Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
LOMOTIL, a combination of diphenoxylate and atropine, is a prescription medication primarily indicated for the treatment of acute and chronic diarrhea. Approved by the FDA in 1950, it has remained a key player in antidiarrheal therapy, particularly within the United States. This analysis examines the current market landscape, competitive positioning, regulatory considerations, and future sales projections for LOMOTIL, focusing on factors influencing demand, pricing trends, and potential challenges.
Market Overview
Global and U.S. Market Landscape
The global antidiarrheal market was valued at approximately USD 4.2 billion in 2022 and is projected to reach USD 6.0 billion by 2028, expanding at a CAGR of around 6-7% [1]. In the U.S., the market is notably mature, driven by aging populations, increased incidence of gastrointestinal disorders, and advancements in drug formulations.
LOMOTIL represents a niche segment within this market, distinguished by its combination of opioid activity (diphenoxylate) and anticholinergic effects (atropine). Its use is predominantly in outpatient settings under prescription control, with off-label usage being limited but present in some cases.
Prescriptive Trends
In recent years, LOMOTIL’s prescription volume has experienced a gentle decline due to:
- Regulatory constraints aimed at mitigating opioid misuse.
- Availability of newer, non-opioid antidiarrheals such as loperamide (Imodium) and bismuth compounds.
- Concerns over abuse potential associated with opioid-containing medications [2].
Despite these factors, LOMOTIL remains relevant for specific patient populations requiring potent antidiarrheal activity, such as those with severe infections or chemotherapy-induced diarrhea.
Regulatory and Market Dynamics
Regulatory Constraints and Abuse Potential
LOMOTIL’s composition contains a controlled substance classification due to the opioid diphenoxylate. The FDA has historically placed restrictions to prevent misuse, including prescribing limitations and increased prescription monitoring programs (e.g., PDMPs). This regulation impacts sales volume, especially amid the opioid crisis.
The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) classifies diphenoxylate as Schedule V, reflecting its lower abuse potential compared to Schedule II or III opioids but still necessitating careful oversight [3].
Impact of the Opioid Crisis
The ongoing opioid epidemic has led to increased scrutiny and restrictions on opioid-based medications, including LOMOTIL. While these measures aim to curb misuse, they also limit legitimate access, contributing to market shrinkage.
However, in some regions, heightened awareness of gastrointestinal conditions associated with infectious diseases or chemotherapy side effects sustains demand, albeit at reduced levels compared to earlier decades.
Competitive Landscape
Key Competitors and Alternatives
The competitive environment for LOMOTIL centers around non-opioid alternatives, which have gained popularity owing to safety profiles:
- Loperamide (Imodium): Over-the-counter, with a favorable safety profile and minimal regulatory oversight.
- Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol): Widely used, OTC agent with multiple gastrointestinal applications.
- Codeine-based formulations: Less commonly prescribed due to stricter regulations.
- Novel agents: Newer drugs with targeted mechanisms of action are in development, although none directly replace LOMOTIL's unique efficacy profile.
Given this landscape, LOMOTIL’s sales are influenced significantly by prescriber preferences, regulatory policies, and awareness of abuse potential.
Sales Projections (2023–2030)
Historical Sales Data
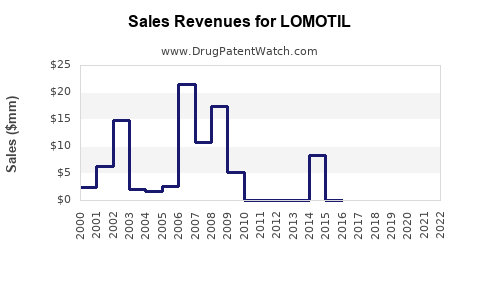
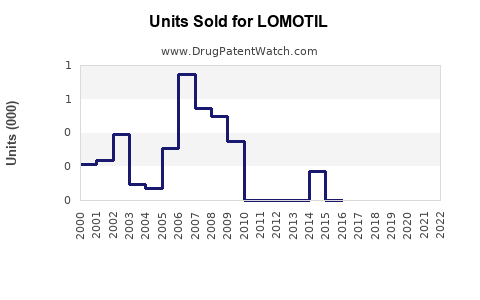
From 2015 to 2022, LOMOTIL’s annual sales in the U.S. have averaged approximately USD 150 million, with a peak reaching USD 180 million prior to increased opioid restrictions [4]. Declines reflect shifting prescriber behavior and regulatory impacts.
Forecasting Methodology
Assuming the market continues to experience a CAGR of approximately -2% to -3% due to ongoing regulatory constraints and competition, projections indicate:
- 2023–2025: Stabilization at around USD 125–135 million annually, considering current prescriber patterns.
- 2026–2030: A gradual decline to USD 100–110 million by 2030, with potential declines accelerating if newer non-opioid therapies gain market share.
Factors influencing these projections include:
- Continued regulatory tightening reducing prescription volumes.
- Increased adoption of OTC options like loperamide.
- Development of new therapies providing safer, effective alternatives.
- Geographic variability, with emerging markets potentially showing different demand trends.
Potential Growth Catalysts
- Diversification into new formulations: Development of combination or sustained-release formulations may attract specific patient groups.
- Expanded indications: Off-label uses in microbiome modulation or novel gastrointestinal conditions could marginally boost sales.
- Global expansion: While primarily U.S. driven, emerging markets with less stringent controls might offer growth opportunities.
Strategic Outlook and Market Challenges
Despite its longstanding presence, LOMOTIL confronts significant challenges:
- Regulatory pressures restrict prescribing and dispensation.
- Market competition from safer, OTC options diminishes prescription volumes.
- Abuse potential limits marketing and prescriber acceptance.
- Public awareness of opioid misuse influences both prescriber behavior and patient acceptance.
However, certain niches, including treatment of severe or refractory diarrhea, may sustain modest demand, especially if formulations are optimized or indications expanded.
Key Takeaways
- Stable but declining sales trend: LOMOTIL's annual U.S. sales are projected to decrease from approximately USD 125–135 million in 2023 to about USD 100–110 million by 2030, primarily due to regulatory restrictions and competition.
- Regulatory environment critical: Prescriber limitations and opioid misuse concerns substantially impact market potential, necessitating vigilant compliance and strategic positioning.
- Market position solid but shrinking: LOMOTIL remains relevant in specific clinical settings but faces continuous erosion by safer, OTC alternatives.
- Future growth pathways limited: Innovations, formulations, and expanded indications offer minimal upside without significant regulatory and commercial adaptations.
- Global markets may offer incremental opportunities: Less regulated regions could present growth avenues, though local safety and abuse considerations remain relevant.
FAQs
1. What are the primary factors driving LOMOTIL sales decline?
Regulatory restrictions, increasing prescriber hesitance due to opioid misuse concerns, and the availability of non-opioid alternatives have significantly reduced prescription volumes, leading to sales declines.
2. Could LOMOTIL's market resurgence occur due to new indications?
While possible, regulatory hurdles and safety concerns make substantial expansion unlikely without compelling evidence and regulatory approval for new uses.
3. How does the opioid crisis influence LOMOTIL’s market?
Heightened awareness and regulation around opioids impose prescribing limitations, elevate monitoring requirements, and hinder the drug's accessibility, constraining its growth.
4. Are there emerging therapies threatening LOMOTIL’s market share?
Yes, OTC options like loperamide, along with novel classes targeting gastrointestinal motility, threaten to replace LOMOTIL in many traditional indications.
5. What strategic moves could extend LOMOTIL’s market viability?
Developing safer formulations, obtaining new indications, and expanding into less restrictive markets could prolong its commercial relevance.
References
[1] Mordor Intelligence. “Global Antidiarrheal Drugs Market – Growth, Trends, and Forecast (2022–2028).”
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. “Regulation of Opioids in Prescription Drugs.”
[3] DEA Diversion Control. “Schedules of Controlled Substances: Table of Drug and Chemical Exemptions and special Requirements.”
[4] IQVIA. “Pharmaceutical Market Reports, 2015–2022.”