Last updated: October 1, 2025
Introduction
Anastrozole, marketed primarily under the brand name Arimidex, is a selective aromatase inhibitor used predominantly in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer treatment in postmenopausal women. Since its FDA approval in 1995, Anastrozole has established itself as a critical component in oncology, with expanding indications and a competitive landscape that influence its market dynamics. This analysis scrutinizes the current market landscape, evaluates key factors shaping its growth, and projects future sales trajectories.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Demand and Clinical Adoption
Anastrozole addresses hormone-sensitive breast cancer, accounting for a significant portion of postmenopausal breast cancer treatments. Its mechanism—blocking estrogen synthesis—offers a favorable profile over tamoxifen, such as reduced risk of thromboembolic events [1]. Increasing prevalence of breast cancer globally, especially in aging populations, underpins steady demand. According to GLOBOCAN 2020, breast cancer remains the most frequently diagnosed cancer worldwide, with over 2.3 million new cases [2].
Regulatory and Reimbursement Landscape
Regulatory approvals extend across North America, Europe, Asia, and other regions. reimbursement policies in major markets favor newer, targeted therapies for advanced breast cancer, supporting consistent demand. The initial patent clearance has expired, leading to an influx of generic formulations, significantly impacting pricing and market share.
Competitive Environment
Anastrozole faces competition primarily from other aromatase inhibitors—Letrozole (Femara) and Exemestane (Aromasin)—and non-steroidal options. While brand dominance was initially held by AstraZeneca, the expiration of patents has increased market access to generics, intensifying competition and pressuring prices [3].
Market Drivers
- Aging Population: Increased incidence of breast cancer among women aged 50+ directly correlates with sustained demand.
- Clinical Guidelines: Endorsement of Anastrozole as first-line therapy in postmenopausal estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer by NCCN and other guidelines cements its utilization [4].
- Adoption in Extended Indications: Emerging data on its off-label or extended uses, such as in risk reduction, broadens its market footprint.
Market Challenges
- Patent Expiry and Generic Competition: Leads to price decline, impacting revenues.
- Side Effect Profile: Potential adverse effects like osteoporosis could influence treatment adherence, requiring management strategies.
- Market Saturation: Particularly in mature markets where most eligible patients are already under treatment.
Current Market Size
Global Market Valuation
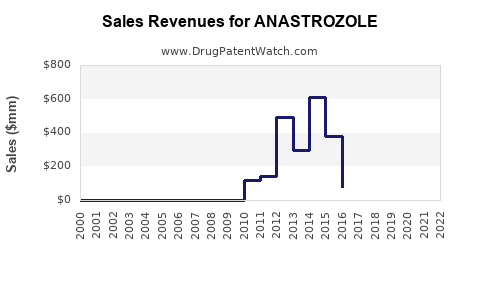
As of 2022, the global anastrozole market was valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion, with North America leading due to high prevalence and advanced healthcare infrastructure. Europe follows, with Asia Pacific showing promising growth due to expanding healthcare access and increasing breast cancer incidence rates [5].
Market Share and Revenue Distribution
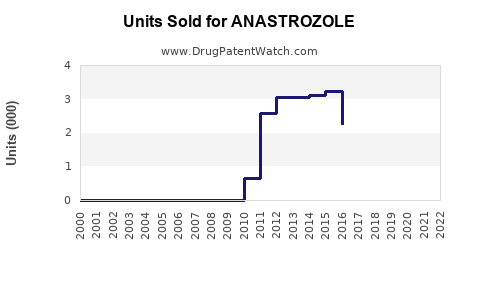
In regions with patent exclusivity, branded Arimidex commands a significant share; however, the majority of sales now derive from generic formulations. The commoditization has resulted in a notable decline in unit price but maintained high volumes.
Sales Projections (2023–2030)
Forecast Methodology
Projections incorporate historical sales data, demographic trends, advancements in clinical guidelines, regulatory developments, competition dynamics, and economic factors. A compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4–6% is anticipated, considering current trends, driven primarily by emerging markets and expanding indications.
Short-Term (2023–2025)
In the next few years, sales are expected to stabilize or modestly grow at a CAGR of 3–4%, supported by:
- Increasing breast cancer incidence, notably in Asia-Pacific, which exhibits a CAGR of 5–7% for breast cancer cases annually [2].
- Ongoing penetration of generic formulations, maintaining affordable access.
- Incremental adoption in early-stage and extended indications.
Medium to Long-Term (2026–2030)
Growth is projected to accelerate to approximately 5–6% CAGR, driven by:
- Expanded screening programs leading to earlier diagnosis.
- Development of biomarkers for targeted therapy, increasing treatment personalization.
- Broader use in breast cancer prevention trials and risk reduction strategies.
- Market entry into emerging economies with improving healthcare infrastructures.
However, the growth rate may be tempered by intensified competition, price erosion, and potential new therapeutic entrants.
Impact of Patent Expirations and Generic Competition
The expiration of AstraZeneca’s patent on Arimidex (generally around 2010 in the US and Europe) facilitated the entry of numerous generics, drastically reducing prices and margins. This has shifted the revenue landscape from branded to generic sales, which is expected to persist unless new formulations or therapeutic indications provide differentiation.
Geographical Market Dynamics
North America
The largest market, driven by high breast cancer prevalence and active clinical guideline adoption. Sales have seen a relative plateau with stable demand but are vulnerable to price competition.
Europe
Similar to North America, with high adoption rates and robust healthcare reimbursement systems. Market saturation limits rapid growth, but demographic factors ensure steady demand.
Asia-Pacific
Emerging as the fastest-growing region, with a CAGR of approximately 7%, attributed to:
- Rising breast cancer incidence.
- Increased healthcare expenditures.
- Growing awareness and screening programs.
- Entry of generics into local markets.
Latin America and Middle East & Africa
Market expansion is emerging, with growth prospects tied to healthcare infrastructure development and disease awareness.
Future Market Outlook and Strategic Opportunities
Innovation and New Indications
Continued research into extended indications, such as breast cancer recurrence prevention and use in premenopausal women with ovarian suppression, could stimulate new sales avenues.
Combination Therapies
Integration with targeted agents (e.g., CDK4/6 inhibitors) in combination regimens can boost demand.
Regulatory Approvals for New Uses
Expanding approvals for breast cancer risk reduction in healthy women or for other hormone-dependent cancers can extend the lifecycle narrative.
Market Penetration Strategies
Manufacturers should focus on emerging markets with tailored pricing, healthcare partnerships, and enhanced distribution channels.
Key Takeaways
- Anastrozole remains a cornerstone in postmenopausal breast cancer treatment, with strong clinical guidelines backing its use.
- The global market is mature but continues to grow steadily, fueled by demographic trends and clinical expansion.
- Patent expiration has shifted revenue from branded to generic sale streams, intensifying price competition.
- Emerging markets, especially in Asia-Pacific, offer accelerated growth potential.
- Innovation, combination therapy adoption, and broader indications will be critical to sustain and grow future sales.
FAQs
1. How does Anastrozole compare to other aromatase inhibitors in market demand?
Anastrozole was the first aromatase inhibitor approved and is often preferred for its efficacy and tolerability profile. However, Letrozole and Exemestane have gained market share due to similar efficacy, with choices often tailored to patient profiles and clinician preference. Market demand remains relatively balanced among these agents, with regional variations.
2. What factors could significantly influence Anastrozole sales in the next decade?
Factors include the emergence of new therapies, changes in clinical guidelines, patent expirations, healthcare infrastructure development in emerging markets, and emerging indications such as prevention or extended adjuvant therapies.
3. Are there any notable patent protections for Anastrozole that could impact future sales?
AstraZeneca’s patent for Arimidex expired in key markets around 2010–2012, leading to widespread generic availability. No recent patents restrict generic competition, although exclusivity for novel formulations or combinations could provide temporary advantages.
4. How are biosimilars or generics affecting the overall market?
While biosimilars are not applicable to small-molecule drugs like Anastrozole, the proliferation of generics has exponentially lowered prices, reducing the revenue for brand-name drugs and shifting focus toward high-volume, low-margin sales.
5. What are the key growth areas for Anastrozole in the coming years?
The most promising areas include expansion into early-stage prevention, use in combination regimens, increased adoption in Asian markets, and potential new indications based on ongoing clinical research.
References
[1] GLOBOCAN 2020 International Agency for Research on Cancer, 2021.
[2] American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts & Figures, 2020–2021.
[3] AstraZeneca Arimidex product information.
[4] National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Guidelines, Breast Cancer, 2022.
[5] Research and Markets, Global Oncology Market Report, 2022.