Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for insulin aspart
✉ Email this page to a colleague
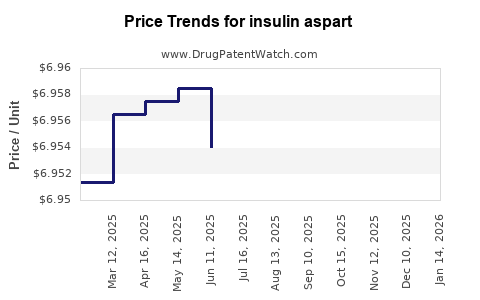
Average Pharmacy Cost for insulin aspart
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART MIX 70-30 VIAL | 73070-0200-11 | 6.93550 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| INSULIN ASPART 100 UNIT/ML VL | 73070-0100-11 | 6.95487 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| INSULIN ASPART FLEXPEN 100 UNIT/ML PEN | 73070-0103-15 | 8.95828 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART MIX 70-30 FLEXPEN | 73070-0203-15 | 8.94670 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Insulin Aspart
Introduction
Insulin aspart, a rapid-acting insulin analog marketed under brand names such as NovoLog and Fiasp, plays a pivotal role in the management of diabetes mellitus. As the global prevalence of both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes surges, the demand for insulin analogs like insulin aspart escalates correspondingly. This article provides a comprehensive market analysis and price projection outlook for insulin aspart, emphasizing current dynamics, competitive factors, regulatory influences, and future pricing trends.
Market Overview
Global Diabetes Epidemic and Impact on Insulin Demand
The International Diabetes Federation estimates that over 537 million adults worldwide live with diabetes, projected to rise to 643 million by 2030 [1]. Insulin therapy remains the cornerstone of management, especially for Type 1 diabetics, who constitute approximately 10% of the diabetic population. The increasing adoption of insulin analogs, including insulin aspart, reflects their superior pharmacokinetic profiles—offering rapid onset and flexible dosing.
Market Size and Growth Trajectory
In 2022, the global insulin market was valued at approximately USD 26.7 billion, with insulin analogs accounting for over 70% of this figure, driven by preferences for rapid-acting and long-acting formulations [2]. The insulin aspart segment represents a significant share within rapid-acting insulins, characterized by a CAGR of around 8% over the past five years, and poised for continued expansion.
Key Geographic Markets
- United States: The largest market, attributed to high diabetes prevalence, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and insurance coverage.
- Europe: Notable for early adoption, regulatory support, and evolving reimbursement policies.
- Asia-Pacific: Exhibits rapid growth potential due to rising disease burden, expanding healthcare access, and population size.
- Emerging Markets: Countries like Brazil, Russia, and India are experiencing increased insulin adoption amidst improving healthcare systems.
Competitive Landscape
Major Players
- Novo Nordisk: Produces NovoLog (insulin aspart), dominating the market with a market share estimated above 50%.
- Eli Lilly and Company: Offers Insulin Lispro but competes indirectly via rapid-acting insulin offerings.
- Sanofi: Focuses on long-acting formulations but is a key competitor in the broader insulin segment.
- Emerging Biosimilar Manufacturers: Several biosimilar insulin aspart products are entering markets, intensifying price competition.
Biosimilar Integration
In recent years, biosimilar versions of insulin aspart have received regulatory approval in regions like Europe and Asia, with some launched at 20-30% lower prices than originators. Their entry signifies a potential downward pressure on prices and expanded access.
Regulatory Environment and Reimbursement Dynamics
Regulatory agencies, including the FDA and EMA, have streamlined biosimilar approvals, fostering market entry. Reimbursement policies significantly influence pricing; countries with aggressive rebate strategies and government negotiations tend to achieve lower insulin prices.
In the U.S., Medicare and private payers actively negotiate prices, leading to a complex pricing landscape. Conversely, emerging markets often have less stringent price controls, allowing for higher variability.
Price Trends and Forecast
Historical Pricing Patterns
- Originator insulin aspart products (e.g., NovoLog): Historically, prices in the US have increased annually by approximately 5-7% since launch, driven by R&D costs, manufacturing, and market exclusivity.
- Biosimilar products: Initial prices are typically 20-30% lower than originators, although discounts tend to narrow over time with market consolidation.
Projected Price Movements (2023–2030)
Based on current trends and market dynamics:
- North America: Expect a gradual stabilization of insulin prices for originator products, with biosimilar market penetration leading to a 10-15% average reduction in retail prices by 2030.
- Europe: Prices are anticipated to decline by 15-25%, owing to robust biosimilar adoption and national reimbursement negotiations.
- Asia-Pacific and Emerging Markets: Prices are expected to decrease modestly (5-10%) due to increased biosimilar presence, improved healthcare infrastructure, and government initiatives.
Key Factors Influencing Future Prices
- Biosimilar Competition: Accelerated approvals and market entry will exert downward pressure.
- Policy and Reimbursement Changes: Countries implementing aggressive price controls and price transparency measures will see lower insulin prices.
- Innovation and Value-Based Pricing: Introduction of novel formulations or delivery systems might temporarily maintain higher prices but could shift towards value-based models over time.
- Manufacturing Costs: Advances in biosimilar manufacturing technologies may further reduce production costs, enabling lower consumer prices.
Market Risks and Opportunities
Risks:
- Regulatory delays and hurdles for biosimilar approval.
- Patent litigations prolonging market exclusivity.
- Healthcare funding constraints, especially in low- and middle-income countries.
Opportunities:
- Expansion into underserved markets with aging populations.
- Development of ultra-rapid acting insulins and novel delivery devices creating premium pricing avenues.
- Strategic partnerships with payers and governments to enhance affordability.
Conclusion
The insulin aspart market is positioned for steady growth, driven primarily by the escalating global diabetes epidemic and technological advancements. Price trends suggest a gradual decline over the next decade, primarily fueled by biosimilar competition and regulatory tightening. Market players and stakeholders must navigate complex reimbursement landscapes, regulatory pathways, and manufacturing innovations to optimize profitability and access.
Key Takeaways
- The global insulin market, with insulin aspart at the forefront, is expanding at a CAGR of approximately 8%, with Asia-Pacific and emerging markets demonstrating significant growth potential.
- Biosimilar insulin aspart products are emerging as key disruptors, expected to reduce prices by up to 25% in mature markets by 2030.
- Reimbursement policies and regulatory environments remain critical determinants in pricing trajectories across different regions.
- Despite incremental price reductions, value-added features like innovative delivery devices may sustain premium pricing segments.
- Strategic collaborations and early biosimilar adoption can provide competitive advantages amid ongoing market convergence.
FAQs
1. How will biosimilars impact the insulin aspart market pricing?
Biosimilars are expected to increase price competition, leading to reductions of 20-30% over originator prices, especially in regions with active regulatory pathways and reimbursement support.
2. What factors are driving the growth of insulin aspart globally?
The rising prevalence of diabetes, improved treatment guidelines favoring rapid-acting insulins, and advancements in insulin formulations contribute to robust market growth.
3. Are insulin prices declining uniformly worldwide?
No. Price declines vary significantly; high-income countries are experiencing gradual reductions due to biosimilar competition and negotiations, while emerging markets see more stable or marginal decreases.
4. What regulatory changes could influence future insulin pricing?
Streamlined biosimilar approval processes, stricter price controls, and policies promoting generic substitution could accelerate price reductions.
5. How might technological innovations affect insulin aspart prices?
Innovations such as ultra-rapid formulations or delivery devices might command higher prices initially but could lead to cost efficiencies and broader access over time.
Sources:
[1] International Diabetes Federation. (2022). IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th Edition.
[2] MarketWatch. (2023). Global Insulin Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis.
More… ↓
