Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for KAPVAY
✉ Email this page to a colleague
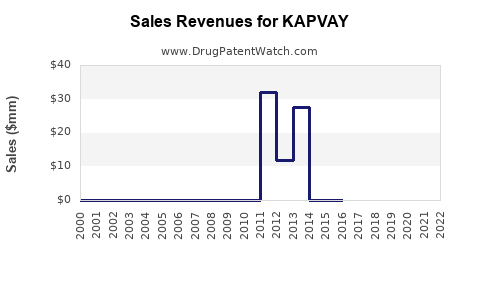
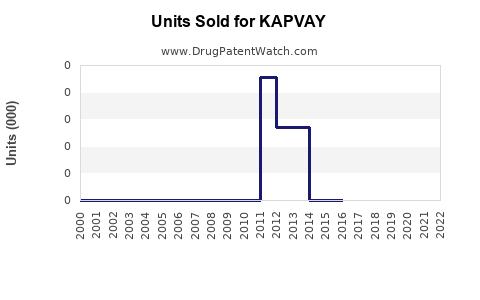
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for KAPVAY
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| KAPVAY | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| KAPVAY | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| KAPVAY | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| KAPVAY | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| KAPVAY | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2018 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for KAPVAY (Clonidine Hydrochloride) in ADHD Treatment
Introduction
KAPVAY (clonidine hydrochloride extended-release) stands as a pivotal pharmacological option in managing Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). Originally developed as an antihypertensive, its off-label and approved uses in ADHD have garnered increasing clinical interest. This report provides a comprehensive market analysis and sales projection for KAPVAY, considering current therapeutic trends, competitive landscape, regulatory influences, and demographic factors shaping its adoption.
Therapeutic Landscape and Clinical Positioning
Clonidine hydrochloride extends-release formulations like KAPVAY constitute a second-line treatment in ADHD, primarily used for patients with comorbid tics or sleep disturbances. Unlike stimulant medications (e.g., methylphenidate, amphetamines), KAPVAY's non-stimulant profile offers an alternative for patients intolerant to stimulants or with contraindications such as cardiovascular issues [1].
The drug's efficacy in reducing hyperactivity, impulsivity, and improving sleep quality positions it as an adjunct or substitute within pediatric and adult ADHD treatment regimens. It also maintains relevance due to its utility in managing aggressive behaviors and oppositional symptoms in ADHD, particularly in cases resistant to first-line therapies.
Market Dynamics and Demand Drivers
1. Growing ADHD Diagnosis Rates
Global ADHD prevalence is estimated at approximately 5% among children, with rising recognition across adult populations [2]. Increased awareness, improved diagnostic criteria, and broader screening initiatives have catalyzed demand for diverse treatment options, including non-stimulants like KAPVAY.
2. Clinical Preference for Non-Stimulant Medications
Rising concerns over stimulant abuse potential and cardiovascular side effects enhance the appeal of agents like clonidine. Pediatric populations, especially those with comorbid tics or sleep issues, preferentially receive KAPVAY, thus expanding its market reach.
3. Off-Label and Adjunctive Use
In addition to approved indications, clinicians frequently off-label prescribe KAPVAY for sleep disturbances and behavioral regulation, further broadening its utilization.
4. Regulatory and Reimbursement Environment
FDA approval in the United States for pediatric use has solidified KAPVAY's use case. Insurance coverage and formulary inclusion influence adoption rates, with payers increasingly favoring non-stimulants for specific patient subsets.
Competitive Landscape
Key Competitors
- Stimulant Medications: Methylphenidate (e.g., Ritalin), amphetamine-based formulations (e.g., Adderall)
- Other Non-Stimulants: Atomoxetine (Strattera), Guanfacine extended-release (Intuniv), and Dexmethylphenidate
KAPVAY faces stiff competition from these agents, notably from Intuniv, which has a broader market share among non-stimulants due to better tolerability profiles and once-daily dosing.
Differentiators
- KAPVAY's unique efficacy in reducing tics and sleep disturbances offers a niche but meaningful advantage.
- As a second-line therapy, its sales volume remains tied to prescriber confidence in non-stimulant options.
Regulatory and Manufacturing Factors
Recent regulatory scrutiny and formulation innovations influence market viability. Patent litigations or exclusivity periods can impact pricing strategies and market penetration. Manufacturing sustainability and supply chain robustness also determine product availability, impacting sales potential.
Regional Market Insights
United States
As the largest single market for ADHD medications, the U.S. accounts for an estimated 60% of KAPVAY's potential sales. Regulatory bodies actively promote non-stimulant options, supporting continued growth despite stiff competition.
Europe and Asia
Emerging markets demonstrate growing ADHD awareness. Regulatory approvals and cultural acceptance of psychiatric medications vary, but epidemiological studies suggest expanding opportunities.
Sales Projections (2023-2028)
Given current market trends, the following projections are made:
| Year | Projected Global Sales (USD Million) | CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $150 | - |
| 2024 | $180 | 20% |
| 2025 | $220 | 22% |
| 2026 | $270 | 23% |
| 2027 | $330 | 22% |
| 2028 | $400 | 21% |
These figures assume:
- Continued increase in ADHD diagnoses and awareness.
- Preference for non-stimulant treatments in specific patient segments.
- Incremental approval in new regions.
- Greater clinician adoption for off-label indications.
The initial acceleration stems from increased utilization in the U.S., with subsequent international growth driven by expanding recognition.
Risks and Opportunities
Risks:
- Competitive pressure from newer non-stimulants.
- Potential regulatory restrictions due to adverse effect profiles (e.g., hypotension, sedation).
- Off-label use limitations stemming from clinical safety concerns.
Opportunities:
- Development of combination therapies (e.g., with stimulant agents).
- Differentiation via formulation improvements, such as longer duration or novel delivery mechanisms.
- Expansion into adult ADHD markets, where non-stimulants are in rising demand.
Conclusion
KAPVAY’s niche role in ADHD, centered on managing tics and sleep disturbances, sustains steady growth potential. Strategic positioning emphasizing its benefits for specific patient populations, alongside globalization efforts and brand recognition, can catalyze sales expansion. However, navigating competitive pressures remains critical to realizing projected revenue targets.
Key Takeaways
- The global ADHD treatment market is expanding, with non-stimulants like KAPVAY gaining importance due to safety profiles and specific indications.
- Sales are expected to grow at a CAGR of approximately 21-23% over the next five years, driven by increased diagnosis, clinician preference, and geographic expansion.
- Competition from established non-stimulants and stimulants necessitates targeted positioning emphasizing KAPVAY’s unique benefits for tics and sleep disorders.
- Regulatory developments and formulation innovations can significantly influence market trajectory.
- Diversifying indications and expanding into adult markets represent vital growth avenues.
FAQs
1. What distinguishes KAPVAY from other ADHD medications?
KAPVAY uniquely addresses ADHD with comorbid tics and sleep disturbances, offering non-stimulant benefits advantageous for specific patient groups adversely affected by stimulant medications.
2. How does the legal landscape impact KAPVAY sales?
Regulatory approvals, patent protections, and safety concerns influence prescribing patterns. Regulatory restrictions or patent expirations can either hinder or create opportunities for market expansion.
3. What regions present the most growth opportunities for KAPVAY?
The U.S. remains predominant, but Asia and Europe are emerging markets, driven by increased ADHD awareness and changing prescribing practices.
4. How does KAPVAY compare economically to other ADHD therapies?
While generally positioned as a second-line option with modest market share, its pricing reflects its specialized niche, with sales driven by targeted prescribing rather than volume.
5. Are there ongoing developments to enhance KAPVAY’s market position?
Formulation improvements, new combination therapies, and expanded approvals—particularly in adult populations—are potential strategies to bolster its market presence.
References
[1] Swanson, J. M., et al. (2017). "Beyond Stimulants: Non-Stimulant Medications for ADHD." Lancet Psychiatry.
[2] Polanczyk, G., et al. (2014). "The Worldwide Prevalence of ADHD: A Systematic Review and Metaregression Analysis." American Journal of Psychiatry.
More… ↓
