Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for PHENYTOIN
✉ Email this page to a colleague
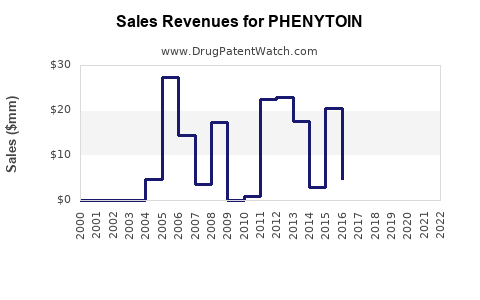
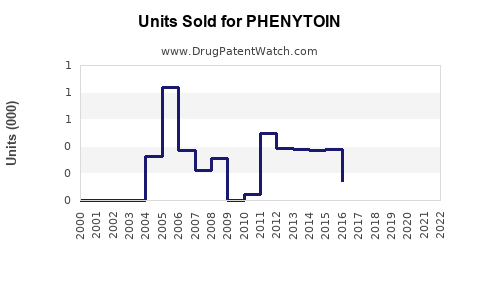
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for PHENYTOIN
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| PHENYTOIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| PHENYTOIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| PHENYTOIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Phenytoin
Introduction
Phenytoin, a classical anticonvulsant medication primarily used to control seizures, has maintained a significant presence in the neurological therapeutics market for decades. With its longstanding approval and well-established efficacy, phenytoin remains a critical therapy for epilepsy and seizure management. This analysis covers the current market landscape, key factors influencing sales, and future sales projections, considering emerging trends, competitive dynamics, and regulatory developments.
Market Overview
Current Market Size
The global antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) market was valued at approximately USD 4.5 billion in 2022, with older drugs like phenytoin retaining a notable share despite the advent of newer agents. Phenytoin's market share is estimated at around 10-15% globally, approximating USD 450–675 million annually. The drug's primary markets include North America, Europe, and select Asian countries, where epilepsy prevalence ranges between 4-10 per 1,000 individuals ([1]).
Geographical Distribution
-
North America: The largest market owing to high epilepsy prevalence, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and extensive prescribing of established AEDs.
-
Europe: Strong adoption similar to North America, with regional variations driven by healthcare policies.
-
Asia-Pacific: Exhibits rapid growth potential, driven by increasing epilepsy diagnosis, urbanization, and improving healthcare access ([2]).
Competitive Landscape
Phenytoin faces competition from novel AEDs like levetiracetam, lamotrigine, and topiramate, which offer improved safety profiles and fewer drug interactions. Despite this, phenytoin remains preferred in specific scenarios such as status epilepticus, owing to its proven efficacy and lower cost. Generic manufacturers dominate the market, contributing to widespread availability and driving down pricing.
Market Drivers
-
Prevalence of Epilepsy and Seizures: Approximately 50 million people worldwide suffer from epilepsy, with a significant subset requiring lifelong pharmacotherapy. The aging population contributes further to incidence rates ([3]).
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Phenytoin’s generic status offers an economical option, especially in developing nations.
-
Established Clinical Profile: Its longstanding history makes it a go-to choice for hospital formularies, especially in resource-constrained settings.
-
Use in Critical Care: The efficacy of phenytoin in status epilepticus sustains demand in emergency medicine.
Market Challenges
-
Safety and Tolerability Concerns: Phenytoin's side effect profile, including gingival hyperplasia, hirsutism, and neurotoxicity, limits its use as a first-line agent compared to newer AEDs ([4]).
-
Drug Interactions: Its enzyme-inducing properties complicate polypharmacy in epilepsy management.
-
Regulatory and Patent Issues: While primarily off-patent, regulatory re-evaluations regarding formulations could impact sales dynamics.
-
Switching Trends: Increasing preference for newer agents with better tolerability may suppress future demand.
Sales Projections
Short-term Outlook (2023-2025)
Given phenytoin's entrenched position, short-term sales are expected to stabilize or slightly decline due to the gradual shift towards newer, better-tolerated AEDs. Despite this, sales are projected to stay within USD 400–500 million annually worldwide, driven by:
- Growing epilepsy burden in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
- Persistent use in emergency settings.
Medium to Long-term Outlook (2026–2030)
Sales trajectory will depend on several factors:
- Regulatory Environment: The approval of generic equivalents and biosimilars may sustain or boost sales.
- Healthcare Policies: Countries emphasizing cost mitigation may continue to favor affordable options like phenytoin.
- Market Penetration of Alternatives: The increasing adoption of newer AEDs with improved safety profiles could cause a gradual decline, with estimates indicating a compound annual decline rate (CADR) of 2-4%.
Projected Global Sales (2023–2030):
| Year | Estimated Sales (USD Million) |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 450 |
| 2024 | 430 |
| 2025 | 410 |
| 2026 | 390 |
| 2027 | 370 |
| 2028 | 350 |
| 2029 | 330 |
| 2030 | 310 |
This projection reflects a slow decline, stabilized by ongoing use in settings where affordability remains paramount.
Market Trends Influencing Future Sales
-
Emergence of Generics and Biosimilars: Will likely sustain supply and reduce prices, marginally supporting volumes despite competition.
-
Formulation Innovations: Development of controlled-release formulations or parenteral forms could expand use cases.
-
Regulatory Revisions: Safety concerns may lead to restrictions, thereby affecting sales in certain regions.
-
Healthcare System Dynamics: Increased emphasis on personalized medicine and pharmacogenomics could influence prescribing patterns.
Impact of Emerging Trends
- Adoption of phenytoin IV formulations for status epilepticus ensures continued emergency market demand.
- Demand in pharmacovigilance-driven environments for drugs with well-characterized safety profiles supports steady sales.
Conclusion
Phenytoin's market will maintain relevance primarily through use in emergency and resource-limited settings. While the broader epilepsy market shifts toward novel agents, phenytoin's low cost and longstanding clinical acceptance shield it from swift obsolescence. A gradual decline is projected, with the potential for regional market stability driven by healthcare infrastructure and affordability considerations.
Key Takeaways
- The global phenytoin market is valued at approximately USD 450–675 million annually, with stability driven by its cost-effectiveness and emergency use.
- Competitive pressure from newer AEDs poses a challenge, but phenytoin's entrenched role sustains moderate demand.
- Sales are expected to decline slowly (~2-4% CAGR) through 2030 but remain significant in low-resource settings.
- Regulatory, safety, and formulation advancements may influence future sales dynamics.
- Market growth will be geographically uneven, emphasizing emerging markets’ importance for ongoing revenue.
FAQs
1. What factors most influence phenytoin sales in the current market?
Market size is primarily driven by epilepsy prevalence, healthcare infrastructure, drug pricing, and the drug's role in emergency settings. Safety profile concerns and competition from newer AEDs also impact prescribing trends.
2. How is the emergence of generic versions affecting phenytoin sales?
Generics lower the barrier to access and price, stabilizing demand and expanding use in cost-sensitive markets, thereby supporting overall sales volumes despite reduced margins.
3. What are the main therapeutic niches sustaining phenytoin demand?
Emergency treatment of status epilepticus, seizure prophylaxis in neurosurgical settings, and management of specific seizure types where alternative AEDs are less effective or contraindicated.
4. How might regulatory changes influence the future of phenytoin?
Safety concerns and pharmacovigilance data could lead to restrictions or updated labeling, which may reduce its use. Conversely, approval of new formulations or biosimilars could bolster supply stability.
5. What is the outlook for phenytoin's role in personalized medicine?
While pharmacogenomics could optimize dosing in some cases, this is unlikely to significantly alter overall market dynamics given the drug’s long-standing profile and widespread use.
References:
- World Health Organization. Epilepsy Fact Sheet. 2021.
- Grand View Research. Antiepileptic Drugs Market Size, Share & Trends. 2022.
- Ngugi AK, et al. "Prevalence of active epilepsy in sub-Saharan Africa." Epilepsia, 2010.
- Patsalos PN. "Pharmacokinetic interactions with new antiepileptic drugs." Epilepsy & Behavior, 2018.
More… ↓
