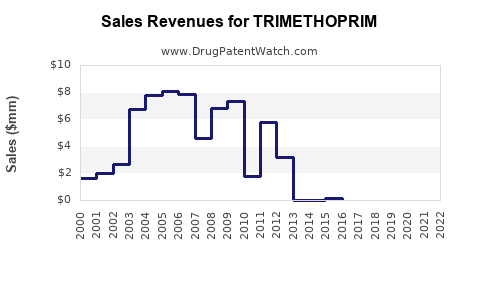
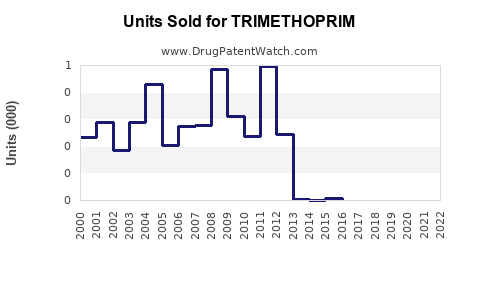
Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Trimethoprim is a synthetic antibiotic predominantly used to treat bacterial infections, notably urinary tract infections (UTIs), respiratory infections, and certain gastrointestinal conditions. Approved for decades, its integration into clinicians’ therapeutic arsenals is supported by established efficacy and a generally favorable safety profile. This market analysis provides a comprehensive review of trimethoprim’s current positioning, emerging trends, competitive landscape, regulatory environment, and future sales projections.
Pharmacological Profile and Clinical Use
Trimethoprim functions by inhibiting bacterial dihydrofolate reductase, leading to impaired DNA synthesis and bacterial growth suppression [1]. Its off-label uses and combination therapies, especially with sulfamethoxazole (as co-trimoxazole), enhance its therapeutic utility. Mono-therapy remains standard for uncomplicated UTIs, especially in regions where resistance patterns are favorable.
Clinicians favor trimethoprim due to its oral bioavailability, cost-effectiveness, and relatively low side-effect profile, making it a first-line treatment for uncomplicated UTIs per guidelines from organizations such as the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) [2].
Market Landscape
Global Market Size
The global antimicrobial drugs market, valued at approximately USD 55 billion in 2022, continues to expand driven by rising infection rates, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), and increasing healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets [3]. Trimethoprim, as a subdivision of this market, accounts for an estimated USD 3-4 billion, representing roughly 7% of the broad antimicrobial portfolio.
Regional Distribution
-
North America: Dominates with a significant market share due to high antibiotic usage, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and robust prescribing guidelines. Canada and the US collectively represent about 45% of global trimethoprim sales.
-
Europe: Gradually increasing demand, driven by rising UTI cases, especially among aging populations. The European market accounts for approximately 30%.
-
Asia-Pacific: The fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 4-5%, fueled by rising bacterial infection prevalence, improved pharmaceutical distribution channels, and government health initiatives expanding access to antibiotics.
-
Emerging Markets: Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East show increasing consumption but face challenges related to antimicrobial resistance, regulation, and affordability.
Market Drivers
-
Rising Incidence of UTIs: Annually, over 150 million UTIs are diagnosed globally, with women being disproportionately affected [4].
-
Evolving Resistance Patterns: While resistance to trimethoprim remains moderate in some regions, rising resistance in certain areas prompts the need for combination therapy or alternative treatments.
-
Introduction of Generics: The availability of inexpensive generic formulations continues to sustain high-volume prescribing.
-
Guideline Endorsements: Clinical guidelines endorsing trimethoprim as first-line therapy bolster demand, especially where resistance remains low.
Competitive Landscape
Key players include generic pharmaceutical manufacturers, with major brands like Teva Pharmaceuticals, Mylan, and local regional producers dominating the landscape. Patent expiry of several brand-name formulations has led to a saturated market with price competition and increased penetration of generics.
Emerging alternative antibiotics, such as fosfomycin and nitrofurantoin, are gaining ground in certain regions, especially where resistance limits trimethoprim's effectiveness [5].
Regulatory Environment and Impact
Regulatory agencies, including the FDA (USA), EMA (Europe), and WHO, continually update guidelines based on resistance data. They influence prescribing behaviors and approve new formulations, combinations, or delivery modes.
Furthermore, antimicrobial stewardship initiatives globally aim to optimize antibiotic utilization, which can affect volume growth in the long term. These programs tend to favor narrow-spectrum agents like trimethoprim when appropriate, supporting its continued market relevance.
Sales Projections (2023-2030)
Forecast Assumptions
- Steady growth in global infection prevalence.
- Continued expansion in emerging markets.
- Moderate impact of increasing antimicrobial resistance.
- Increasing use of combination therapies to counter resistance.
- Regulatory and stewardship policies remain balanced, neither sharply restricting nor excessively promoting use.
Projected Growth Trends
Based on conservative analysis, trimethoprim’s global sales are expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 3.5% from 2023 to 2030, reaching an estimated USD 4.8–5.2 billion by the end of this period.
Key Factors Influencing Sales
-
Increased Incidence of Long-term UTIs: Rising in aging populations, especially in Japan, Europe, and North America.
-
Emerging Resistance: Potential shifts in prescribing protocols in response to resistance patterns, possibly leading to increased combination therapies or shifts to alternative antibiotics.
-
New Formulations: Development of fixed-dose combinations and extended-release formulations could stimulate sales.
-
Global Health Initiatives: Efforts to combat AMR may temper growth, emphasizing judicious use over volume expansion.
Market Challenges
-
Rising Resistance: Particularly in regions like Asia and Southern Europe, where resistance to trimethoprim approaches critical thresholds, may limit sales growth.
-
Alternative Therapies: Increased use of newer antibiotics or non-antimicrobial modalities may substitute trimethoprim.
-
Regulatory Stringency: Potential restrictions on antibiotic prescribing to curb AMR, including tighter guidelines on trimethoprim use, could curb sales.
Opportunities
-
Personalized Medicine: Tailored therapy based on resistance profiles can promote optimal use.
-
Combination Therapies: Development of novel combination formulations can tap into treatment guidelines favoring multi-drug regimens.
-
Regional Expansion: Targeted marketing in rapidly developing markets with expanding healthcare access.
Conclusion
Trimethoprim maintains a significant footprint within the global antimicrobial market, supported by its longstanding efficacy, affordability, and role in managing common bacterial infections. While resistance patterns and stewardship policies pose challenges, the overall sales trajectory remains positive, with projected growth reflecting ongoing demand, especially in emerging markets and aging populations.
Key Takeaways
-
Steady Global Demand: The trimethoprim market is expected to grow at approximately 3.5% CAGR until 2030, reaching over USD 5 billion.
-
Regional Dynamics: North America and Europe dominate, while Asia-Pacific offers high growth potential due to expanding healthcare infrastructure.
-
Resistance Challenges: Monitoring resistance trends is crucial, as rising resistance may necessitate shifts in prescribing or development of new formulations.
-
Market Opportunities: Innovation via combination therapies and targeted marketing in emerging markets can boost future sales.
-
Regulatory Impact: Evolving stewardship policies will influence prescribing practices and market size sustainability.
FAQs
1. What factors could most significantly impact trimethoprim sales in the next decade?
Resistance development, changes in clinical guidelines, regulatory restrictions, and competition from newer or alternative antibiotics will chiefly influence sales trajectories.
2. How does antimicrobial resistance affect the future of trimethoprim?
Increasing resistance reduces drug efficacy, potentially limiting long-term use and prompting shifts to alternative therapies or combination formulations, thereby impacting sales volume.
3. Are new formulations or combinations of trimethoprim being developed?
Yes. Ongoing research focuses on fixed-dose combinations, extended-release formulations, and adjunct therapies to enhance efficacy and circumvent resistance.
4. How do global health initiatives influence the trimethoprim market?
Stewardship efforts aim to optimize antibiotic prescribing, which could restrict unnecessary use but also promote targeted, guideline-compliant therapy, ensuring sustained demand.
5. What are the key markets for expansion for trimethoprim manufacturers?
Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific and Latin America represent significant growth opportunities due to expanding healthcare access, rising infection rates, and increasing awareness of effective antibiotic therapies.
References:
[1] Barratt, M. J., & O'Neill, C. A. (2014). "Mechanisms of action of trimethoprim." Clinical Pharmacology, 6, 87-95.
[2] Gupta, K., et al. (2011). "International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infection." Clinical Infectious Diseases, 52(5), e103-e120.
[3] MarketWatch. (2022). "Global antimicrobial drugs market report."
[4] Foxman, B. (2014). "Urinary tract infection syndromes: frequency, resistance, and emerging resistance." Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology, 35(S3), S16-S20.
[5] Hooton, T. M., et al. (2014). "Emerging resistance patterns and alternative therapies for urinary tract infections." American Journal of Medicine, 127(3), 271-278.