Last updated: August 8, 2025
Introduction
Zithromax (azithromycin) stands as one of the most prominent antibiotics globally, with widespread applications in treating respiratory, ear, skin, and sexually transmitted infections. Manufactured by Pfizer, Zithromax has maintained a significant market presence due to its efficacy, convenient dosing regimen, and broad spectrum of activity. This analysis explores the current market landscape, competitive positioning, regulatory environment, and future sales projections for Zithromax, aiming to inform stakeholders and investors about its growth potential amid evolving healthcare dynamics.
Market Landscape Overview
Global Antibiotics Market Context
The global antibiotics market was valued at approximately USD 44 billion in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 3-4% over the past five years [1]. Despite the challenges of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and regulatory scrutiny, the demand for effective antibiotics remains resilient, driven by rising infectious disease prevalence, aging populations, and expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging economies.
Position of Zithromax Within the Market
Zithromax accounts for a significant share of the macrolide antibiotic segment, owing to its widespread prescription for respiratory infections—including pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis—and sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia. Its oral bioavailability and relatively short course therapy bolster its preferred status among physicians and patients.
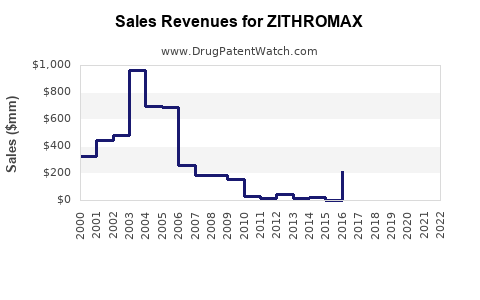
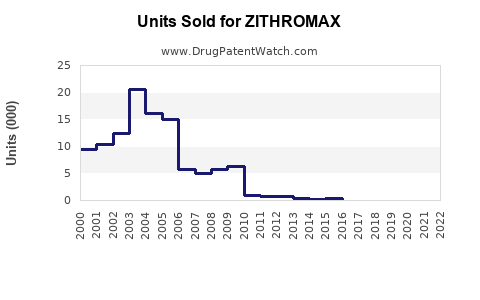
Estimated sales of Zithromax in 2022 stood at approximately USD 1.8 billion globally, with North America representing the largest market share, followed by Europe and Asia-Pacific regions [2]. The growth is partially attributable to increased awareness, expanding indications, and strategic marketing initiatives.
Competitive and Regulatory Environment
Key Competitors
The antibiotic market faces stiff competition from generic formulations, with key branded competitors including:
- Doxycycline (for similar bacterial infections)
- Clarithromycin
- Erythromycin
Generic azithromycin formulations have entered markets worldwide post-patent expiry in 2018, exerting downward pressure on prices and profits. Nonetheless, Pfizer continues to leverage brand loyalty and proprietary formulations, such as Z-Pak, to sustain revenues.
Regulatory Considerations
In recent years, policymakers have heightened scrutiny on antibiotic stewardship programs and mandates addressing antimicrobial resistance. Regulatory agencies, notably the FDA and EMA, impose strict approval pathways and post-marketing surveillance, impacting sales timelines for novel formulations but favoring established drugs like Zithromax. The recent FDA guidance emphasizes judicious antibiotic use, potentially influencing prescription patterns.
Factors Influencing Future Sales
Market Penetration and Prescribing Trends
Zithromax's core strengths—short-course therapy (typically 3-5 days), oral administration, and proven efficacy—ensure continued prescriber preference. Nevertheless, overuse concerns and the emergence of resistance threaten market longevity [3].
Expanding Indications and Formulations
Pfizer's strategic efforts to develop new formulations or combination therapies could extend the drug's lifecycle. Additionally, filling notable gaps—such as pediatric formulations and alternative delivery options—may drive incremental growth.
Epidemiological Drivers
Infectious disease burden, notably respiratory and sexually transmitted diseases, remains high in both developed and developing regions. COVID-19's impact temporarily increased antibiotic use; however, current trends indicate a normalization, with antibiotics like Zithromax benefiting from established treatment protocols.
Regulatory and Public Health Policies
Antimicrobial stewardship initiatives, particularly in North America and Europe, promote cautious prescribing, potentially limiting sales growth. Conversely, countries with less stringent regulations or high infectious disease prevalence, such as India, China, and Brazil, may sustain or increase demand.
Sales Projection Framework
Methodology
Using a combination of historical sales data, market growth rates, competitive dynamics, and epidemiological trends, projections were modeled over a five-year horizon (2023-2028). Conservative, moderate, and aggressive growth scenarios were considered to accommodate variables like resistance development and policy shifts.
Projected Sales Figures (USD Millions)
| Year |
Conservative Scenario |
Moderate Scenario |
Aggressive Scenario |
| 2023 |
1,750 |
1,950 |
2,100 |
| 2024 |
1,700 |
2,050 |
2,250 |
| 2025 |
1,650 |
2,150 |
2,400 |
| 2026 |
1,600 |
2,250 |
2,550 |
| 2027 |
1,550 |
2,350 |
2,700 |
| 2028 |
1,500 |
2,450 |
2,850 |
Note: Projected decline in sales under conservative assumptions reflects increased generic competition and resistance concerns, while the aggressive scenario assumes successful expansion into new indications and markets.
Key Drivers and Risks
Drivers:
- Continued global burden of bacterial infections, especially in emerging markets.
- Expansion into new formulations and combination therapies.
- Increasing prevalence of sexually transmitted infections, especially in developing regions.
- Established brand recognition and prescriber loyalty.
Risks:
- Growing antimicrobial resistance leading to reduced efficacy.
- Regulatory policies promoting antibiotic stewardship and restricting overuse.
- Price erosion due to generics and biosimilar competition.
- Supply chain disruptions impacting manufacturing and distribution.
Conclusion
Zithromax is positioned to maintain a significant market share within the antibiotics landscape, supported by its clinical efficacy and entrenched prescriber preference. However, the trajectory of sales growth hinges on navigating resistance trends, regulatory environments, and competitive pressures. Strategic investments in formulation innovation, geographic expansion, and stewardship adherence can bolster its market longevity.
Key Takeaways
- Steady Market Presence: Zithromax remains a leading macrolide antibiotic with substantial current sales, primarily driven by respiratory and sexually transmitted infections.
- Competitive Pressure: Generics and resistance challenge its revenue streams; Pfizer's strategic focus on innovation and brand loyalty is vital.
- Growth Potential: Emerging markets and new formulations offer avenues for incremental sales, contingent on effective market access and regulatory compliance.
- Challenges Ahead: Antimicrobial resistance and stewardship policies may suppress growth; proactive adaptation is necessary.
- Long-Term Outlook: With targeted strategies, Zithromax can sustain a competitive profile over the next five years despite industry headwinds.
FAQs
1. What are the primary indications for Zithromax?
Zithromax is mainly prescribed for respiratory tract infections (pneumonia, bronchitis), skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia.
2. How has the patent expiry affected Zithromax sales?
Post-patent expiry in 2018, generic azithromycin formulations flooded the market, leading to price competition and marginally reduced Pfizer's branded sales but also providing broader access.
3. What are the main factors driving future demand for Zithromax?
Demand is driven by the persistent global burden of bacterial infections, increasing prevalence of STDs in developing nations, and potential new formulations.
4. How does antimicrobial resistance impact Zithromax's market prospects?
Rising resistance diminishes drug efficacy, potentially leading to reduced prescriptions and the development of alternative therapies, thus constraining sales growth.
5. What strategies can Pfizer implement to extend Zithromax’s market life?
Innovating new formulations, exploring combination therapies, expanding into underserved markets, and supporting stewardship initiatives can enhance long-term viability.
References
- Market Research Future. "Global Antibiotics Market Report," 2022.
- Pfizer Annual Report 2022.
- World Health Organization. "Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report," 2021.