Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
LANTUS (insulin glargine) is a long-acting basal insulin developed by Sanofi, designed to provide consistent, 24-hour glucose control for individuals with diabetes. Since its approval in 2000, LANTUS has become a cornerstone therapy for managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This analysis evaluates its current market landscape, competitive positioning, and future sales prospects, considering global demand shifts, technological innovations, and evolving treatment paradigms.
Market Landscape
Global Diabetes Epidemic and Market Potential
The increasing prevalence of diabetes—estimated at 537 million adults worldwide in 2021 [1]—drives persistent demand for insulin therapies. With type 2 diabetes accounting for approximately 90-95% of cases, basal insulins like LANTUS predicate much of the treatment regimens. The International Diabetes Federation projects this figure to reach 643 million by 2030, underscoring the long-term growth potential for insulin products.
Competitive Positioning
LANTUS's primary competition stems from biosimilars, fixed-ratio combinations, and emerging ultra-long-acting insulins. Notable rivals include:
- Basaglar (insulin glargine) biosimilar (Eli Lilly/Biocon): Approved in multiple markets, offering a cost-effective alternative.
- Toujeo (insulin glargine U300) by Sanofi: Provides a more concentrated, prolonged action profile.
- Tresiba (insulin degludec) by Novo Nordisk: An ultra-long-acting insulin with superior flexibility.
- Insulin analogs and combination therapies: Both branded and biosimilar products targeting analogous patient segments.
Despite intense competition, LANTUS retains a robust market share due to its established clinical profile, brand recognition, and widespread clinician familiarity.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Factors
Global market access depends heavily on regulatory approvals, reimbursement landscapes, and pricing strategies. Sanofi’s proactive biosimilar launches and collaborations have mitigated some risks associated with patent expirations, preserving market competitiveness in key regions like the US and Europe.
Sales Performance and Trends
Historical Sales Data
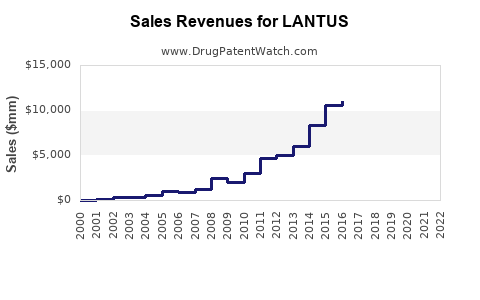
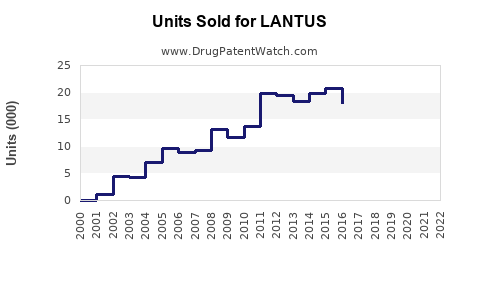
LANTUS achieved peak sales of approximately €7.4 billion (~$8.8 billion) in 2014, driven by its broad adoption. Post-2015, the patent expiration in major markets facilitated biosimilar entry, resulting in revenue erosion. Nevertheless, Sanofi’s diversified insulin portfolio, including Tresiba and Toujeo, has supported sustained sales, cumulatively exceeding €6 billion annually in recent years.
Impact of Biosimilars and Market Dynamics
The advent of biosimilars (e.g., Basaglar) introduced price competition, with some markets seeing a decline in LANTUS sales by approximately 15-20% annually since 2016. The US market experienced early biosimilar penetration due to favorable regulatory policies, while European markets saw variable uptake depending on reimbursement strategies.
Emerging Trends Impacting Sales
- Preference shifts towards ultra-long insulins: Tresiba's growing market share, especially among patients requiring flexible dosing, threatens LANTUS’s dominance.
- Fixed-ratio combination therapies: Such as Sanofi's Soliqua (insulin glargine/lixisenatide), enhance treatment efficacy and patient adherence but also cannibalize monotherapy sales.
- Digital health integration and smarter insulin delivery: Innovations like insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring influence insulina utilization patterns.
Future Sales Projections
Factors Supporting Continued Demand
- Rising diabetes prevalence: Sustains baseline demand for basal insulins globally.
- Physician familiarity and long-term safety data: Strengthen retention of LANTUS’s market position.
- Expanding access in emerging markets: Improving healthcare infrastructure and affordability initiatives bolster sales.
Drivers of Growth
- Generics and biosimilar competition: While initially suppressive, competitive pressures stimulate pricing strategies, potentially stabilizing revenues.
- New formulations and delivery methods: Development of concentrated or premixed formulations can unlock untapped patient segments.
Forecast Outlook (2023–2030)
Sanofi projects that LANTUS will maintain a significant share within the long-acting insulin segment, albeit with declining absolute sales attributable to biosimilar competition. Considering current trends and market shifts, estimated global annual sales are projected to decline to approximately €2-3 billion (~$2.4-$3 billion) by 2030, assuming ongoing biosimilar penetration and technological advancements.
However, strategic diversification—such as integrating digital health solutions and expanding into emerging markets—could mitigate declines. Additionally, the increasing preference for ultra-long-acting insulins like Tresiba might lead to a gradual phase-out in some regions, but the global size of the insulin market suggests LANTUS's niche will persist in various therapeutic contexts.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Must innovate to sustain or grow revenues, leveraging biosimilar development, fixed-dose combinations, or next-generation insulin formulations.
- Healthcare Providers: Will likely prioritize therapies offering better flexibility and patient adherence, influencing demand.
- Payers and Regulators: Focus on cost-effectiveness and access policies that impact product utilization.
Key Takeaways
- Persistent Necessity: The enduring global diabetes epidemic ensures sustained demand for basal insulins like LANTUS.
- Competitive Challenges: Biosimilars and new ultra-long-acting insulins are eroding peak sales but create opportunities for innovation.
- Market Dynamics: Prices and reimbursement policies significantly influence sales, with emerging markets presenting growth avenues.
- Forecasted Decline: Overall, LANTUS sales are expected to decline steadily through 2030, but the product remains integral in diabetes management.
- Strategic Position: Continued differentiation through formulations, delivery methods, and digital integration is vital for longevity.
FAQs
1. Will LANTUS regain market dominance amid rising biosimilar competition?
While biosimilars have impacted LANTUS's market share, its strong brand recognition and clinician familiarity provide some resilience. However, sustained growth is unlikely absent innovation or repositioning strategies.
2. How does the rise of ultra-long-acting insulins affect LANTUS sales?
Insulins like Tresiba offer greater flexibility and a more favorable pharmacokinetic profile, leading to preferential prescribing in some cases. This trend gradually shifts demand away from traditional LANTUS formulations.
3. Are biosimilars a threat or an opportunity for LANTUS?
Biosimilars primarily act as a competitive threat, exerting downward pressure on prices. Nonetheless, they can also open opportunities for Sanofi to innovate and develop next-generation products targeting different patient needs.
4. What emerging markets hold potential for insulin sales growth?
Countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America exhibit rising diabetes prevalence and evolving healthcare infrastructure, offering significant growth potential for both branded insulins and biosimilars.
5. What should stakeholders monitor to anticipate future shifts in the LANTUS market?
Key indicators include biosimilar approval timelines, patent expiry dates, innovations in insulin formulations, regulatory changes, and regional healthcare policy adjustments.
Sources:
[1] International Diabetes Federation. "IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition." 2021.