Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for VIREAD
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Average Pharmacy Cost for VIREAD
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
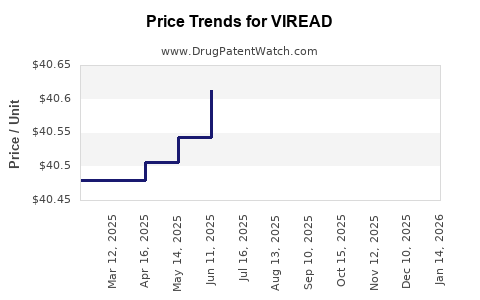
| VIREAD 300 MG TABLET | 61958-0401-01 | 40.72981 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| VIREAD 300 MG TABLET | 61958-0401-01 | 40.72019 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| VIREAD 300 MG TABLET | 61958-0401-01 | 40.67378 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| VIREAD 300 MG TABLET | 61958-0401-01 | 40.66147 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| VIREAD 300 MG TABLET | 61958-0401-01 | 40.61547 | EACH | 2025-08-20 |
| VIREAD 300 MG TABLET | 61958-0401-01 | 40.58297 | EACH | 2025-07-23 |
| VIREAD 300 MG TABLET | 61958-0401-01 | 40.61336 | EACH | 2025-06-18 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for VIREAD
Introduction
VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) remains a cornerstone in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. As a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, VIREAD has established a strong market presence due to its efficacy, safety profile, and widespread adoption. This analysis evaluates current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory considerations, and future price trajectories to inform stakeholders’ strategic decisions.
Market Overview
Global Market Landscape
VIREAD garnered approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2001 for HIV treatment and later expanded indications for HBV. The drug's global footprint is substantial; North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific collectively constitute the primary markets, with emerging markets increasingly contributing due to expanding HIV and HBV burdens.
The global antiviral drug market, driven by growing HIV prevalence and chronic hepatitis cases, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 4% over the next five years (2023–2028). VIREAD, as a first-line agent, benefits from this demand, although its market share faces stiff competition from newer drugs.
Sales Performance and Market Penetration
In 2022, VIREAD generated approximately $2.2 billion in worldwide sales, according to IQVIA data. North America accounts for the largest share, driven by high HIV/AIDS prevalence and reimbursement coverage. Europe follows, with significant use in both HIV and HBV populations. The Asia-Pacific region, with its expanding HIV/AIDS programs and HBV endemicity, shows increasing adoption, albeit constrained by pricing and generic competition.
Patient Demographics and Therapy Trends
Approximately 37 million people globally live with HIV, while over 250 million are affected by chronic HBV, underlining the sizeable potential market for VIREAD. Treatment guidelines favor potent, well-tolerated antivirals, reinforcing VIREAD’s relevance, especially in regions with limited access to the latest therapies.
Competitive Landscape
Key Competitors
VIREAD faces competition from several antiviral agents:
- Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF): Marketed as Vemlidy (for HBV) and Viread for HIV, TAF offers an improved safety profile with less renal and bone toxicity, leading to potential market share erosion for VIREAD.
- Emtricitabine and Lamivudine: Often combined with other agents, providing alternative regimens.
- Third-generation integrase inhibitors (e.g., Dolutegravir) are increasingly preferred for HIV treatment due to improved tolerability and resistance profiles.
Patent and Generic Landscape
VIREAD's primary patent protections expired in 2020, initiating generic manufacturing, which exerts downward pressure on pricing. Generic versions in key markets have significantly reduced VIREAD’s price, especially in developed economies.
Market Differentiation Factors
VIREAD’s longstanding efficacy, extensive clinical data, and broad indication formulations sustain its demand. However, safety concerns related to nephrotoxicity and bone mineral density loss have prompted shifts toward TAF-based therapies, especially in higher-income markets.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Dynamics
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies continue to endorse VIREAD’s use, but the growing preference for TAF reflects a shift in clinical guidelines emphasizing safety. The FDA's approval of generic versions accelerates access but also intensifies price competition.
Reimbursement Considerations
Reimbursement policies heavily influence price trajectories. In the U.S., VIREAD benefits from Medicaid, Medicare, and private insurance coverage but faces cost containment pressures. In emerging markets, government procurement strategies and price negotiations mainly govern affordability.
Pricing Trends and Future Projections
Historical Pricing
Pre-generic, VIREAD’s wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) in the U.S. hovered around $30-$35 per month per patient. Post-generic entry, prices plummeted by over 70%, with some generic formulations available at less than $5/month.
Projected Price Trends
- Near-term (1-2 years): Given patent expiration, aggressive generic competition is expected to maintain low prices. The mean retail price might stabilize around $1–$3 per month in many markets.
- Mid-term (3-5 years): As newer formulations like TAF become standard, VIREAD’s demand may decline further. Price erosion could continue, with some markets experiencing a plateau at highly subsidized rates.
- Long-term (5+ years): VIREAD’s role may diminish primarily to secondary or limited use cases, with prices converging close to production costs, especially in price-sensitive regions.
Influence of Patent Litigation and Drug Substitutes
Patent disputes and litigation delays can temporarily stabilize prices but are unlikely to reverse the overall downward trend driven by generic proliferation and healthcare shifts towards safer alternatives.
Strategic Implications for Stakeholders
Stakeholders must recognize VIREAD’s declining pricing due to patent expiry and competitive pressures. Manufacturers should prioritize lifecycle management, possibly through formulation improvements or combination therapies, to maintain relevance. Payers and healthcare providers should evaluate cost-effectiveness, especially as newer agents demonstrate reduced toxicity, influencing formulary decisions and reimbursement policies.
Conclusion
The VIREAD market faces a landscape characterized by rapid generics entry, evolving clinical preferences favoring TAF, and declining prices. While current revenue streams remain significant, the long-term outlook calls for strategic planning around aging formulations and emerging competition. Market players should leverage data on price trends and therapeutic shift dynamics to optimize product positioning and investment decisions.
Key Takeaways
- Patent expiration has ushered in aggressive generic competition, leading to substantial price erosion for VIREAD globally.
- Emerging alternatives like TAF threaten VIREAD’s market share, especially in higher-income countries focused on safety profiles.
- Pricing in developed markets is expected to stabilize at low levels ($1–$3/month), whereas in less mature markets, prices may vary depending on procurement strategies.
- Market volume is projected to decline long-term as newer therapies gain dominance, but VIREAD remains relevant in resource-limited settings.
- Stakeholders should focus on lifecycle management and cost-effective utilization amid declining prices and shifting standards of care.
FAQs
-
What is the primary factor driving VIREAD’s declining price?
Patent expiration and the entry of generic versions have created intense price competition, reducing VIREAD’s wholesale and retail prices globally. -
Will VIREAD remain relevant long-term given newer alternatives?
While its market share is decreasing, VIREAD retains relevance in resource-limited settings and for specific indications, especially where cost considerations are paramount. -
How does the shift towards TAF affect VIREAD’s market value?
TAF offers a superior safety profile, prompting clinicians and payers to prefer it over VIREAD, thereby diminishing VIREAD’s market share and price. -
What are the implications of generic entry for licensing and revenue?
Generics significantly lower prices, which can erode profit margins. License-holders need to strategize around lifecycle management or transition to newer formulations. -
How do regulatory policies influence VIREAD pricing?
Reimbursement and procurement policies, especially in low- and middle-income countries, often accelerate price reductions post-patent expiry to enhance access.
References
- IQVIA. Pharmaceutical Market Data. 2022.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. VIREAD (tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) approval documents. 2001.
- Clinical guidelines on HIV/AIDS and HBV management, World Health Organization. 2022.
- Market Research Future. Antiviral Drugs Market Analysis. 2023.
- Published patent and legal case documents related to VIREAD.
More… ↓
