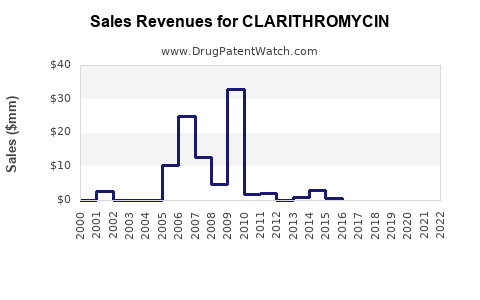
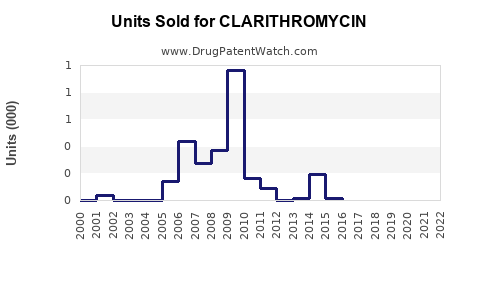
Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
Clarithromycin, a macrolide antibiotic developed by Abbott Laboratories in the 1980s, remains a cornerstone in antimicrobial therapy. Its broad-spectrum activity against respiratory tract infections, Helicobacter pylori, and skin infections, compounded by its favorable pharmacokinetic profile, sustains its global demand. This analysis evaluates the current market landscape and forecasts sales trajectories for clarithromycin, considering factors such as therapeutic indications, regulatory environment, competitive landscape, and emerging trends.
Market Landscape Overview
The global antibiotics market, valued at approximately USD 50 billion in 2022, is projected to grow at a CAGR of around 3.5% (2023–2030) (source: Grand View Research). Clarithromycin’s segment occupies a significant niche owing to its efficacy-profile and existing patent expirations, which facilitate generic proliferation. The drug's primary indications include respiratory infections (e.g., pneumonia, bronchitis), Helicobacter pylori eradication in peptic ulcer disease, and skin infections.
Geographically, North America and Europe dominate the market due to high healthcare expenditures and antimicrobial prescribing practices. Asia-Pacific presents a burgeoning opportunity driven by rising prevalence of infectious diseases and expanding healthcare infrastructure. The high rate of antibiotic resistance, however, poses challenges that could modify demand dynamics.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
Clarithromycin's patents expired in many jurisdictions during the early 2000s, catalyzing a surge in generic formulations, thus intensifying market competition and exerting downward pressure on prices. Nonetheless, branded versions retain market share in specific regions through formulation or patent extensions. Regulatory environments emphasizing antimicrobial stewardship and approval of combination therapies influence sales potential, especially with the development of novel formulations or fixed-dose combinations.
Therapeutic Competition and Resistance Trends
The emergence of resistant strains, notably macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae and Helicobacter pylori, impacts prescription patterns. Molecular surveillance indicates increased resistance rates, particularly in Europe and North America, prompting clinicians to adopt alternative therapies such as azithromycin or doxycycline. This resistance trend necessitates ongoing formulation innovation and may constrain overall market growth.
Market Drivers
- Established Efficacy and Safety: Clarithromycin’s proven track record sustains prescribing confidence.
- Combination Therapy Synergy: Approved fixed-dose combinations for H. pylori eradication bolster demand.
- Expanding Indications: Off-label and new clinical applications could open additional sales channels.
- Generic Availability: Economical formulations enhance accessibility, especially in emerging markets.
Market Constraints
- Antimicrobial Resistance: Resistance-driven prescribing shifts may reduce demand in certain indications.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Stringent antimicrobial stewardship policies limit overuse.
- Competition: Generics and alternative antibiotics challenge market share and pricing.
Sales Projections (2023–2030)
Forecasting clarithromycin sales involves multiple scenarios. Under conservative assumptions—with continued generic competition, resistance trends, and cautious prescribing—annual sales are projected to decline modestly at a CAGR of approximately -1% to -2%. However, in regions where new indications or formulations are introduced, or where stewardship policies relax, stabilization or slight growth may occur.
| Year |
Projected Global Sales (USD billion) |
Notes |
| 2023 |
1.20 |
Baseline, ongoing generic competition |
| 2024 |
1.17 |
Slight decline due to resistance and market saturation |
| 2025 |
1.15 |
Resistance impact persists, with some expansion in APAC |
| 2026 |
1.12 |
Entry of new formulation or indicational approvals |
| 2027 |
1.10 |
Continued market consolidation |
| 2028 |
1.08 |
Persistent resistance challenges |
| 2029 |
1.05 |
Resistance plateau, focus on stewardship |
| 2030 |
1.02 |
Slight decrease, stable demand in niche indications |
This projection accounts for the maturation of the market, resistance genetics, and the influence of emerging formulations. Regions such as Asia-Pacific may experience a less steep decline or plateau due to rising healthcare access and innovation, whereas mature markets may see more consistent reductions.
Strategic Opportunities
- Development of resistance-evading formulations or synergistic combinations.
- Targeted marketing of niche indications with lower resistance rates.
- Expansion into emerging markets with strategic pricing and local partnerships.
- Investing in stewardship programs that promote appropriate prescribing, preserving clarithromycin’s utility.
Risks and Mitigation
- Accelerated antimicrobial resistance could diminish efficacy and demand.
- Regulatory restrictions could restrict broad prescribing.
- Competitive pressures from entrenched generics and new antibiotics.
Vigilant monitoring of resistance patterns, ongoing clinical research, and adaptive marketing strategies are essential prescription for future success.
Conclusion
While clarithromycin’s global sales are projected to decline slightly over the next decade due to factors like resistance and competition, strategic repositioning and formulation innovations can sustain its market relevance. Industry stakeholders should focus on resistance management, exploring new indications, and regional expansion to offset headwinds and maximize value.
Key Takeaways
- Market is consolidating, with a slight decline forecasted (~1–2% CAGR) driven by resistance and generic competition.
- Regional disparities favor Asia-Pacific, offering opportunities for sales growth or stabilization.
- Resistance evolution remains a critical factor, influencing prescribing and formulation development.
- Innovation in combinations and new indications can breathe new life into clarithromycin’s market prospects.
- Strategic stewardship and market adaptation are vital for maintaining relevance amid evolving therapeutic landscapes.
FAQs
1. What are the main therapeutic indications driving clarithromycin sales?
Clarithromycin is primarily used for respiratory tract infections, Helicobacter pylori eradication in peptic ulcers, and skin infections. Its role in combination therapies for H. pylori is particularly significant.
2. How does antibiotic resistance affect clarithromycin’s market outlook?
Rising resistance, especially in S. pneumoniae and H. pylori, limits efficacy, shifts prescribing practices towards alternatives, and constrains sales growth in key markets.
3. Are there any recent innovations that may influence clarithromycin sales?
Formulation advancements, such as fixed-dose combinations, and exploration of new indications could mitigate declining trends and open new markets.
4. Which regions offer the most growth potential for clarithromycin?
Asia-Pacific presents promising growth due to expanding healthcare infrastructure, increasing infectious disease prevalence, and emerging markets, despite resistance challenges.
5. What strategies can pharmaceutical companies adopt to sustain clarithromycin’s market presence?
Investing in resistance mitigation, developing new formulations or indications, expanding geographically, and engaging in stewardship programs are critical.
Sources:
[1] Grand View Research. "Antibiotics market analysis." 2022.
[2] World Health Organization. "Antimicrobial resistance surveillance reports." 2021.
[3] MarketWatch. "Global antibiotics market outlook." 2023.