Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for sulindac
✉ Email this page to a colleague
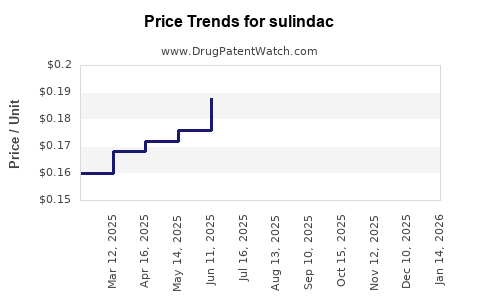
Average Pharmacy Cost for sulindac
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SULINDAC 150 MG TABLET | 24658-0770-05 | 0.18016 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| SULINDAC 150 MG TABLET | 42806-0018-01 | 0.18016 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| SULINDAC 150 MG TABLET | 00904-7334-60 | 0.18016 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| SULINDAC 150 MG TABLET | 42806-0018-05 | 0.18016 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| SULINDAC 150 MG TABLET | 00591-5661-01 | 0.18016 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| SULINDAC 200 MG TABLET | 53489-0479-01 | 0.23216 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Sulindac
Introduction
Sulindac, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), is primarily used to treat pain, swelling, and inflammation associated with conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and certain polyp conditions, especially familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). Since its approval in the 1970s, sulindac's market dynamics have evolved, influenced by competition, regulatory pathways, patent statuses, and broader trends in NSAID utilization. This report provides a detailed market analysis and projected pricing outlook for sulindac, focusing on current market conditions, potential growth drivers, constraints, and strategic implications for stakeholders.
Market Overview
-
Market Size and Current Demand
The global NSAID market was valued at approximately USD 16.0 billion in 2022, with traditional NSAIDs like ibuprofen and naproxen dominating due to widespread OTC availability. Sulindac’s share, however, remains niche, estimated at USD 50–100 million annually, primarily driven by its use in treating familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and particular inflammatory indications. The demand for sulindac in oncology and chemoprevention, especially FAP, is notable, but overall utilization remains limited relative to other NSAIDs. -
Target Indications and Patient Demographics
Sulindac’s unique application in FAP management—an inherited condition leading to multiple colorectal polyps—positions it as a specialized drug within the oncology supportive care segment. Patients with FAP represent a small, hereditary subset, limiting market size. Conversely, for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, standard NSAIDs have predominantly replaced sulindac owing to familiarity and OTC availability, constraining its broader market potential. -
Competitive Landscape
Multiple NSAIDs, both prescription and OTC, compete with sulindac—including ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac, and celecoxib. In the chemopreventive niche, sulindac’s closest competitors include other agents used off-label for polyp reduction or colorectal cancer prevention, such as celecoxib and aspirin. -
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Sulindac’s patent protections have long expired, transitioning it to a generic status. The absence of patent exclusivity limits direct manufacturer investments and price premiums, often resulting in commoditized pricing. Regulatory authorities, including the FDA and EMA, have approved sulindac for decades, with few recent modifications to its label, although new formulations or combination therapies are under investigational consideration.
Market Drivers
- Growing Incidence of Colorectal Polyps and Cancer: Increased detection and screening have heightened interest in chemopreventive agents; sulindac's role in FAP remains relevant.
- Advances in Personalized Medicine: Genetic profiling facilitates targeted prophylactic interventions, potentially expanding sulindac's niche.
- Cost-effectiveness of Generic Drugs: Price sensitivity among healthcare providers supports pharmacies' and hospitals' preferences for low-cost options like sulindac.
Market Constraints
- Safety and Tolerability Concerns: Long-term NSAID use is associated with gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, and renal risks, which limit wider adoption in preventive contexts outside rare indications.
- Competition from Established NSAIDs and Biologics: The dominance of OTC NSAIDs and the emergence of biologic therapies for inflammatory conditions restrict sulindac's market expansion.
- Limited Patent Protection: Inhibits incentivization for novel formulations or new therapeutic indications, constraining revenue potential.
Price Trends and Projections
-
Current Price Point
As a generic drug, sulindac's wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) hovers approximately between USD 0.10 to 0.20 per tablet (e.g., 200 mg). Retail prices fluctuate based on health insurer negotiations, pharmacy benefits, and regional factors, but overall, sulindac remains a low-cost NSAID. -
Historical Price Trends
Over the past decade, sulindac's price has been relatively stable owing to its generic status. Slight reductions correlate with increasing market penetration of newer NSAIDs and the availability of over-the-counter alternatives. -
Projected Price Trajectory
Given the key market constraints, significant price increases are unlikely in the short to medium term. However, specialized formulations (e.g., extended-release) or new delivery mechanisms could pose opportunities for modest premium pricing, albeit with high development costs.
Future Price Outlook (Next 5 Years)
| Scenario | Price Trend | Factors Influencing Prices |
|---|---|---|
| Conservative | Stable/Declining | Continued generic competition, pressure for cost savings |
| Moderate Growth | Slight increase (~5–10%) | Niche indication expansion, specialty formulary adoption |
| Optimistic | Potential premium (~10–20%) for formulations or associated indications | Development of novel delivery systems or combination therapies |
In all scenarios, cost pressures and regulatory constraints favor an overall neutral to modest decline trend for sulindac prices unless strategies emerge to commercially differentiate its use.
Market Opportunities and Strategic Recommendations
- Niche Expansion: Pursuing clinical development for sulindac in colorectal cancer chemoprevention or other oncologic applications could create premium options, boosting pricing power.
- Formulation Innovation: Sustained-release or combination formulations could justify increased pricing.
- Regulatory Pathways: Investigating new indications via accelerated approval mechanisms or orphan drug designations could open monetization avenues.
- Partnerships and Licensing: Collaborations with biotech firms developing targeted therapies might facilitate niche market growth.
Potential Risks
- Market Saturation and OTC Competition: The widespread availability of OTC NSAIDs exert downward pressure.
- Safety Profile Limitations: Adverse effects restrict expansion into broader populations.
- Regulatory Barriers: Stringent approval processes for new indications, formulations, or combination therapies pose challenges.
Key Takeaways
- Market size for sulindac remains modest, primarily confined to rare indications like FAP, with limited scope for substantial growth.
- Pricing is expected to remain low due to generic status, with minor upward adjustments possible through formulation innovations or niche expansion.
- Competitive pressures and safety concerns restrain broad adoption, particularly for preventive uses.
- Strategic focus on developing new formulations or indications could unlock premium pricing opportunities, but require significant R&D investment and navigational hurdles.
- Stakeholders should monitor regulatory developments and evolving clinical evidence that may alter sulindac’s positioning within the NSAID market.
FAQs
-
What factors influence sulindac's market price?
Its generic status, competition with OTC NSAIDs, safety profile, and limited indications predominantly influence pricing, which tends to remain low and stable. -
Can sulindac become more profitable despite its generics status?
Yes. Developing novel formulations, expanding indications, or targeting niche markets like chemoprevention in high-risk populations can justify higher pricing and improve profitability. -
What are the primary challenges facing sulindac's market growth?
Competition from well-established NSAIDs, safety concerns related to long-term NSAID use, and limited patent protection restrict expansion. -
Is there potential for sulindac in personalized medicine markets?
Potential exists in targeting genetically predisposed populations, such as FAP patients, although the overall market remains small. -
How might regulatory changes impact sulindac’s pricing or market access?
New approvals for additional indications or formulations could allow for higher prices, whereas increased safety regulations might restrict use or impose additional costs.
References
[1] Global NSAID Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report (2022).
[2] FDA Drug Approval History for Sulindac.
[3] Market Intelligence Data on Generic Drug Pricing Trends.
[4] Recent Clinical Trials on Sulindac in Chemoprevention.
[5] Regulatory Incentives for Orphan Drugs and New Indications.
More… ↓
