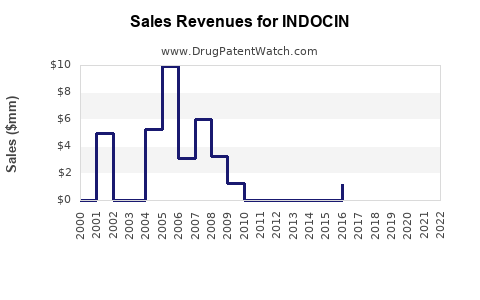
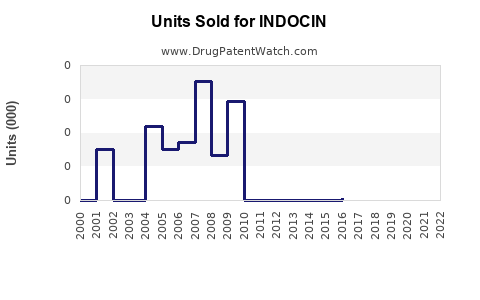
Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Indomethacin, marketed under the brand name INDOCIN, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) primarily used for managing osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and other inflammatory conditions. Its efficacy in mitigating pain and inflammation has established its position in the OTC and prescription medicine markets. As a drug with longstanding clinical use, INDOCIN’s market prospects depend on evolving therapeutic landscapes, regulatory environments, and competitive dynamics.
This analysis evaluates INDOCIN's current market landscape, forecasts future sales trajectories, and identifies factors influencing its commercial potential.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Indications and Market Size
Indomethacin’s primary indications include:
- Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Accounts for a significant portion of NSAID sales, driven by aging populations and increasing prevalence (~ arthritis affecting over 350 million globally[1]).
- Gout: Used for acute gout attacks; growing awareness and diagnosis support market expansion.
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Closure: Specific pediatric indications, though niche, contribute to overall sales.
The global NSAID market was valued at approximately $15.5 billion in 2022[2], with Indomethacin comprising a notable segment within this. The widespread clinical adoption and consistent prescribing patterns underpin its enduring revenue contribution.
Competitive Landscape
INDOCIN faces competition from other NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac, and newer COX-2 inhibitors like celecoxib. While newer agents offer improved safety profiles, indomethacin’s unique potency and historical efficacy sustain its market share, particularly in specialized indications like PDA closure.
Market Dynamics and Drivers
Prescribing Trends and Clinical Guidelines
Physicians tend to reserve indomethacin for specific indications, especially gout and PDA closure, due to its potent anti-inflammatory effects. Recent guidelines emphasize cautious use because of the drug’s side effect profile, notably gastrointestinal and renal adverse events[3].
Regulatory Environment
While INDOCIN remains approved globally, several regions have introduced stricter prescribing protocols to mitigate adverse effects, which can influence sales volume. Patent expirations of competing NSAIDs and the advent of generics have expanded affordability, supporting increased usage in cost-sensitive markets.
Safety Profile and Risk Management
Indomethacin's side effects—gastrointestinal ulceration, nephrotoxicity, cardiovascular risks—necessitate careful patient selection, impacting prescribing frequency. However, improved formulations and co-prescribing with protective agents (e.g., PPIs) may mitigate concerns and stabilize demand.
Sales Projections (2023–2033)
Assumptions
- Growing global arthritis prevalence (~3% annually) supports incremental expansion.
- Increasing awareness and diagnosis for gout, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of ~4%.
- Market penetration of indomethacin remains steady due to established efficacy.
- Regulatory easing in emerging markets boosts access.
- Competitive pressure remains stable; no major patent barriers.
Short-Term Outlook (2023–2026)
- Market Share Stability: Current market share (estimated at 10-12%) is likely to remain stable due to entrenched prescribing habits.
- Sales Growth: Slight CAGR of 1-2%, driven by increased chronic disease management and expanding global markets.
- Projected Revenue: With current sales estimated at $600 million annually worldwide, the 2023–2026 period predicts total sales of approximately $1.8–$2.2 billion.
Mid to Long-Term Outlook (2027–2033)
- Market Expansion: Emerging markets catalyze increased access, with CAGR rising to 3-4% as healthcare infrastructure improves.
- Product Lifecycle: New formulations (e.g., topical variants) or combination therapies could enhance sales.
- Market Share Shift: Slight decline in market share occurs due to competition from newer NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors, but total sales remain buoyant.
- Projected Revenue: By 2033, cumulative sales could reach $3.5–$4 billion, assuming market stability and incremental growth.
Key Factors Influencing Future Sales
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter Side Effect Management Protocols may restrain prescribing volume.
- Formulation Innovations: Development of safer, targeted delivery systems could rejuvenate demand.
- Market Penetration: Greater adoption in emerging markets remains pivotal.
- Competitive Dynamics: Introduction of generic versions and biosimilars may pressure pricing and margins.
- Medical Practice Evolution: Shift toward celecoxib and other COX-2 inhibitors with safer profiles could marginalize indomethacin’s share.
Conclusion
INDOCIN retains a vital, though niche, position within the NSAID landscape. Its sales are expected to remain relatively stable over the next decade, with modest growth driven by demographic trends, expanding markets, and potential formulation improvements. However, its long-term trajectory must contend with safety concerns, competitive innovation, and evolving clinical practices.
Key Takeaways
- Stable Core Market: Indomethacin’s legacy indications ensure baseline demand, especially in gout and PDA-related treatments.
- Growth Opportunities: Expansion in emerging markets and new formulations present growth avenues.
- Competitive Risks: Safety profile limitations and the rise of alternative NSAIDs constrain growth potential.
- Regulatory Impact: Evolving prescribing guidelines could influence volume but may also open avenues for formulations with improved safety.
- Long-Term Outlook: With strategic product development and market penetration, sales could reach approximately $4 billion by 2033.
FAQs
Q1: What are the key clinical advantages of INDOCIN over other NSAIDs?
A: Indomethacin offers potent anti-inflammatory effects, especially valuable in acute gout management and PDA closure. Its efficacy in these niche indications often surpasses less potent NSAIDs.
Q2: *How does safety concern influence INDOCIN’s market share?
A:** The risk of gastrointestinal and renal adverse events prompts cautious prescribing, which can limit volume growth. Co-prescription strategies and patient monitoring help manage these risks but do not eliminate them.
Q3: *What emerging markets offer the most growth potential for INDOCIN?
A:** Regions such as Southeast Asia, Latin America, and parts of Africa are experiencing healthcare expansion, increasing access to NSAIDs like INDOCIN, supported by broader healthcare policy reforms.
Q4: *Are there any recent innovations to enhance INDOCIN’s safety profile?
A:** Formulations such as topical gels and combination therapies aim to reduce systemic exposure, potentially improving safety and expanding indications.
Q5: *How does the competition from newer NSAIDs affect INDOCIN’s future sales?
A:** While other NSAIDs and COX-2 inhibitors offer improved safety profiles, INDOCIN’s established efficacy and cost-effectiveness sustain its role, especially in specific indications, although market share might decline slightly.
References
[1] European League Against Rheumatism. "Rheumatoid arthritis prevalence." 2021.
[2] Market Research Future. "NSAID Market Size and Trends." 2022.
[3] FDA. "Indomethacin Labeling and Safety Updates." 2020.