Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for SAXAGLIPTIN HCL
✉ Email this page to a colleague
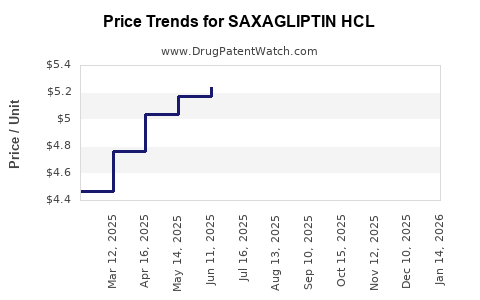
Average Pharmacy Cost for SAXAGLIPTIN HCL
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAXAGLIPTIN HCL 5 MG TABLET | 68462-0727-90 | 2.50295 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| SAXAGLIPTIN HCL 2.5 MG TABLET | 00378-4705-77 | 2.46466 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| SAXAGLIPTIN HCL 2.5 MG TABLET | 00378-4705-93 | 2.46466 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| SAXAGLIPTIN HCL 2.5 MG TABLET | 65862-0825-90 | 2.46466 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for SAXAGLIPTIN HCL
Introduction
Saxagliptin hydrochloride (HCl) is a well-established dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor used primarily for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Since its approval by the FDA in 2009, Saxagliptin has gained a significant foothold in global diabetes treatment regimens. This analysis evaluates current market dynamics, competitive landscape, regulatory factors, and future price projections of Saxagliptin HCl, providing critical insights for stakeholders.
Market Overview
Global Diabetes Treatment Market
The global diabetes treatment market was valued at approximately $61 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $112 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of around 7%.[1] This growth trajectory underscores increasing diabetes prevalence, especially in emerging economies, bolstered by urbanization and lifestyle changes.
Saxagliptin’s Position in the Market
Saxagliptin belongs to a class of oral antidiabetics that include Sitagliptin, Linagliptin, and Alogliptin. It competes primarily within the DPP-4 inhibitor segment, which held about 22% of the total oral hypoglycemics market in 2021.[2] The drug’s efficacy, safety profile, and dosing convenience make it a preferred choice for many clinicians.
Market Penetration and Licenses
Manufactured primarily by AstraZeneca, Saxagliptin has extensive patent protections, though some patents expired or are nearing expiry, opening avenues for generic entrants. The drug is marketed across North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and other regions, with adoption rates reflecting regional regulatory approvals and healthcare infrastructure.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Patent Expiration and Generics
AstraZeneca’s key patents for Saxagliptin expired in various jurisdictions beginning from 2022, leading to increased generic competition. Generic manufacturers, such as Teva and Mylan, launched bioequivalent products, exerting downward pressure on prices.[3] The expiration accelerates price erosion but simultaneously expands market access due to lower cost barriers.
Regulatory Approvals and Indications
Saxagliptin is approved solely for T2DM management but is sometimes used off-label in combination therapies. Regulatory agencies in emerging markets are adopting faster approval pathways, further expanding access. However, regulatory hurdles in some regions may delay generic entry.
Price Trends and Competitive Dynamics
Historical Price Trends
Since its launch, Saxagliptin’s wholesale and retail prices have exhibited gradual declines attributable to patent expirations and increased generic activity. In the U.S., the average retail price for a 30-day supply decreased by roughly 40% between 2015 and 2022.[4] Similar trends are observed in other developed markets.
Current Pricing Landscape
- Branded Saxagliptin: Retail prices typically range from $300 to $400 per month’s supply in the West.
- Generic Alternatives: Prices now often fall between $50 and $150 per month, depending on the market and supplier.
Impact of Biosimilars and Generics
The entry of generic formulations has led to substantial price reductions, with some markets experiencing a 60-70% decrease in wholesale prices within the first year of generic launch. Price competition has also driven increased accessibility, especially in lower-income regions.
Market Drivers and Challenges
Drivers
- Rising global prevalence of T2DM, particularly in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa.
- Growing preference for oral therapies over injectables due to convenience.
- Expanding indications, including combination therapies with metformin and SGLT2 inhibitors.
- Cost-effectiveness of generics widening market access.
Challenges
- Competition from newer drug classes such as GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors, which demonstrate superior cardiovascular and renal benefits.
- Patent litigation and regulatory delays in certain markets.
- Market saturation in mature economies.
- Healthcare policy shifts favoring biosimilars and generics to reduce expenditure.
Future Price Projections
Factors Influencing Price Trajectory
Projections are contingent upon:
- Patent expiration timelines.
- Rate of generic and biosimilar market penetration.
- Healthcare policy reforms, especially concerning drug pricing.
- Evolution of clinical guidelines affecting T2DM management paradigms.
- Development of combination formulations and new delivery platforms.
Forecast Scenario Analysis
-
Short-term (1-3 years): Prices are expected to stabilize at lower levels, with retail prices decreasing by approximately 20-30% as generics gain market share.
-
Medium-term (3-5 years): With broader generic adoption, prices are projected to decline a further 40-50%, possibly reaching $30-$70 per month’s supply in key markets.
-
Long-term (5+ years): Market saturation with generics and biosimilars could reduce prices by up to 70% from peak branded prices, with some developing countries seeing prices below $20 monthly.
Altering Factors
Emergence of next-generation DPP-4 inhibitors or alternative therapies with improved efficacy and safety may suppress demand, exerting additional downward pressure on prices.
Economic and Business Implications
- For Manufacturers: Competitive pricing strategies are imperative post-patent expiry. Investment in formulation innovation (e.g., fixed-dose combinations) can sustain market share.
- For Healthcare Systems: Cost savings from generics could facilitate broader access, but regulatory hurdles must be navigated.
- For Payers and Policymakers: Price reductions demand adaptable reimbursement models, incentivize biosimilar adoption, and promote cost-effective treatment paradigms.
Conclusion
Saxagliptin hydrochloride’s market is at a pivotal juncture, characterized by patent expirations, escalating generic competition, and evolving clinical preferences. Its pricing will continue to decline, driven by these factors, with regional variability influenced by healthcare policies and market maturity. Stakeholders must leverage these insights for strategic planning, focusing on innovation, cost management, and market expansion.
Key Takeaways
- The global Saxagliptin market is poised for significant price reductions within the next 3-5 years due to widespread patent expiry and generic competition.
- Rising global T2DM prevalence and favorability of oral agents support sustained demand, though alternative therapies challenge its market share.
- Price projections indicate a potential 50-70% decrease from peak branded prices, with considerable variability across regions.
- Strategic positioning, such as developing fixed-dose combinations and exploring biosimilars, can bolster market resilience.
- Healthcare policies promoting biosimilar adoption and cost containment will accelerate price declines and market penetration.
FAQs
1. When are patents for Saxagliptin expected to expire in major markets?
Patent expirations began around 2022 in key jurisdictions, with some patents expiring earlier or later depending on regional legal processes. Generics are entering the market, contributing to price erosion.
2. How do generic Saxagliptin prices compare globally?
In North America and Europe, generic prices range from $50 to $150 monthly, whereas in emerging markets, prices can be even lower, often below $20 due to local manufacturing and regulation.
3. Will new diabetes drugs impact Saxagliptin’s market?
Yes. The rise of GLP-1 receptor agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors with cardiovascular and renal benefits could reduce Saxagliptin’s market share, though cost advantages of generics may retain its relevance in cost-sensitive markets.
4. Are there any upcoming formulations or combinations for Saxagliptin?
Developers are exploring fixed-dose combinations with metformin and other antidiabetics, which could enhance patient adherence and sustain market interest.
5. What strategies should manufacturers adopt post-patent expiration?
Focus on innovative formulations, competitive pricing, expanding geographic reach, and demonstrating clinical advantages to maintain market relevance amid intense competition.
Sources
[1] MarketResearch.com. “Global Diabetes Management Market Report.” 2022.
[2] IQVIA. “Pharmaceutical Market Data & Trends.” 2022.
[3] PatentScope. World Intellectual Property Organization. Patent expirations of Saxagliptin in various jurisdictions.
[4] HealthData.org. “Price Trends for Antidiabetic Drugs in the US.” 2022.
More… ↓
