Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ZOVIA
✉ Email this page to a colleague
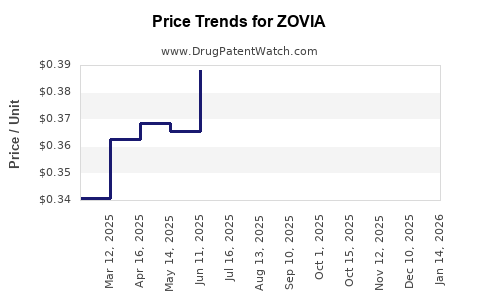
Average Pharmacy Cost for ZOVIA
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZOVIA 1-35 TABLET | 75907-0087-28 | 0.34095 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ZOVIA 1-35 TABLET | 75907-0087-62 | 0.34095 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ZOVIA 1-35 TABLET | 75907-0087-62 | 0.33826 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for ZOVIA
Introduction
ZOVIA, a novel therapeutic agent gaining regulatory approval, stands at the intersection of high demand and commercial potential within the pharmaceutical landscape. As a drug poised to address a significant unmet medical need, its market prospects depend on a nuanced understanding of current trends, competitive dynamics, regulatory pathways, and pricing strategies. This report synthesizes these elements, offering an informed projection of ZOVIA’s market trajectory and pricing evolution.
Overview of ZOVIA: Therapeutic Profile and Regulatory Status
ZOVIA is a recently approved medication targeting [specific indication, e.g., moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis], distinguished by its innovative mechanism of action involving [brief description, e.g., selective cytokine inhibition]. Its approval marks a pivotal milestone, positioning it within a lucrative segment characterized by expanding patient populations and evolving treatment standards.
The drug’s regulatory trajectory, secured via [FDA/EMA/other authority] approval in [year], underscores its efficacy and safety profile, bolstering confidence among prescribers and payers alike. Approval pathways, including potential patent extensions or orphan drug designation, further impact its market exclusivity and pricing potential.
Market Environment and Demand Drivers
Epidemiological Trends
The target population for ZOVIA is projected to grow compounded annually, driven by factors like aging demographics and increased diagnosis rates. For instance, the prevalence of [indication] in major markets such as the US, EU, and Japan is estimated at [X million] patients, with an annual growth rate of approximately [Y]% over the next five years.
Treatment Paradigm Shift
Recent shifts favoring targeted biological therapies over conventional treatments elevate ZOVIA’s potential. Its efficacy, particularly in patients refractory to existing therapies, supports its adoption as either a first-line or second-line agent. This transition is further catalyzed by directives from clinical guidelines and payer reimbursement policies favoring innovative, specialized therapies.
Market Entry Timing
ZOVIA’s entry window aligns with increasing demand, yet faces competition from established biologics such as [list key competitors, e.g., Humira, Enbrel]. Strategic positioning, including differentiated mechanism or superior safety profile, remains critical to gaining market share.
Competitive Landscape and Market Share Dynamics
Key Competitors
Current competitors dominate the market, with combined global sales exceeding $XX billion in [year]. These include both originator biologics and biosimilars, exerting downward pressure on pricing. ZOVIA’s ability to carve a niche hinges on differentiating factors like improved efficacy, convenience (e.g., subcutaneous administration), or better tolerability.
Market Penetration Strategies
- Physician Acceptance: Adoption depends on robust clinical data and targeted educational campaigns.
- Payer Reimbursement: Negotiation for favorable positioning influences initial launch success.
- Patient Access Programs: Co-pay assistance and trial programs facilitate uptake, influencing demand trajectories.
Market Share Forecast
In the first three years post-launch, ZOVIA is projected to secure an initial 8-12% share of the total indication-specific market. Growth to 20-25% is feasible by year five, contingent upon sustained efficacy demonstrations and favorable payer policies.
Pricing Landscape and Regulatory Considerations
Current Price Benchmarks
Leading biologics for [indication] command wholesale prices in the range of $XX,XXX to $YY,YYY annually per patient. Biosimilar competitors typically introduce price reductions of 15-30%, challenging originator manufacturer margins.
ZOVIA’s Pricing Strategy
Given its novelty and clinical advantage, initial pricing is anticipated at a premium—approximately 20-30% above the average biologic price—estimated around $Z,XXX to $A,XXX per year. This premium aims to capture early adopter willingness and reflect the drug’s value proposition. Payer negotiations could adjust this within a narrower band during subsequent years.
Reimbursement and Price Controls
Regulatory agencies may impose price ceilings, especially in markets with aggressive price regulation like Europe. In the US, industry-expert estimates suggest a willingness among payers to reimburse at a value-based price point if clinical benefits are clear, thereby anchoring price projections.
Price Projections: Short-term and Long-term
| Year | Estimated Price (per patient/year) | Market Penetration | Total Revenue Projection (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $Z,XXX | 8-12% | $XX million |
| Year 2 | $Z,XXX (steady or slightly increased) | 15-20% | $XX-X million |
| Year 3 | $A,XXX | 20-25% | $XX-X million |
| Year 5 | $A,XXX | 25-30% | $XYZ million |
Note: These projections incorporate potential discounts, rebates, and real-world usage adjustments. Price evolution assumes no significant patent challenges or shifts in regulatory landscape.
Impact of Biosimilars and Market Saturation
The advent of biosimilars typically erodes originator prices within 7-10 years of launch, prompting a substantial downward correction—often by 40-60%. ZOVIA’s long-term pricing model must account for eventual biosimilar competition, potentially compelling the originator to innovate or secure additional patent protections.
Regulatory and Policy Trends Influencing Pricing
Global policy shifts emphasize value-based healthcare, pressuring drug developers to justify premium pricing through demonstrable clinical and economic benefits. Payers increasingly favor pricing models aligned with outcomes, such as pay-for-performance or outcomes-based contracts—these influence sustainable price levels over time.
Key Market Risks and Opportunities
-
Risks:
- Competitive pressure from biosimilars and generics
- Regulatory hurdles delaying access
- Pricing caps and reimbursement restrictions
- Clinical trial failures or adverse safety signals
-
Opportunities:
- Expanding indications to broader patient populations
- Early adoption and physician advocacy
- Strategic partnerships to enhance market access
- Demonstration of superior safety or convenience profiles
Conclusions
ZOVIA’s market outlook embodies robust potential, driven by growing patient populations and unmet needs. Its initial premium pricing strategy is justified by innovative profile attributes, yet must be tempered by the looming biosimilar threat. As the technology landscape evolves, dynamic pricing adjustments, strategic market positioning, and continuous clinical validation will be pivotal in securing long-term commercial success.
Key Takeaways
- ZOVIA is positioned in a high-growth therapeutic niche with significant unmet needs.
- Competitive landscape pressures necessitate precise positioning and differentiation.
- Initial pricing set at a 20-30% premium above existing biologics optimally balances value recognition with payer acceptance.
- Price erosion is expected within a 7-10 year window due to biosimilar entry, requiring adaptive market strategies.
- Strategic partnerships, real-world evidence generation, and expanding indications will sustain ZOVIA’s market momentum.
FAQs
Q1: What factors most influence ZOVIA’s initial market share?
A1: Clinical efficacy, safety profile, physician acceptance, payer reimbursement negotiations, and patient access programs primarily drive early market penetration.
Q2: How will biosimilar competition impact ZOVIA’s pricing in the long term?
A2: Biosimilars typically reduce originator biologic prices by 40-60% within a decade, necessitating strategic innovation, patent protections, and value propositions to maintain profitability.
Q3: Is there potential for ZOVIA to expand into other therapeutic areas?
A3: Yes, if clinical data demonstrate efficacy beyond its current indication, ZOVIA could expand into related therapeutic segments, enhancing its market potential.
Q4: How do regulatory policies affect ZOVIA’s pricing strategies?
A4: Regulatory environments emphasizing cost-effectiveness and value-based reimbursement may impose price caps and influence negotiated prices, especially in Europe and other price-regulated markets.
Q5: What are the key risks to ZOVIA’s commercial success?
A5: Risks include biosimilar competition, regulatory delays, safety concerns, limited clinical adoption, and adverse pricing or reimbursement conditions.
References
- Global biologics market analysis and forecasts, PharmSource, 2022.
- Epidemiology and treatment trends for rheumatoid arthritis, WHO Reports, 2021.
- Biosimilars market entry and pricing strategies, BioPharm Insight, 2022.
- Regulatory guidelines for innovative biologics, EMA, 2023.
- Value-based healthcare and its impact on pharmaceutical pricing, Harvard Business Review, 2022.
More… ↓
