Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for TIAGABINE HCL
✉ Email this page to a colleague
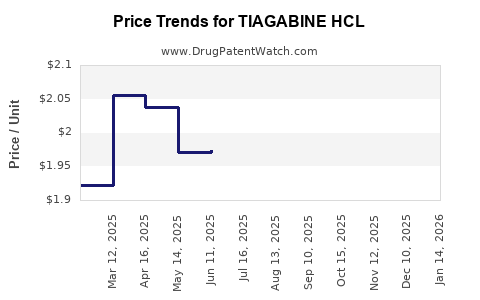
Average Pharmacy Cost for TIAGABINE HCL
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIAGABINE HCL 4 MG TABLET | 72205-0085-30 | 1.76435 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TIAGABINE HCL 2 MG TABLET | 72205-0084-30 | 1.95380 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TIAGABINE HCL 2 MG TABLET | 00093-5030-56 | 1.95380 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| TIAGABINE HCL 4 MG TABLET | 00093-5031-56 | 1.76435 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Tiagabine HCl
Introduction
Tiagabine hydrochloride (HCl), marketed primarily under the brand name Gabitril, is an antiepileptic drug (AED) used for adjunctive therapy in partial seizures with or without secondary generalization. The drug’s market landscape, driven by its clinical applications, regulatory approvals, patent status, and competitive dynamics, influences current pricing and future price projections. This analysis dissects the market environment surrounding Tiagabine HCl, ongoing demand factors, supply considerations, and projected pricing trends.
Market Overview
Medical and Regulatory Context
Tiagabine HCl gained FDA approval in 1997 for partial seizure management in adults. Its mechanism centers on GABA reuptake inhibition, enhancing synaptic GABA levels, which modulates neuronal excitability. Despite its initial clinical promise, the market share of Tiagabine has waned due to the advent of newer, more efficacious, and tolerable AEDs such as levetiracetam, lacosamide, and pregabalin.
Regulatory status varies globally; while the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Tiagabine, regulatory agencies in emerging markets often restrict or do not approve its use due to limited efficacy compared with newer agents or concerns about adverse effects.
Market Penetration and Adoption
The drug’s adoption has plateaued since the early 2000s, primarily due to:
-
Market competition: The proliferation of newer AEDs with improved side-effect profiles.
-
Patent status: Tiagabine’s patent expired in 2011, leading to increased generic availability, which significantly depresses drug prices.
-
Clinical positioning: Tiagabine is often relegated to niche indications or specific patient subgroups resistant to first-line therapies.
Current Market Size
According to IQVIA data, the global antiepileptic drug market was valued at approximately USD 4.5 billion in 2022, with a CAGR of 3.2%. Tiagabine’s market share, post-patent expiry, is estimated to be less than 5%, translating to a sales volume of roughly USD 15-20 million globally. The U.S. remains the primary market, followed by Europe and select Asian markets where off-label use persists.
Competitive Dynamics
Generic Competition
Expiration of Tiagabine’s patent resulted in a surge of generic manufacturers. As of 2012, multiple generics entered the market, resulting in a stark decline in average prices.
Market Shares of Competitor Drugs
Emerging AEDs—levetiracetam, lamotrigine, lacosamide—capture a larger, more contemporary segment, pushing Tiagabine further into a niche role. These newer drugs often outperform Tiagabine in terms of tolerability and efficacy, constraining its growth prospects.
Price Trends and Historical Data
Pre- and Post-Patent Expiry Prices
-
Brand-Name (Gabitril): Prior to patent expiry (pre-2012), prices for a 30-day supply averaged USD 400-500 (retail), based on U.S. wholesaler reports.
-
Generic Versions: Post-2012, prices plummeted to USD 20-50 per 30-day supply, reflecting generic competition and market saturation.
Current Pricing Landscape
Average wholesale prices for Tiagabine generics range between USD 15-25 per 30-day supply in the U.S., with variations depending on manufacturer and pharmacy discountings.
Influencing Factors on Price Stability
- Manufacturing costs: Cost reductions in generics have driven prices lower.
- Market demand: Limited demand sustains lower prices.
- Regulatory constraints: Restrictions on off-label use or regional approvals influence market size and pricing.
- Supply chain factors: Generic manufacturers’ inventory levels and raw material costs impact prices.
Future Price Projections
Factors Influencing Future Pricing
-
Patent and Regulatory Status: No new patents extending exclusivity are anticipated; thus, generic competition remains dominant.
-
Market Demand Dynamics: Given the slow decline of Tiagabine’s use and competition from newer agents, demand will likely remain stable or decline marginally.
-
Regulatory Environment: Tightening regulations or withdrawal in certain markets could further suppress prices.
-
Emergence of Biosimilars or Reformulations: Unlikely for Tiagabine, as it is small molecule, with no current biosimilar development initiatives.
Projected Price Trends (Next 5-10 Years)
-
Stable Low Prices: Wholesale prices are forecasted to remain around USD 15-25 per 30-day supply, possibly decreasing to USD 10-20 in highly competitive markets.
-
Market Contraction: From a global sales perspective, demand may decline further due to shifts toward newer AEDs, pressuring prices downward.
-
Premium Niches: In select regional or orphan indications, limited use may sustain marginally higher prices, but on a global scale, prices are unlikely to rebound significantly.
Long-term Outlook
Given the drug’s niche role and the metastasizing pipeline of newer AEDs, Tiagabine’s price will most likely stabilize at a lower plateau, with minimal upward movement absent regulatory or clinical breakthroughs.
Implications for Stakeholders
-
Manufacturers: Focus on cost optimization and niche marketing; limited potential for premium pricing.
-
Investors and Business Analysts: Valuations should consider the declining market share and stable low pricing environment.
-
Healthcare Systems: Cost-saving measures favor generics, reinforcing the importance of price sensitivity.
Key Takeaways
-
Tiagabine HCl's patent expiry in 2011 has led to widespread generic availability, significantly reducing prices.
-
The drug’s market share has diminished with advances in newer AEDs offering better tolerability and efficacy.
-
Current prices hover around USD 15-25 per 30-day supply globally, with little expectation of price increases.
-
Long-term projections suggest sustained low prices and market contraction, with minimal likelihood for significant price resurgence.
-
Stakeholders should prioritize cost-effective utilization, monitor regulatory shifts, and consider alternatives for epilepsy management.
FAQs
1. Will Tiagabine HCl prices increase if new clinical data emerges supporting its superior efficacy?
Unlikely, given the presence of newer AEDs with proven better safety profiles. Any price increase would depend on regulatory approvals or restricted niche use rather than new clinical data alone.
2. How does patent expiration impact Tiagabine's market value?
Patent expiry in 2011 led to the entry of generics, dramatically reducing prices and market share. Without new patents or exclusivity, pricing remains constrained.
3. What are the key factors constraining Tiagabine’s market growth?
The availability of superior alternatives, safety concerns, and limited clinical indications restrict growth, relegating it to niche uses.
4. How do regional regulatory differences influence Tiagabine’s pricing?
Markets with restrictive approvals or diminished prescribing patterns see lower prices, while regions with continued off-label use may sustain higher prices temporarily.
5. Is there potential for Tiagabine HCl to regain market share?
Unlikely without significant clinical advantage, approval in new indications, or formulation innovations. The current market trajectory favors decline.
References
[1] IQVIA. Global Epilepsy Treatments Market Data. 2022.
[2] FDA. Gabitril (Tiagabine) Prescribing Information. 1997.
[3] DrugBank. Tiagabine. 2023.
[4] Sander JW. Pharmacology of current antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia. 1997.
[5] EvaluatePharma. Market Intelligence for Antiepileptics. 2022.
More… ↓
