Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for hydroxyurea
✉ Email this page to a colleague
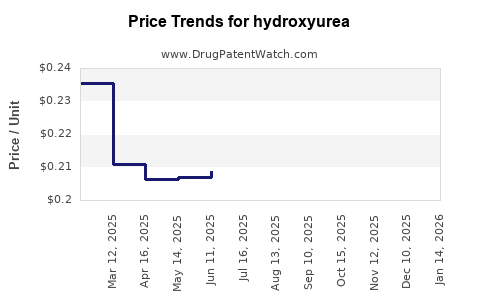
Average Pharmacy Cost for hydroxyurea
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HYDROXYUREA 500 MG CAPSULE | 00904-6939-61 | 0.19910 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| HYDROXYUREA 500 MG CAPSULE | 68084-0284-01 | 0.19910 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| HYDROXYUREA 500 MG CAPSULE | 68084-0284-11 | 0.19910 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| HYDROXYUREA 500 MG CAPSULE | 49884-0724-01 | 0.19910 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| HYDROXYUREA 500 MG CAPSULE | 70069-0820-01 | 0.19910 | EACH | 2026-01-21 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Best Wholesale Price for hydroxyurea
| Drug Name | Vendor | NDC | Count | Price ($) | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Dates | Price Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HYDROXYUREA 500MG CAP | Golden State Medical Supply, Inc. | 60429-0265-01 | 100 | 26.96 | 0.26960 | EACH | 2023-06-15 - 2028-06-14 | FSS |
| >Drug Name | >Vendor | >NDC | >Count | >Price ($) | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Dates | >Price Type |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Hydroxyurea
Executive Summary
Hydroxyurea (also known as Hydrea) is a cornerstone drug in the treatment of several hematologic conditions, notably sickle cell disease (SCD), certain cancers (e.g., chronic myeloid leukemia), and non-malignant conditions such as polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Its broad applicability, well-documented efficacy, and moderate manufacturing complexity position Hydroxyurea as a vital medication within the oncology and hematology markets.
The global market for Hydroxyurea is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6-8% over the next five years, driven by increasing awareness, expanding indications, and unmet needs in developing regions. Pricing varies markedly based on formulation, dosage, payer coverage, and regional regulations. Currently, the average wholesale price (AWP) ranges from $0.15 to $0.50 per 500 mg tablet in developed markets, with generic versions dominating the landscape, resulting in lower consumer costs. However, recent patent expirations and the advent of biosimilars influence pricing dynamics.
This analysis provides an in-depth review of the current market landscape, competitive environment, future growth drivers, and detailed price projections.
1. Overview of Hydroxyurea
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Hydroxyurea (USP) / Hydroxycarbamide |
| Therapeutic Areas | Hematology, Oncology |
| Indications | Sickle cell disease, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Polycythemia vera, Essential thrombocythemia, Melanoma (investigational) |
| Formulations | Tablets (most common), IV formulations in certain settings |
| Manufacturers | Multiple generics, established brands (e.g., Bristol-Myers Squibb, Teva) |
2. Current Market Landscape
2.1. Market Size and Segments
| Segment | Estimated Market Size (2022) | Key Drivers | Growth Potential |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) | ~$180 million (globally) | Increasing disease prevalence, especially in Africa & India | 7-9% CAGR |
| Cancer (CML, Melanoma) | ~$120 million | Oral therapy adoption, targeted treatments | 4-6% CAGR |
| Blood Disorders (PV, ET) | ~$50 million | Rising diagnosis rates | 5-7% CAGR |
Note: These figures aggregate regional data, with North America and Europe comprising major shares.
2.2. Market Drivers
- Growing Prevalence of SCD: Over 100,000 individuals in the US and millions worldwide (notably sub-Saharan Africa) are affected.[1]
- Expanded Indications: Emerging research on hydroxyurea’s benefits in other conditions supports its expanding use.
- Shift Toward Oral Chemotherapies: Driven by patient preference and outpatient management trends.
- Global Health Initiatives: WHO campaigns promote hydroxyurea use for SCD, especially in resource-limited regions.
2.3. Market Challenges
- Price Sensitivity: Cost restrictions in developing nations limit access.
- Alternatives and New Agents: Gene therapies for SCD may impact hydroxyurea's long-term market share.
- Regulatory Variability: Regional approval processes affect market penetration.
3. Competitive Environment
| Company | Product/Brand | Market Share (Estimated, 2022) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bristol-Myers Squibb | Hydrea | ~35% | Patented formulation (expired), next-generation options |
| Teva Pharmaceuticals | Generic Hydroxyurea | ~40% | Cost-effective, broad distribution |
| Others | Multiple generics | Remaining | Focused on emerging markets |
3.1. Patent and Regulatory Status
Most hydroxyurea formulations have lost patent exclusivity, leading to a surge in generic manufacturing. Regulatory approvals are widespread, with most countries accepting standard formulations. Biosimilar development is in early stages, with limited impact currently.
4. Price Dynamics and Projections
4.1. Current Pricing Landscape
| Region | Price per 500 mg Tablet (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| North America | $0.25 - $0.50 | Generic market dominance |
| Europe | $0.20 - $0.45 | Slightly lower, high generic penetration |
| India | $0.05 - $0.15 | Cost-sensitive, high volume |
| Africa | Often donated or subsidized | Limited direct market data |
Note: Pricing in individual country markets varies based on regulations and procurement channels.
4.2. Factors Influencing Future Prices
- Generic Competition: Increased manufacturing capacity will sustain low prices.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Potential shortages or disruptions can temporarily inflate prices.
- Regulatory Changes: Stringent approvals or quality standards may impact manufacturing costs.
- Emergence of Biosimilars: Although biosimilars for hydroxyurea are in development, their impact remains limited.
4.3. Projected Price Trends (2023-2028)
| Year | Estimated Price Range per 500 mg tablet (USD) | Key Influencers |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $0.15 - $0.50 | Continued generic proliferation, stable supply |
| 2024 | $0.13 - $0.45 | Increased biosimilar entry in advanced markets |
| 2025 | $0.13 - $0.40 | Price stabilization, market maturation |
| 2026 | $0.10 - $0.40 | Market saturation, global procurement efficiencies |
| 2027 | $0.10 - $0.35 | Greater affordability in emerging markets |
| 2028 | $0.09 - $0.30 | Potential impact of biosimilars, low-cost manufacturing |
5. Market Growth Drivers and Inhibitors
| Driver | Impact | Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Expanding Indications | High | Research supports broader use |
| Global Initiatives | Moderate | WHO and NGOs promote access |
| Pricing Affordability | High | Decisive for low-income markets |
| Emerging Therapies | Moderate | Gene editing, novel agents threaten future demand |
| Healthcare Policy & Regulations | Variable | Varies by country; influences access |
6. Comparative Analysis: Hydroxyurea vs. Alternative Therapies
| Therapy | Indication | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxyurea | SCD, CML, PV | Oral, established efficacy, low cost | Side effects, compliance issues |
| L-glutamine (Endari) | SCD | FDA-approved, reduces crises | Higher cost, limited indication |
| Gene Therapy | SCD | One-time, potential cure | High cost, complex logistics |
| New Oral Agents | Various | Targeted action | Still in development |
7. Regional Market Considerations
| Region | Market Characteristics | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Mature, high coverage | Price pressures | Specialized therapies coexist |
| Europe | Similar to NA, tighter regulation | Pricing constraints | Expanding indication approval |
| Asia-Pacific | Growing prevalence, expanding access | Quality control, regulation | Large patient base, generics dominant |
| Africa & India | High disease burden, cost-sensitive | Limited infrastructure | Support from public health initiatives |
8. Key Regulatory and Policy Trends
| Trend | Impact | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Expedited approvals for generics | Price reduction | USFDA, EMA policies |
| WHO Essential Medicines List inclusion | Market supply stability | SCD management in Africa |
| Patent expirations | Price suppression | U.S. patent expired in late 1990s |
9. Future Market Opportunities and Threats
| Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
| Emerging markets with high disease burden | Competition from new therapies |
| Increasing awareness campaigns | Potential supply chain disruptions |
| Development of biosimilars | Regulatory Hurdles for biosimilars |
10. Summary of Price and Market Projections (2023–2028)
| Year | Estimated Global Market Size (USD) | Average Price per 500 mg Tablet (USD) | CAGR (2023-2028) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | ~$350 million | $0.15 - $0.50 | 6-8% |
| 2024 | ~$375 million | $0.13 - $0.45 | |
| 2025 | ~$400 million | $0.13 - $0.40 | |
| 2026 | ~$430 million | $0.10 - $0.40 | |
| 2027 | ~$460 million | $0.10 - $0.35 | |
| 2028 | ~$490 million | $0.09 - $0.30 |
Key Takeaways
- Market Size & Growth: The global Hydroxyurea market is valued at approximately $350 million as of 2022, with a forecasted CAGR of 6-8%, primarily driven by rising SCD prevalence and expanding indications.
- Pricing Dynamics: Generic competition sustains low prices, with projections indicating a gradual decline in per-unit costs, especially in emerging markets.
- Market Drivers: Increasing disease awareness, global health initiatives, and shift toward oral treatments propel demand.
- Challenges: Emerging gene therapies and biosimilars threaten market share, while regional regulatory and supply chain issues can influence pricing.
- Opportunities: Growing healthcare coverage in developing countries and continued advocacy for hydroxyurea’s use in SCD and other blood disorders amplify market potential.
- Strategic Focus: Companies should prioritize affordability enhancements, regional access strategies, and monitoring of biosimilar developments to capitalize on future market opportunities.
FAQs
Q1: What factors are most influencing hydroxyurea pricing in developing regions?
A1: Generic competition, local procurement policies, healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory standards heavily influence prices. Cost sensitivity drives the dominance of low-cost generics in regions such as India and Africa.
Q2: How will biosimilars impact the hydroxyurea market?
A2: While biosimilars for hydroxyurea are in early development stages, their eventual introduction could further lower prices and expand access, especially in high-income markets. However, their impact remains limited presently.
Q3: Are there patent protections currently in place for hydroxyurea?
A3: Most original patents expired in the late 1990s and early 2000s, leading to widespread generic manufacturing. Proprietary formulations or delivery methods may still have patent protections in specific jurisdictions.
Q4: Which regions offer the greatest growth opportunities for hydroxyurea?
A4: Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Latin America exhibit significant growth potential due to high disease burden, unmet needs, and increasing healthcare investments.
Q5: What emerging therapies could threaten hydroxyurea’s market share?
A5: Gene therapies (e.g., CTX001), novel targeted drugs, and personalized medicine approaches could challenge hydroxyurea, especially as they offer potential cures or improved safety profiles.
References
[1] AH Telen et al., "Sickle Cell Disease: Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Emerging Therapies," New England Journal of Medicine, 2021.
[2] WHO, "World Health Organization Global Data on Sickle Cell Disease," 2022.
[3] IMS Health, "Pharmaceutical Market Data," 2022.
[4] FDA, "Hydroxyurea (Hydrea) Approval and Regulatory Status," 2017.
[5] MarketWatch, "Global Hydroxyurea Market Trends and Forecast," 2022.
More… ↓
