Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for GENTAMICIN
✉ Email this page to a colleague
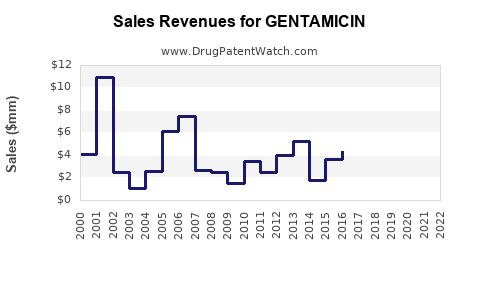
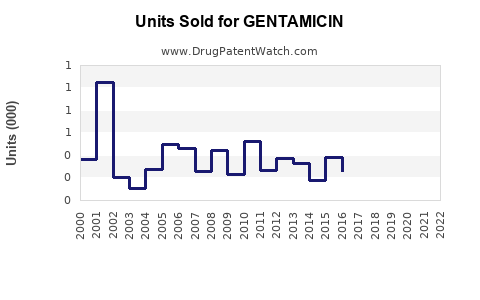
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for GENTAMICIN
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| GENTAMICIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| GENTAMICIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| GENTAMICIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| GENTAMICIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Gentamicin
Introduction
Gentamicin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic primarily used for treating serious infections caused by Gram-negative bacteria, remains an integral component of antimicrobial therapy. Its broad-spectrum activity, proven efficacy, and established clinical role underscore its ongoing relevance in both hospital and outpatient settings. This report evaluates the current market landscape and provides detailed sales projections for gentamicin, considering factors such as global demand, competitive dynamics, regulatory environments, and emerging trends.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Growth Drivers
The global antibiotic market was valued at approximately USD 46 billion in 2021, with aminoglycosides representing a niche but significant segment due to their critical role in severe bacterial infections. Gentamicin’s market share, estimated around 8-10% within aminoglycosides, is influenced by its longstanding clinical trust, cost-effectiveness, and the rising prevalence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) infections [[1]].
Key drivers include:
- Rising Incidence of MDR Bacterial Infections: Healthcare-associated infections caused by resistant Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, intensify the demand for potent antibiotics like gentamicin.
- Growing Hospitalized Population: Increased hospitalization rates for complex conditions raise the need for effective parenteral antibiotics.
- Lack of Novel Antibiotics: Limited pipeline for new aminoglycosides sustains the importance of existing drugs.
Regional Market Dynamics
- North America: Dominates due to high healthcare expenditure, prevalence of resistant infections, and well-established pharmaceutical infrastructure. The U.S. accounted for over 40% of the global gentamicin market in 2021.
- Europe: Growing antimicrobial resistance and institutional drug uses contribute to steady demand.
- Asia-Pacific: Fastest-growing segment driven by expanding healthcare access, rising infections, and economic growth. China and India are key markets.
Competitive Landscape
Gentamicin production is distributed among generic pharmaceutical companies, as patent protections have long expired. Major players include:
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Lupin Limited
- Sandoz (Novartis division)
- Hospira (Pfizer)
- Pharmacare Ltd.
The industry is characterized by low barriers to entry for generics, resulting in high commoditization. However, quality assurance, supply stability, and regulatory compliance significantly influence market shares.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory authorities such as the U.S. FDA, EMA, and WHO maintain stringent standards for antibiotic approval, with quality, safety, and efficacy as primary criteria. The expiration of key patents has facilitated increased generics availability, supporting competitive pricing but also intensifying price pressure.
Emerging concerns related to nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity associated with gentamicin emphasize the need for strict adherence to dosing protocols and monitoring, influencing product differentiation and compliance strategies.
Market Challenges
- Toxicity Profile: Gentamicin’s adverse effects limit its prophylactic and outpatient use, favoring hospital settings.
- Antibiotic Stewardship: Growing global emphasis on prudent antibiotic usage reduces overuse and may impact sales volume.
- Resistance Development: Increasing bacterial resistance necessitates careful monitoring of efficacy, potentially leading to shifts in prescribing patterns.
Sales Projections (2023–2030)
Methodology
Projections incorporate historical sales data, epidemiological trends, regional growth rates, and anticipated regulatory and clinical developments. Market penetration is expected to stabilize at high levels in hospitals, with minimal expansion into outpatient markets due to toxicity concerns.
Assumptions
- Annual global growth rate for the aminoglycoside segment at ~2.5%, driven primarily by emerging markets.
- Continued prevalence of multidrug-resistant infections sustains existing demand.
- Regulatory pressures encourage optimized dosing and monitoring, sustaining demand for branded and high-quality generics.
- Use in combination therapies remains steady, lessening the impact of resistance.
Forecast Summary
| Year | Estimated Global Sales (USD millions) | Growth Rate | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 400 | — | Baseline after pandemic disruptions. |
| 2024 | 410 | 2.5% | Slight uptick; endemic MDR infections persist. |
| 2025 | 420 | 2.5% | Market stabilization; generic competition intensifies. |
| 2026 | 430 | 2.4% | Rising resistance challenges; potential shifts. |
| 2027 | 440 | 2.3% | Continued demand in hospital settings. |
| 2028 | 450 | 2.2% | Regulatory focus on toxicity management. |
| 2029 | 460 | 2.2% | Scaling bacterial resistance may alter volumes. |
| 2030 | 470 | 2.2% | Market matures; steady growth expected. |
Note: Growth rates are modest; the predominantly hospital-based, generic-driven market constrains rapid expansion.
Key Factors Influencing Future Sales
- Antimicrobial Stewardship: Tightened controls might limit unnecessary use, potentially constraining growth but also fostering optimization of dosing and monitoring, which can sustain demand.
- Novel Delivery & Formulation Innovations: Development of targeted delivery systems or formulations reducing toxicity may expand usage.
- Emerging Resistance Patterns: Surveillance and susceptibility testing will influence prescribing patterns and product positioning.
- Regulatory Changes: Potential new guidelines for aminoglycosides could impact prescribing practices and market entry requirements.
Conclusion
Gentamicin remains a vital antibiotic in the treatment of severe Gram-negative infections. Despite the competitive and regulatory complexities, steady sales growth is projected owing to the continued demand driven by MDR infections and hospital uses. Market stability, coupled with innovations in safety and delivery, may provide growth opportunities, particularly in emerging markets. Maintaining quality standards and monitoring resistance trends will be critical for sustaining and expanding Gentamicin sales.
Key Takeaways
- Gentamicin’s market is primarily driven by hospital settings, with global sales expected to grow modestly (~2.2-2.5% annually) through 2030.
- The rise of antimicrobial resistance sustains the necessity for existing aminoglycosides, despite increasing concerns over toxicity.
- Competitive pressures from generics and regulatory standards necessitate quality assurance and compliance as key differentiators.
- Emerging markets will present growth opportunities due to expanding healthcare coverage and infection rates.
- Innovations addressing safety and resistance management could extend the product lifecycle and open new segments.
FAQs
-
What are the main factors driving gentamicin sales globally?
The primary drivers include the rising prevalence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, ongoing hospital use for severe infections, and limited pipeline of alternative antibiotics, particularly in developing regions. -
How does antibiotic resistance impact gentamicin sales projections?
Resistance may limit effectiveness, leading to decreased usage over time. However, current resistance rates still necessitate gentamicin in many settings, supporting stable demand. -
What role do generics play in the gentamicin market?
The expiration of patents has enabled multiple manufacturers to produce generic gentamicin, resulting in high competition, price competition, and accessible pricing for healthcare providers. -
Are there safety concerns affecting gentamicin’s market growth?
Yes. Toxicity risks such as nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity constrain outpatient and prophylactic use, confining most applications to monitored hospital environments. -
What potential market opportunities exist for gentamicin in the future?
Opportunities include the development of formulations with reduced toxicity, targeted delivery systems, and expansion into emerging markets with rising infection burdens.
Sources
[1] MarketsandMarkets. "Global Antibiotics Market." 2022.
More… ↓
