Share This Page
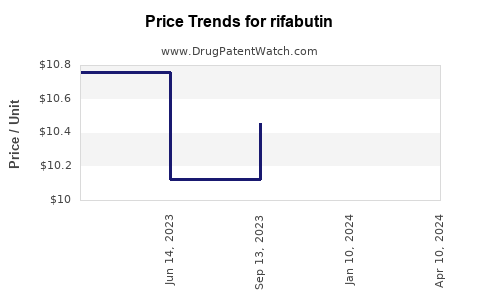
Drug Price Trends for rifabutin
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Average Pharmacy Cost for rifabutin
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIFABUTIN 150 MG CAPSULE | 70954-0041-10 | 9.32397 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| RIFABUTIN 150 MG CAPSULE | 59762-1350-01 | 9.32397 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| RIFABUTIN 150 MG CAPSULE | 70954-0041-10 | 9.09606 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| RIFABUTIN 150 MG CAPSULE | 59762-1350-01 | 9.09606 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| RIFABUTIN 150 MG CAPSULE | 70954-0041-10 | 8.73314 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Rifabutin: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Rifabutin, a semi-synthetic antibiotic within the rifamycin class, has carved a niche in the treatment of complex tuberculosis (TB) cases and prophylactic regimens for opportunistic infections in HIV-positive patients. With its distinct pharmacological profile, rifabutin faces a unique market landscape shaped by evolving medical guidelines, patent statuses, and global health initiatives. This article explores current market dynamics, forecasted price trends, and fundamental factors influencing rifabutin's commercial trajectory.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Indications and Clinical Adoption
Developed primarily as an alternative to rifampin, rifabutin exhibits activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). Its primary indication remains in latent and active TB, especially in cases where patients exhibit resistance or intolerance to first-line therapies. Additionally, rifabutin's role in preventing MAC infections in HIV/AIDS patients under antiretroviral therapy (ART) enhances its clinical importance.
Market Segmentation and Global Utilization
The global TB market is centralized, with significant consumption in high TB-burden regions such as India, China, and sub-Saharan Africa [1]. HIV-associated opportunistic infections further expand rifabutin's market, notably in regions with high HIV prevalence—sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. North America and Europe primarily use rifabutin within specialized treatment protocols, often linked to drug resistance cases.
Patent and Regulatory Landscape
While rifabutin was approved in the late 1990s (FDA approval in 1998), patent protections have largely expired in many jurisdictions, fostering increased generic manufacturing. Notably, patent expiry in key markets has precipitated price competition, directly impacting the drug's price trajectory [2].
Market Drivers
- Rising TB and HIV Co-infection Rates: The ongoing global burden of TB, compounded by HIV, underscores the demand for effective antimycobacterial agents like rifabutin.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Growing resistance to rifampin and other first-line agents promotes the utilization of rifabutin as an alternative.
- Guideline Recommendations: WHO and CDC guidelines increasingly incorporate rifabutin for specific patient subsets, bolstering clinical adoption.
- Generic Market Expansion: Post-patent expiry, a surge in generic manufacturing enhances affordability and access, especially in low-income countries.
Market Challenges
- Cost and Accessibility Challenges: Despite generics, pricing disparities persist, particularly in developing regions.
- Limited Formulation Variability: Existing formulations restrict innovation and price differentiation.
- Competition with Other Agents: The availability of newer antimicrobials and combination therapies may influence rifabutin’s market share.
- Regulatory Barriers: Variations in approval statuses hinder global harmonization and market expansion.
Competitive Landscape
The market is characterized by several generic producers, including Indian, Chinese, and South American pharmaceutical companies, which dominate due to lower production costs. No large pharmaceutical incumbents currently hold dominant patents, fostering a competitive environment driven principally by price.
Key players include:
- Cipla Ltd.
- Mylan (now part of Viatris)
- Sun Pharmaceuticals
- Various regional generic manufacturers
The absence of proprietary formulations in many markets facilitates broader access but limits profit margins for manufacturers.
Price Trends and Forecasts
Historical Pricing Dynamics
Data from IQVIA and WHO reflects that initial brand-name rifabutin formulations traded at premium prices (~$150–$200 per 300mg tablet in the early 2000s). Post-patent expiration, generic versions drove prices down significantly, with current retail prices typically ranging from $10 to $50 per 300mg tablet in high-income countries [3].
Current Market Prices
- High-income markets: Approximately $15–$35 per tablet for generics.
- Emerging markets: Prices drop to $5–$15 per tablet due to increased competition.
- Cost-effective formulations: In regions like India, prices can be as low as $2–$5 per tablet, bolstered by local manufacturing.
Projected Price Trajectory (Next 5–10 Years)
The following factors will influence future pricing:
- Increased generics penetration: Continued entry of manufacturers will exert downward pressure.
- Regional purchasing power: Markets with financing support from Gavi or Global Fund could see lower prices.
- Formulation innovations: Development of fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) may influence prices due to manufacturing complexities but could favor broader use.
Projections suggest steady decline of up to 20–30% in retail prices over the next decade, particularly as supply chains stabilize and production costs decrease.
Influencing Factors
- Patent expiries in major markets remove market exclusivity.
- Global health incentives aimed at TB eradication could subsidize prices further.
- Regulatory approvals for biosimilars or new formulations may alter the competitive landscape.
Market Opportunities and Risks
Emerging Markets
Growing TB burden and expanding HIV programs ensure sustained demand, especially if pricing remains accessible via generics. Government health policies that promote affordable antimicrobials could incentivize increased procurement.
Innovation Potential
Pharmaceutical research into combination therapies involving rifabutin or novel formulations (e.g., sustained-release, inhalable forms) offers potential premium pricing opportunities but is likely distant from near-term expansion.
Risks
- Market saturation: Widespread generic availability could lead to pricing stagnation.
- Regulatory hurdles: Variations across countries affect supply stability.
- Resistance development: Increasing drug resistance might limit effectiveness and reduce demand.
- Shifts in treatment guidelines: Adoption of newer agents or combination regimens could diminish rifabutin relevance.
Regulatory and Market Outlook
The global health community's emphasis on TB elimination aligns with broader access initiatives, impacting rifabutin’s market prospects. Continued support from organizations like WHO, GAVI, and the Global Fund could significantly influence demand and prices, especially in resource-limited settings.
Key Takeaways
- The global rifabutin market is characterized by high generic competition, leading to significant price reductions compared to its initial launch.
- Patent expirations and increased manufacturing capacity are pivotal factors contributing to declining prices.
- Emerging markets represent the highest growth potential due to the expanding TB and HIV epidemics coupled with affordability needs.
- The future of rifabutin prices hinges on global health policies, resistance patterns, and formulation innovations.
- Despite challenges, rifabutin maintains a vital role in specific clinical scenarios, ensuring a sustained demand in targeted populations.
FAQs
1. Will rifabutin prices continue to decline in the coming years?
Yes. Significant price reductions are expected, especially as generic manufacturing expands and patent protections expire, increasing supply and competition.
2. Which regions will see the most significant impact on rifabutin pricing?
Emerging markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America will experience the most notable price declines due to local manufacturing and international procurement programs.
3. Can innovation and new formulations influence rifabutin’s market price?
Potentially. The development of fixed-dose combinations or alternative delivery methods could command higher prices, but current trends favor cost reductions driven by generics.
4. How does resistance impact rifabutin’s market outlook?
Rising resistance to rifampin may enhance rifabutin's clinical value, maintaining or increasing demand in resistant TB cases, potentially affecting pricing upward in niche segments.
5. What role do global health initiatives play in rifabutin access?
Organizations like WHO and Gavi aim to improve access to essential medicines in low-income countries, which could subsidize rifabutin prices and facilitate broader distribution.
References
[1] World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. WHO; 2022.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Rifabutin Drug Approval Details, 1998.
[3] IQVIA. Medicine Price Trends, 2022 Data.
More… ↓
