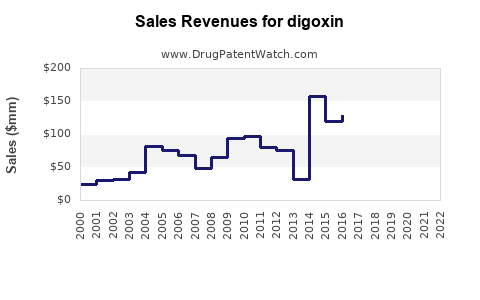
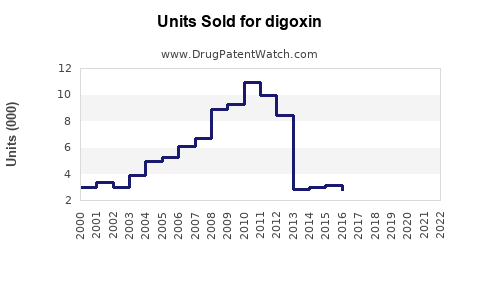
Last updated: July 28, 2025
Introduction
Digoxin, a cardiac glycoside primarily used to treat heart failure and arrhythmias, remains a significant component of cardiovascular therapy despite the advent of newer medications. Its unique mechanism, cost-effectiveness, and longstanding clinical use contribute to its sustained market presence. This analysis explores the current market landscape, key drivers, competitive environment, and future sales forecasts for digoxin over the upcoming years.
Market Overview
Historical Context and Current Usage
Since its approval in the late 1950s, digoxin has maintained a niche role within cardiology. It is primarily prescribed for atrial fibrillation and heart failure management, especially in patients intolerant to other agents. The drug's pharmacodynamics involve inhibition of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump, leading to increased cardiac contractility but also necessitating caution due to its narrow therapeutic window.
In recent years, the global demand for digoxin has fluctuated, driven by evolving clinical guidelines, emerging alternative therapies, and healthcare policy shifts. Despite these changes, it remains widely available, especially in regions with limited access to newer, costly drugs.
Market Size and Regional Dynamics
As of 2022, the global cardiac glycoside market, with digoxin as a core component, was valued at approximately USD 150 million. North America accounts for around 40% of this market, owing to high cardiovascular disease prevalence and advanced healthcare infrastructure. Europe follows, with similar factors. Emerging markets in Asia and Latin America exhibit growing demand, driven by rising cardiovascular disease incidence and increased access to pharmaceuticals.
Key Players and Supply Sources
Despite generic availability, some specialty pharmaceutical companies produce branded forms, emphasizing manufacturing quality and clinical support. The majority of sales derive from generic suppliers, with companies such as Pfizer, Novartis, and Teva holding significant market share due to established distribution channels and competitive pricing. Manufacturing complexity and the drug's narrow therapeutic index necessitate stringent quality controls, influencing supply dynamics.
Market Drivers
Rising Cardiovascular Disease Prevalence
Global studies predict a continued rise in heart failure and atrial fibrillation prevalence, particularly in aging populations. The World Heart Federation reports that over 64 million people worldwide suffer from heart failure, supporting sustained demand for therapies like digoxin.
Cost-Effectiveness and Accessibility
Generic formulations confer significant price advantages, making digoxin a preferred choice in cost-sensitive markets. The drug's affordability supports its continued use, especially where healthcare resources are limited.
Clinical Practice Trends
While newer agents such as angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) and direct-acting oral anticoagulants are replacing digoxin for some indications, clinical guidelines still endorse its use in specific cases. Its role in combination therapy, especially in resource-limited settings, sustains its market relevance.
Regulatory Considerations
In regions where regulators emphasize affordability, digoxin remains a recommended option. However, its narrow therapeutic window mandates ongoing clinician education and post-market surveillance, influencing regulatory policies and market stability.
Market Challenges
Safety Concerns and Narrow Therapeutic Window
The potential for toxicity limits widespread use. Advances in monitoring and dosage optimization are critical but may hinder broader uptake, particularly in less-equipped healthcare settings.
Emerging Therapies
The development of novel heart failure drugs, such as SGLT2 inhibitors and ARNIs, threatens to displace digoxin further. Transitioning clinical practices toward these agents may curtail future demand.
Limited Innovation and Patent Landscape
As a generic drug, digoxin lacks significant patent protection or innovation incentives. This impacts marketing strategies and limits revenue growth potential.
Sales Projections (2023–2033)
Baseline Assumptions
- Steady growth in global cardiovascular disease prevalence, especially among aging populations.
- Continued reliance on generic formulations owing to cost considerations.
- Moderate climate of clinical guideline updates maintaining digoxin's role in specific indications.
- Incremental adoption in emerging markets due to increasing healthcare penetration.
Projected Market Growth
Based on current trends, the digoxin market is expected to grow modestly at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2.5% over the next decade. The total market value is projected to reach USD 210–220 million by 2033.
Key Growth Regions
- North America: Market stability with slight growth, driven by aging demographics and ongoing clinical use.
- Europe: Similar trends, with potential declines in some countries as newer agents gain popularity.
- Asia-Pacific: Significant growth (~4% CAGR), driven by expanding healthcare infrastructure and increasing cardiovascular disease burden.
- Latin America and Africa: Gradual uptick as access improves, with regional markets presenting low-to-moderate growth potentials.
Impact of Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
The widespread availability of generics suppresses price premiums, but volume growth can sustain revenue. Limited innovation reduces upside potential, emphasizing market share retention through marketing and supply consistency.
Competitive Landscape and Strategic Opportunities
Market Share Dynamics
The market remains fragmented, with dominant generic manufacturers competing primarily on price and distribution. Specialty producers focusing on quality assurance and clinical support differentiate themselves.
Strategic Initiatives
- Enhanced Pharmacovigilance: Emphasizing safety profiles to reinforce clinical confidence.
- Market Penetration: Increasing access in underdeveloped regions through partnerships and price adjustments.
- Product Differentiation: Developing formulations with improved stability or dosing convenience.
Regulatory Environment
Global regulatory bodies prioritize medication safety and efficacy, with specific guidelines for narrow-therapeutic-index drugs like digoxin. Manufacturers must comply with strict quality controls and post-market surveillance, impacting production and distribution strategies.
Conclusion
Despite the advent of newer therapies, digoxin's role in heart failure and arrhythmia management endures, primarily driven by its affordability and well-established clinical efficacy. The global market is poised for steady growth, especially in emerging regions. Strategic focus on supply chain stability, safety management, and market expansion can enhance revenue sustainability.
Key Takeaways
- The global digoxin market is valued at approximately USD 150 million, with modest growth prospects (~2.5% CAGR) over the next decade.
- Rising cardiovascular disease prevalence and cost-effective therapy sustain its demand, particularly in resource-limited settings.
- Competition centers on generic manufacturing, emphasizing quality, pricing, and supply consistency.
- The impending emergence of novel therapies poses future displacement risks, but current clinical guidelines support digoxin in select indications.
- Market expansion in Asia-Pacific presents significant growth opportunities, driven by increasing healthcare access and disease burden.
FAQs
Q1. How does digoxin fit into current clinical guidelines for heart failure management?
A1. Guidelines recommend digoxin as a second-line therapy or in cases where symptom control remains inadequate, especially in patients with atrial fibrillation. Its use is supported for symptom relief and reducing hospitalizations, amidst the availability of newer drugs.
Q2. What are the primary safety concerns associated with digoxin?
A2. The drug's narrow therapeutic index raises toxicity risks, including arrhythmias, gastrointestinal symptoms, and visual disturbances. Proper dosing, monitoring, and patient education are vital to mitigate these risks.
Q3. How are emerging therapies affecting digoxin sales?
A3. Newer drugs like ARNIs and SGLT2 inhibitors are replacing digoxin in some indications due to better safety profiles and outcomes, which may slow market growth. However, cost and accessibility considerations sustain demand.
Q4. What regional factors influence digoxin market profitability?
A4. Regions with high cardiovascular disease rates, limited access to expensive therapies, and supportive regulatory policies foster higher demand. Developing economies benefit from affordability and physician familiarity.
Q5. Are there any recent innovations in digoxin formulations?
A5. Currently, market innovation focuses on generic formulations—improvements in stability and dosing accuracy are limited. Most advancements occur through manufacturing process improvements and quality assurance.
Sources:
[1] World Heart Federation, "Global Heart Failure Statistics," 2022.
[2] MarketWatch, "Global Cardiac Glycosides Market Size, Share & Trends," 2023.
[3] American College of Cardiology Guidelines, 2022.