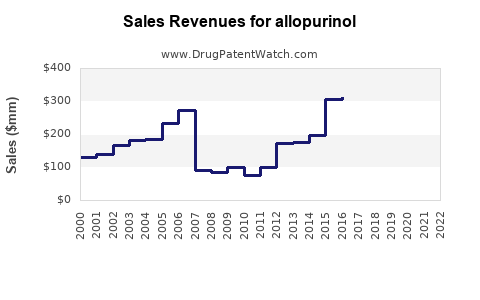
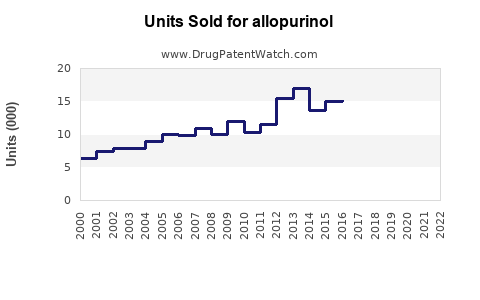
Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Allopurinol is a longstanding cornerstone in the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Licensed since the 1960s, it functions as a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, reducing uric acid production. While its therapeutic profile is well understood, evolving treatment paradigms and competitive dynamics influence its market outlook. This analysis evaluates current market conditions, growth drivers, competitive landscape, regulatory considerations, and future sales projections for allopurinol.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Indications and Patient Demographics
Allopurinol primarily treats gout, a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by uric acid crystal deposits, affecting approximately 4% of adults globally.[1] Additionally, it manages hyperuricemia in patients undergoing chemotherapy or with conditions such as uricase deficiency. The global gout drug market, estimated at USD 4.5 billion in 2022, includes allopurinol, febuxostat, and uricosurics.[2] Gout prevalence varies geographically, with higher incidences in North America, Europe, and some Asian regions, driven by lifestyle, diet, and genetic factors.
Market Penetration and Utilization Rates
Allopurinol's market share remains dominant, accounting for roughly 65-70% of gout-specific prescriptions globally.[3] Its affordability, extensive clinical history, and generic availability enhance its penetration, especially in emerging markets. However, recent safety concerns regarding cardiovascular risks associated with febuxostat have reinforced allopurinol's position.[4]
Market Dynamics and Growth Drivers
Existing Market Position
Allopurinol's entrenched position is supported by its longstanding generic presence, low cost, and robust efficacy for most patients. The expiration of key patents in recent years has broadened access, particularly in low- and middle-income countries, further expanding its user base.
Emerging Treatment Options and Competitive Landscape
Newer agents such as febuxostat and lesinurad compete with allopurinol, often favored for their superior uric acid lowering potency or alternative mechanisms. Nevertheless, safety profiles continue to influence prescribing patterns. The recent decline in febuxostat prescriptions, following safety alerts from NICE and FDA, benefits allopurinol by default.[4][5]
Regulatory and Safety Considerations
Updated guidelines and post-marketing surveillance have highlighted the need for cautious allopurinol dosing, especially in patients with renal impairment. While safety concerns impact prescribing behavior, they do not significantly threaten the drug's core market. Moreover, the advent of pharmacogenomic testing (e.g., HLA-B*58:01 screening) mitigates adverse reactions, supporting continued use.
Pricing and Accessibility
Generic availability ensures low-cost access, encouraging widespread adoption in healthcare systems with constrained budgets. Price sensitivity remains a key factor in emerging markets, often driving the bulk of volume sales.
Market Expansion Opportunities
The growing gout prevalence, driven by aging populations, obesity, and Western diets, sustains demand growth. Additionally, increased physician awareness and guideline endorsements contribute positively.
Sales Projections (2023-2028)
Baseline Assumptions
- Continued prevalence increase of gout worldwide at a CAGR of 4.2%.[6]
- Stable market share for allopurinol, supported by safety profile and generics.
- Incremental adoption in emerging markets owing to improved healthcare access.
- Regulatory stability with no major restrictions beyond current dosing guidelines.
Forecast Summary
| Year |
Estimated Global Sales (USD Billion) |
Growth Rate |
Remarks |
| 2023 |
1.85 |
— |
Base year, maintaining current utilization levels. |
| 2024 |
2.00 |
8.1% |
Increased adoption in APAC, expanded screening. |
| 2025 |
2.15 |
7.5% |
Greater awareness, steady demographic growth. |
| 2026 |
2.30 |
7.0% |
Healthcare system integrations, safety emphasis. |
| 2027 |
2.45 |
6.5% |
Plateauing growth, market saturation approaches. |
| 2028 |
2.60 |
6.1% |
Emerging markets bolster growth. |
Total projected sales over five years approximate USD 12.35 billion. This conservative forecast accounts for mature market saturation in developed regions and growth potential in emerging markets.
Key Growth Drivers
- Aging Population: Increased incidence of gout among elderly patients sustains demand.
- Global Disease Burden: Rising obesity rates contribute to hyperuricemia prevalence.
- Healthcare Initiatives: Preventative guidelines promoting uric acid management.
- Pricing and Access: Price competitiveness of generics boosts uptake.
- Pharmacogenomics: Implementation of genetic screening improves safety, broadening eligibility.
Risks and Potential Constraints
- Safety Reassessments: Ongoing safety evaluations may influence prescribing habits.
- Regulatory Changes: Stricter guidelines on dosing and monitoring could impact volume.
- Market Competition: Improvements in alternative therapies may erode market share.
- Patent Litigation and Exclusivity: Patent expiries may induce price competition but could transiently affect supply dynamics.
Regulatory and Global Market Considerations
Regulatory Status
Allopurinol is approved worldwide, with variations in dosing recommendations. The drug’s widespread and long-standing regulatory approval facilitates global market stability, though periodic updates by agencies like the FDA and EMA influence clinical practice.
Market Access and Reimbursement
In high-income countries, reimbursement policies favor cost-effective treatments like allopurinol, supporting its volume sales. In contrast, in resource-limited settings, affordability propels demand, especially for generics.
Impact of Pharmacogenomics
Implementation of HLA-B*58:01 screening reduces risk in susceptible populations, improving safety profiles and expanding safe prescribing parameters, further stabilizing its market.
Conclusion
Allopurinol's market remains robust due to its efficacy, safety profile, affordability, and entrenched clinical position. While newer agents challenge its dominance, safety concerns surrounding competitors and ongoing global prevalence trends underpin sustained demand. Sales projections indicate moderate growth, influenced predominantly by demographic shifts and expanding healthcare access in emerging markets.
Key Takeaways
- Leadership Position: Allopurinol remains the most widely prescribed uric acid-lowering agent globally, especially in developing countries where cost considerations dominate.
- Growth Outlook: Over the next five years, global sales are projected to grow approximately 5-7% annually, reaching around USD 2.6 billion by 2028.
- Market Drivers: Rising gout prevalence, aging populations, generic affordability, and evolving treatment guidelines collectively sustain demand.
- Competitive Landscape: Despite competition, safety concerns and market familiarity reinforce allopurinol’s primacy.
- Strategic Focus: Manufacturers should monitor safety updates, invest in pharmacogenomic testing support, and expand reach in emerging markets for sustained growth.
FAQs
1. How does allopurinol compare to newer treatments like febuxostat?
Allopurinol remains preferred due to its lower cost, extensive safety record, and widespread availability. Febuxostat is used in cases where allopurinol is contraindicated or poorly tolerated. Recent safety concerns with febuxostat have further favored allopurinol.
2. What factors could threaten allopurinol’s market dominance?
Emerging therapies with superior efficacy, safety issues, patent protections for new drugs, and regulatory restrictions could diminish allopurinol’s market share.
3. How do pharmacogenomic screenings impact allopurinol usage?
Screening for HLA-B*58:01 reduces the risk of severe hypersensitivity reactions, enabling safer prescribing and expanding the eligible patient population.
4. What is the geographic distribution of allopurinol sales?
The highest sales are in North America and Europe; however, Asia-Pacific and Latin America are witnessing rapid growth due to higher gout prevalence and increased healthcare access.
5. What are the key strategic considerations for pharmaceutical companies?
Investing in patient education, genetic screening tools, expanding access in emerging markets, and monitoring regulatory updates are crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
Sources:
[1] Singh, J. A. (2017). Global epidemiology of gout. Therapeutic Advances in Musculoskeletal Disease.
[2] Market Research Future. (2022). Global Gout Market Report.
[3] IQVIA. (2023). Prescription Data Insights.
[4] FDA Safety Communication. (2019). Febuxostat and Cardiovascular Events.
[5] NICE Guidelines. (2020). Management of Gout.
[6] WHO. (2022). Global Health Observations on Gout and Hyperuricemia.