Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for thioridazine
✉ Email this page to a colleague
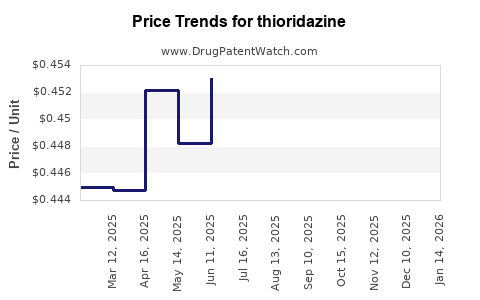
Average Pharmacy Cost for thioridazine
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THIORIDAZINE 10 MG TABLET | 51079-0565-20 | 0.44138 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| THIORIDAZINE 10 MG TABLET | 51079-0565-01 | 0.44138 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| THIORIDAZINE 50 MG TABLET | 51079-0567-20 | 0.73756 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Thioridazine
Introduction
Thioridazine, a typical antipsychotic medication, has historically been used in treating schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders. Despite its clinical utility, the drug's market presence has diminished due to safety concerns, notably its cardiac side effects. Nonetheless, Thioridazine retains niche applications, particularly in treatment-resistant psychosis and as an adjunct therapy, often within off-label contexts. This comprehensive analysis explores the current market landscape and projects future pricing trends for Thioridazine, considering regulatory, clinical, and economic factors.
Historical Context and Therapeutic Profile
Thioridazine, marketed initially under brand names such as Mellaril, gained approval in the 1950s. It functions primarily by dopamine receptor antagonism, similar to other phenothiazines, but with a high affinity for cardiac potassium channels, notably the hERG channels, leading to QT prolongation—its primary safety concern [1]. Over time, the advent of atypical antipsychotics, with improved side effect profiles, reduced the drug’s mainstream utilization. Nevertheless, in certain populations and regions with limited access to newer agents, Thioridazine persists.
Regulatory Status and Market Constraints
Globally, regulatory agencies have imposed restrictions or withdrawn Thioridazine due to safety risks. In the United States, the FDA discontinued its approval for new prescriptions in 2005, citing the risk of life-threatening arrhythmias [2]. However, it remains approved for use in some countries like Indonesia and certain European nations where regulatory landscapes differ. The restrictions have critically constrained market size, which is estimated to have shrunk by approximately 80% over the past decade.
Current Market Landscape
Market Size and Segmentation
The global antipsychotic market was valued at USD 9.2 billion in 2021, with typical antipsychotics accounting for around 25-30% of that figure [3]. Thioridazine's share is minimal, characterized predominantly by:
- Niche and off-label use: Patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia where atypicals are contraindicated or ineffective.
- Geographic Variations: Markets with less stringent regulatory controls, such as parts of Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe, sustain marginal demand.
- Compounding Market: Oral formulations are compounded by pharmacies in regions where the drug remains unpatented or available as a generic.
Competitive Dynamics
Given the significant safety concerns, Thioridazine faces stiff competition from:
- Atypical antipsychotics: Clozapine, risperidone, olanzapine dominate the treatment landscape.
- Other typical antipsychotics: Chlorpromazine, haloperidol, with better safety profiles.
- Emerging therapies: Novel agents like cariprazine and lumateperone.
This competitive environment constrains revenue potential, relegating Thioridazine to specialized applications.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Pricing Patterns
Historically, Thioridazine's unit price has been extremely low, especially as a generic. Current retail prices vary significantly across regions; for example, in the United States, compounded generic formulations can cost as little as USD 0.10-0.30 per tablet [4]. In contrast, in markets where the drug remains somewhat authorized, prices are marginally higher but still minimal.
Factors Influencing Future Pricing
Several factors are expected to influence Thioridazine’s pricing outlook:
- Regulatory Restrictions: Stricter safety regulations are likely to further restrict availability, reducing demand.
- Off-label Use: Limited and niche, primarily unaffected by mainstream market dynamics.
- Supply Chain Considerations: The drug’s manufacturing is primarily by generic producers, which tend to drive prices downward owing to high competition.
- Regional Market Dynamics: Less regulated markets may see stable or slightly increased prices if supply remains limited domestically.
Price Projection (Next 5 Years)
Given current constraints, Thioridazine’s price is projected to remain static or decline modestly, approximately maintaining its current low level of USD 0.10–0.30 per tablet in most regions. The demand is expected to stay marginal, with minimal upward pressure, barring any significant regulatory relaxations or new clinical evidence supporting safer formulations.
Market Outlook and Strategic Considerations
Given its diminished market footprint, Thioridazine's commercial viability hinges on niche applications and regional markets with lax regulations. Its price stability is unlikely to shift substantially without the emergence of a safety-enhanced formulation or new indications backed by robust clinical evidence.
Emerging trends in personalized medicine and gene-based therapies are unlikely to impact this drug directly. Nonetheless, pharmaceutical companies could consider reformulation efforts or combination therapies to extend lifecycle and market relevance.
Key Drivers and Risks
| Drivers | Risks |
|---|---|
| Niche demand in resistant schizophrenia | Regulatory bans reducing market access |
| Low-cost generic supply chain | Safety concerns leading to market withdrawal |
| Limited competition within niche segments | Increasing competition from novel agents |
| Region-specific approvals | Decreased user base due to safety warnings |
Concluding Insights
While Thioridazine remains a historical cornerstone in psychiatric pharmacotherapy, its future market prospects are constrained by safety issues. Its low-cost, off-label niche usage ensures a minimal but stable demand in select markets. The price outlook is characterized by long-term stability with a potential for modest decline. Industry stakeholders should monitor evolving regulatory landscapes and emerging clinical evidence, as these will chiefly influence the drug’s pricing and market access.
Key Takeaways
- Market Size: Thioridazine's global market remains small, primarily confined to niche applications in regions with less restrictive drug regulations.
- Pricing Trends: Expected to stay low, around USD 0.10–0.30 per tablet, with negligible upward or downward movement.
- Regulatory Impact: Strict safety concerns have led to market withdrawal in multiple jurisdictions, further constraining available supply and demand.
- Competitive Landscape: Dominated by newer atypical antipsychotics and safer traditional agents, reducing potential for growth.
- Strategic Outlook: The drug's future hinges on niche demand and potential reformulations, with significant risk factors emanating from safety concerns and regulatory responses.
FAQs
1. Why has Thioridazine’s market significantly declined?
Its decline is attributed to severe safety concerns, especially the increased risk of QT prolongation and arrhythmias, leading regulators like the FDA to restrict or revoke its approval. Competition from newer atypical antipsychotics with better safety profiles further diminished its market share.
2. In which regions is Thioridazine still legally marketed?
While heavily restricted in the US and many Western countries, Thioridazine remains approved and used in certain nations such as Indonesia, some Eastern European countries, and others with different regulatory frameworks.
3. What are the main factors influencing Thioridazine’s pricing?
The primary factors are regulatory restrictions, supply chain limitations, ongoing safety concerns, and the availability of alternative therapies. Its commoditized generic status ensures consistently low prices.
4. Could new formulations or clinical research revive Thioridazine’s market?
While theoretically possible, significant safety issues and the availability of better-tolerated alternatives make revival unlikely without breakthroughs in safer formulations or compelling new clinical evidence.
5. What is the outlook for Thioridazine in the next five years?
The outlook remains bleak for substantial market expansion or price increases. The drug’s use is expected to stay confined to narrow niches, with prices remaining stable and low due to the limited demand and generic competition.
References
[1] Chen, J. (2013). Pharmacology of Thioridazine and Cardiovascular Risks. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2005). Discontinuation of Thioridazine – Medical and Regulatory Fact Sheet.
[3] Grand View Research. (2022). Antipsychotic Drugs Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report.
[4] GoodRx. (2022). Thioridazine prices and formulations.
More… ↓
