Share This Page
Drug Sales Trends for PERCOCET
✉ Email this page to a colleague
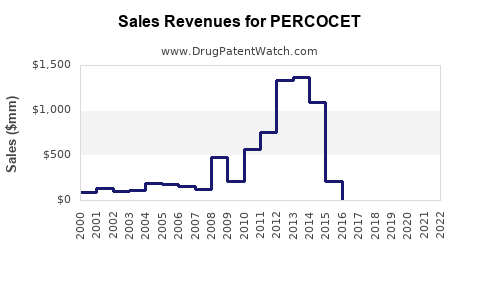
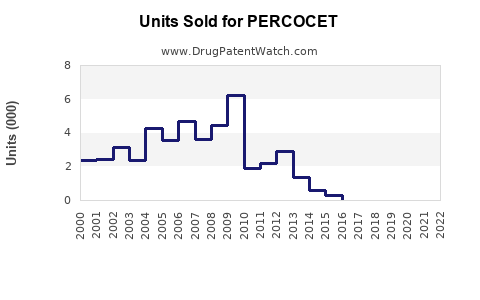
Annual Sales Revenues and Units Sold for PERCOCET
| Drug Name | Revenues (USD) | Units | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| PERCOCET | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2022 |
| PERCOCET | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2021 |
| PERCOCET | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2020 |
| PERCOCET | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2019 |
| PERCOCET | ⤷ Get Started Free | ⤷ Get Started Free | 2018 |
| >Drug Name | >Revenues (USD) | >Units | >Year |
Market Analysis and Sales Projections for PERCOCET
Introduction
PERCOCET, a combination formulation of acetaminophen and oxycodone, has long been a staple in the management of moderate to severe pain. Its widespread prescription exemplifies the ongoing demand for effective analgesics, but recent regulatory scrutinies and withering public perception about opioid risks have profoundly influenced its market trajectory. This comprehensive analysis aims to elucidate the current market environment, forecast future sales, and equip stakeholders with actionable insights.
1. Market Landscape Overview
1.1. Product Profile and Clinical Positioning
PERCOCET combines acetaminophen—a non-opioid analgesic—with oxycodone, a potent opioid. Prescribed primarily for postoperative pain, cancer pain, and chronic pain management, it represents a lower-dose alternative for opioid therapy, intended to mitigate the risk of dependency, albeit still categorized as a controlled substance.
1.2. Regulatory and Legal Environment
Over the last decade, the opioid epidemic has prompted regulatory reforms, notably increased prescribing restrictions, REMS (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies), and enhanced monitoring of opioid distribution. These measures have curtailed prescriptions, impacting sales volumes but also consolidating the market around trusted, regulated formulations like PERCOCET.
1.3. Market Dynamics and Trends
The opioid landscape is characterized by:
-
Decline in Traditional Prescriptions: Data from the CDC shows a reduction in opioid prescriptions from peak levels in 2010-2012, partly driven by prescriber caution and alternative therapies.
-
Shift Toward Non-Opioid Analgesics: There's a growing preference for non-opioid options, including NSAIDs, anticonvulsants, and antidepressants, impacting PERCOCET’s share ([1]).
-
Specialized Pain Management Strategies: Multimodal pain management protocols favor reduced reliance on opioids, favoring formulations with lower doses and alternative delivery methods.
2. Segmentation Analysis
2.1. Geographic Distribution
North America, especially the U.S., remains the principal market due to high opioid consumption and widespread chronic pain prevalence. Europe’s market is comparatively conservative, with heightened regulations reducing PERCOCET’s penetration.
2.2. Demographic Trends
Prescription patterns skew towards adult populations with chronic pain conditions. The aging demographic further influences demand, although the opioid crisis prompts prescribers to exercise increased caution.
2.3. Prescriber Behavior
Physicians' hesitancy to prescribe opioids elevates the importance of pain management guidelines emphasizing non-opioid interventions, diminishing PERCOCET’s volume of prescriptions.
3. Competitive Landscape
PERCOCET faces competition from:
- Generic equivalents: Due to patent expirations, generics have eroded branded sales.
- Alternative analgesics: Non-opioid medications and non-pharmacological treatments.
- Novel formulations: Abuse-deterrent formulations and combination therapies.
Major pharmaceutical players like Endo Pharmaceuticals and Purdue Pharma have historically marketed PERCOCET, but market share diminishes as generics proliferate and regulation tightens.
4. Key Market Drivers and Constraints
4.1. Drivers
- The ongoing need for effective analgesics in acute and chronic pain.
- Prescription for patients intolerant of non-opioid options.
- Institutional use in postoperative care and cancer management.
4.2. Constraints
- Heightened opioid regulation and crackdown on prescribing.
- Rising awareness of opioid misuse and dependency liabilities.
- Preference for non-opioid pain management approaches.
5. Sales Projections
5.1. Methodology
Forecasts utilize historical prescription data, regulatory impact models, and anticipated therapeutic shifts. A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) approach is adopted to estimate future sales, adjusting for macroeconomic and epidemiological factors.
5.2. Short-term Outlook (2023–2025)
Given the persistent regulatory constraints, sales are expected to decline modestly, with a projected CAGR of approximately -3%. Market contraction reflects diminished prescription volumes but stabilizes due to ongoing demand in specific clinical scenarios.
5.3. Medium to Long-term Outlook (2026–2030)
By 2030, sales are anticipated to plateau or decline further, averaging a CAGR of roughly -1% to -2%, assuming continued regulation and the rise of non-opioid alternatives. However, niche markets—such as severe pain management in oncology—may sustain marginal demand.
5.4. Key Assumptions
- Consistent regulatory tightening persists.
- Innovations such as abuse-deterrent formulations do not reverse negative trends.
- Demographic growth in older populations sustains baseline demand.
5.5. Quantitative Estimates
- 2023: Estimated global sales of $1.2 billion.
- 2025: Projected sales of approximately $1.1 billion.
- 2030: Expected sales to decrease to $0.9–1 billion, contingent upon market dynamics.
6. Future Opportunities and Risks
6.1. Opportunities
- Development of abuse-deterrent and fixed-dose combination formulations.
- Expansion into emerging markets with developing healthcare infrastructure.
- Integration with multimodal pain management protocols.
6.2. Risks
- Further regulatory restrictions constraining prescribing.
- Legal liabilities and litigation associated with opioids.
- Growing societal and physician preference for non-opioid therapies.
- Potential patent litigations and market entry of generic competitors.
7. Strategic Recommendations
- Diversification: Invest in alternative formulations and non-opioid pain therapies.
- Regulatory Engagement: Maintain proactive compliance and participate in regulatory dialogues.
- Market Segmentation: Focus on niche segments, such as cancer pain or post-surgical pain, where PERCOCET remains relevant.
- Global Expansion: Target emerging markets with less restrictive opioid regulations.
Key Takeaways
- The PERCOCET market faces a sustained decline driven by regulatory pressures, societal shifts, and clinical practice evolution.
- Despite shrinking sales, niche patient populations and clinical needs sustain residual demand.
- Strategic diversification into less regulated analgesic options and formulations is critical for stakeholders.
- Long-term market stability depends on innovation, regulatory adaptation, and embracing alternative pain management modalities.
- Stakeholders should prioritize emerging markets and specialized pain therapies to offset domestic declines.
FAQs
Q1. How has the opioid epidemic shaped PERCOCET’s market trajectory?
The epidemic prompted stringent regulations, prescription restrictions, and an increased focus on opioid misuse prevention, leading to reduced prescriptions and sales declines for PERCOCET.
Q2. What are the primary factors influencing future sales of PERCOCET?
Regulatory environment, prescriber preferences, availability of non-opioid alternatives, and demographic shifts in pain prevalence critically influence its future sales.
Q3. Are generic formulations impacting PERCOCET’s market share?
Yes. Generics have significantly eroded branded sales, especially as patent protections expired, making cost-driven substitution common.
Q4. What strategies can stakeholders adopt to sustain PERCOCET sales?
Focus on niche markets, develop abuse-deterrent formulations, and explore expanding into emerging markets with different regulatory landscapes.
Q5. Is there potential for PERCOCET resurgence in the future?
Only if regulatory barriers loosen, new formulations emerge that address dependency concerns, or if novel pain management approaches shift prescribing behaviors favorably.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). "2019 Annual Surveillance Report of Drug-Related Risks and Outcomes."
- IMS Health. "The Impact of Regulatory Changes on Opioid Prescriptions."
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). "Opioid Analgesic REMS."
- MarketWatch. "Pain Management Drugs Market Trends and Outlook."
- WHO. "Guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of pain in children."
More… ↓
