Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for glyburide
✉ Email this page to a colleague
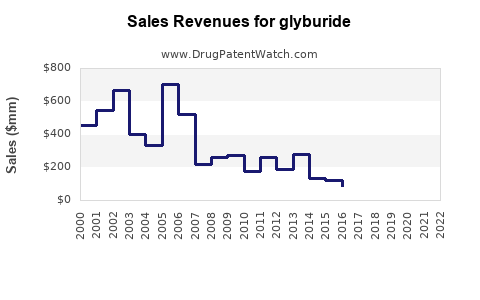
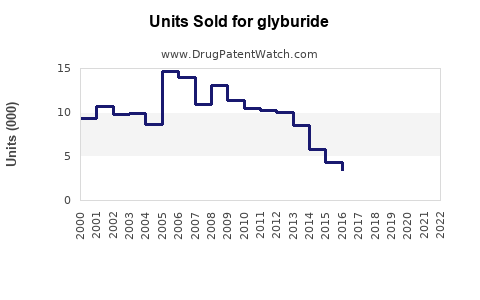
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for glyburide
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLYBURIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| GLYBURIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| GLYBURIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| GLYBURIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| GLYBURIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2018 |
| GLYBURIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2017 |
| GLYBURIDE | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2016 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for Glyburide
Introduction
Glyburide, also known as Glibenclamide, is a longstanding oral hypoglycemic agent used primarily in type 2 diabetes management. As a member of the sulfonylurea class, glyburide stimulates pancreatic insulin secretion, effectively lowering blood glucose levels. Despite the emergence of newer antidiabetic agents, glyburide maintains a significant market position owing to its longstanding clinical use, cost-effectiveness, and broad global availability. This report offers a comprehensive market analysis and sales projection for glyburide, highlighting key drivers, challenges, and opportunities shaping its future trajectory.
Market Overview
Global Diabetes Landscape
The global prevalence of diabetes mellitus continues to grow at an alarming rate. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), approximately 537 million adults aged 20–79 live with diabetes in 2021, a figure projected to reach 783 million by 2045 [1]. The rising burden, particularly in emerging economies, is driven by urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and increasing obesity.
Role of Glyburide in Diabetes Management
Glyburide remains a first- or second-line oral therapy for type 2 diabetes, notably in regions with limited healthcare resources, owing to its low cost and established efficacy. Its inclusion in many national and international treatment guidelines underscores its continued relevance. However, the popularity of newer agents like SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP-1 receptor agonists is gradually impacting glyburide's market share.
Regulatory and Market Penetration
Glyburide is approved in numerous jurisdictions, with generic versions widely accessible. The drug's patent expired decades ago, leading to a saturated generic market. Regulatory agencies such as the U.S. FDA and EMA have approved glyburide formulations, although safety concerns (e.g., hypoglycemia risk) have prompted some regulatory bodies to recommend cautious use.
Current Market Dynamics
Competitive Landscape
Glyburide faces competition primarily from:
-
Newer oral agents, such as metformin, SGLT2 inhibitors, and DPP-4 inhibitors, which offer better safety profiles and additional benefits.
-
Insulin therapies, especially in advanced cases.
-
Generics and biosimilars, which make glyburide affordable but also intensify price competition.
Key Market Drivers
- Cost-effectiveness: Glyburide remains one of the cheapest options, critical in low-income countries.
- Established clinical profile: Long-term safety and efficacy data foster clinician confidence.
- Global distribution: Widespread manufacturing and approval facilitate availability in resource-limited settings.
Market Limiters
- Hypoglycemia risk: Glyburide's association with hypoglycemia limits its usage in high-risk patient groups.
- Safety perception: Growing awareness of adverse effects diminishes prescriber preference.
- Better alternatives: Introduction of agents with cardiovascular and renal benefits shifts prescribing patterns.
Regulatory Trends
Some agencies, such as the FDA, recommend cautious use or limited indications, which may constrain market growth. Furthermore, certain countries have restricted or phased out glyburide in favor of safer alternatives, impacting regional demand.
Sales Projections
Global Sales Outlook (2023–2030)
Given the current landscape, global glyburide sales are expected to experience modest fluctuations, characterized by regional disparities:
- Developed Markets: Declining demand owing to safety concerns and availability of newer therapies; CAGR estimated at –2%.
- Emerging Markets: Steady or slight growth driven by affordability, expanding diabetes prevalence, and high healthcare resource limitations; CAGR projected at +3%.
By 2030, total global glyburide sales are projected to stabilize around $1.1 billion, representing a plateau or mild decrease from approximately $1.3 billion in 2022.
Regional Breakdown
- North America: Market contraction expected due to safety concerns; sales projected at $200 million by 2030.
- Europe: Similar trends as North America; declining to $150 million.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly growing markets, particularly India and China, where cost sensitivity and soaring diabetes prevalence sustain growth; projected sales at $500 million.
- Latin America and Africa: Stable to increasing demand, contributing an estimated $250 million collectively.
Factors Influencing Sales Trajectory
- Policy shifts toward newer agents due to safety profiles.
- Price competition among generics.
- Healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets enabling continued use of cost-effective therapies.
- Patent expirations reinforcing generics' dominance but limiting marketed innovations.
Future Opportunities and Challenges
Opportunities
- Formulation Innovations: Development of fixed-dose combinations with other antidiabetics could enhance adherence and sales.
- Market Expansion: Targeting low-income regions with educational campaigns on cost-effective diabetes management.
- Biosimilars and Generics: Continued proliferation can sustain affordability and accessibility.
Challenges
- Safety concerns: Potential regulatory restrictions stemming from hypoglycemia and cardiovascular risks.
- Market shift: Rapid adoption of newer therapies may marginalize glyburide.
- Supply chain stability: Ensuring availability amid manufacturing constraints.
Conclusion
While glyburide maintains a vital position in global diabetes management—particularly in resource-limited settings—its overall sales landscape faces headwinds from safety concerns and evolving treatment paradigms. Regional differences dominate the outlook, with developing markets likely to sustain modest growth, while mature markets witness gradual decline. Stakeholders should consider opportunities for formulation improvements and strategic positioning within emerging markets to maximize value.
Key Takeaways
- Consensus: Glyburide remains a crucial affordable option for type 2 diabetes treatment in emerging economies amid slowing growth in developed regions.
- Market decline in developed countries: Increasing safety concerns and the availability of novel agents lead to a projected negative CAGR of about –2% through 2030.
- Emerging markets' potential: Growing diabetes prevalence and cost sensitivity suggest a CAGR of +3%, supporting sustained sales growth to approximately $1.5 billion globally.
- Strategic focus: Developing fixed-dose combinations, biosimilars, and targeted marketing in low-income regions can bolster future sales.
- Regulatory considerations: Safety profiles and evolving guidelines necessitate continuous monitoring of regional policies impacting glyburide’s market access.
FAQs
-
What factors are impacting glyburide sales globally?
Safety concerns, competition from newer agents, and regulatory restrictions are key factors reducing sales in developed markets, whereas affordability and high disease prevalence sustain demand in emerging economies. -
Are biosimilars or generics expected to influence glyburide's market?
Yes. The proliferation of low-cost generics boosts accessibility but also intensifies price competition, potentially constraining margins. -
Which regions are driving future glyburide sales growth?
The Asia-Pacific region, especially India and China, is projected to sustain growth due to expanding diabetes prevalence and cost-focused healthcare approaches. -
What emerging innovations could revive glyburide's market?
Fixed-dose combinations and new formulations that mitigate hypoglycemia risk could enhance its appeal and adherence. -
How do safety concerns influence prescriber preferences?
Risks of hypoglycemia and cardiovascular events lead clinicians to favor newer agents with better safety profiles, especially in developed markets, reducing glyburide's use.
References
[1] International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th Edition, 2021.
[2] World Health Organization. Diabetes Fact Sheet, 2022.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Glyburide medication guide, 2021.
[4] Market Research Future. Global Diabetes Drugs Market Report, 2022.
More… ↓
