Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for VYTORIN
✉ Email this page to a colleague
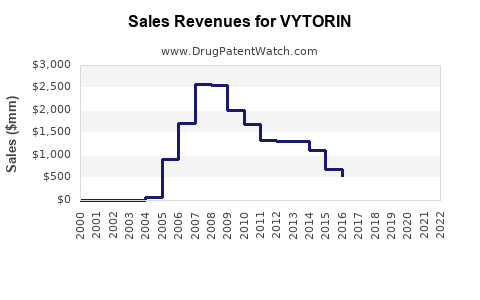
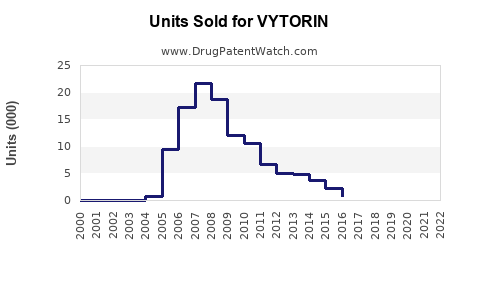
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for VYTORIN
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| VYTORIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| VYTORIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| VYTORIN | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for VYTORIN
Introduction
VYTORIN, a combination drug comprising simvastatin and ezetimibe, gained prominence as a lipid-lowering therapy aimed at managing hypercholesterolemia and reducing cardiovascular risk. Approved by the FDA in 2004, VYTORIN positioned itself as a complementary or alternative therapy to monotherapy statins. This analysis explores the market landscape, competitive dynamics, regulatory influences, and sales forecasts to inform strategic decisions for stakeholders.
Market Landscape and Therapeutic Profile
VYTORIN belongs to the class of drugs known as statin-ezetimibe combinations, designed to provide additive lipid-lowering effects. The total global statin market was valued at approximately USD 15 billion in 2022, driven by growing prevalence of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), increased awareness, and evolving treatment guidelines emphasizing aggressive lipid management. Simultaneously, ezetimibe's role as an adjunct therapy gained recognition following pivotal trials such as IMPROVE-IT (2015), which demonstrated cardiovascular benefits when combined with statins.
Market Dynamics and Competitive Environment
-
Brand and Generic Competition:
VYTORIN's initial success was partly due to its patent protection and innovative combination formulation. However, patent expirations, notably in the United States in 2012, resulted in widespread generic competition. Generic versions of ezetimibe and simvastatin became available, leading to significant price erosion and sales decline for branded VYTORIN. -
Evolving Treatment Guidelines:
The American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guidelines increasingly favored high-intensity statins and simplified regimens over fixed-dose combinations like VYTORIN. This shift diminished prescribing of combination pills in favor of monotherapy options, impacting VYTORIN’s market share. -
Emergence of Alternative Therapies:
Novel lipid-lowering agents such as PCSK9 inhibitors (evolocumab, alirocumab) have entered the market, especially for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia or statin intolerance. While these drugs are more costly, their superior efficacy in specific populations constrains VYTORIN's market penetration. -
Regulatory and Market Access Factors:
Insurance coverage and formulary positioning influence the prescribing patterns of combination drugs. VYTORIN's reduced market exclusivity and competition necessitate strategic positioning based on cost-effectiveness and clinical advantages.
Sales Trends and Historical Performance
-
Pre-Patent Expiry (2004–2012): The drug experienced robust sales driven by initial patent protection and lack of generic competition. Estimated peak annual sales approached USD 300 million worldwide, predominantly in North America and Europe.
-
Post-Patent Expiry (2012 onwards): Generic competition caused sales to decline sharply, with estimates suggesting a decline of over 70% within five years post-generic entry. By 2022, global annual sales hovered around USD 50-75 million, reflecting reduced market share and the impact of newer therapies.
Forecasting Future Sales
Given current market conditions, future sales trajectories for VYTORIN will depend on several factors:
-
Market Penetration of Alternatives
The increasing adoption of generic statins and ezetimibe monotherapies, combined with the rise of PCSK9 inhibitors, constrains VYTORIN's growth potential. Unless repositioned or recategorized, its sales are likely to remain subdued. -
Regulatory and Patent Re-Establishment
Companies explore secondary patents or new formulations to extend exclusivity. If a new, patent-pending formulation or delivery system is developed, sales could see a minor resurgence, potentially reaching USD 100 million annually within five years, primarily through markets with limited access to alternatives. -
Geographical Expansion
Emerging markets with rising CVD prevalence may present growth opportunities if VYTORIN or its equivalents are marketed effectively and priced competitively. However, cost barriers and local generics may limit premium sales. -
Healthcare Trends Toward Combination Therapy
Increased emphasis on personalized medicine and combination regimens in specific patient subgroups (e.g., polyvascular disease) may create niche markets for VYTORIN. Nevertheless, large-scale adoption appears unlikely without significant clinical differentiation.
| Summary of Sales Projections (2023–2028): | Year | Estimated Global Sales (USD Million) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 65–75 | Continued decline, modest niche markets | |
| 2024 | 60–70 | Market saturation with generics, slight decline | |
| 2025 | 55–65 | Further competition, potential regulatory hurdles | |
| 2026 | 50–60 | Limited new indications or formulations | |
| 2027 | 45–55 | Stable but declining trend | |
| 2028 | 40–50 | Market stabilization in mature markets |
Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders:
- Innovation: Invest in novel delivery systems or formulations to extend patent life.
- Market Niches: Focus on underserved markets with limited generic penetration.
- Clinical Differentiation: Conduct clinical trials demonstrating unique benefits over monotherapies to regain prescriber confidence.
- Partnerships: Collaborate with generics manufacturers to maintain a foothold in cost-sensitive markets.
Key Takeaways
- VYTORIN's market share peaked during its patent-protected lifespan but has substantially declined due to generic competition and evolving treatment paradigms.
- The current sales outlook remains modest, primarily driven by niche clinical applications and emerging markets.
- Future growth relies on innovation, strategic repositioning, and tapping into markets with limited generic access.
- Competition from monotherapies and newer agents like PCSK9 inhibitors continues to overshadow VYTORIN’s sales potential.
- Continuous monitoring of clinical guidelines and regulatory changes is essential for accurate forecasting and strategic planning.
FAQs
-
What factors primarily contributed to VYTORIN’s sales decline?
Patent expirations, generic competition, shifting clinical guidelines favoring monotherapy, and the emergence of superior lipid-lowering agents like PCSK9 inhibitors. -
Can VYTORIN regain market share through new formulations?
Potentially, if innovative formulations provide clear clinical benefits or extended patent protection, but such strategies require significant investment and regulatory approval. -
Are there specific patient populations where VYTORIN still shows advantages?
It may benefit patients intolerant to high-dose statins or those requiring combination therapy, but recent guidelines and emerging therapies limit its use. -
How does the rise of PCSK9 inhibitors impact VYTORIN’s future sales?
PCSK9 inhibitors target high-risk, statin-intolerant, or familial hypercholesterolemia patients with superior efficacy, thereby reducing VYTORIN’s potential patient base. -
What strategies could pharmaceutical companies adopt to sustain VYTORIN’s market presence?
Focusing on niche markets, developing new formulations, obtaining clinically meaningful data to support unique benefits, and expanding into emerging markets are vital strategies.
References
[1] GlobalData Pharma Intelligence. (2022). Lipid-lowering Drugs Market Report.
[2] FDA. (2004). VYTORIN (simvastatin/ezetimibe) Approval Documents.
[3] American College of Cardiology. (2018). Lipid Management Guidelines.
[4] IMPROVE-IT Trial Publication. (2015). New England Journal of Medicine.
[5] EvaluatePharma. (2022). Pharmaceutical Market Trends Report.
More… ↓
