Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for QBRELIS
✉ Email this page to a colleague
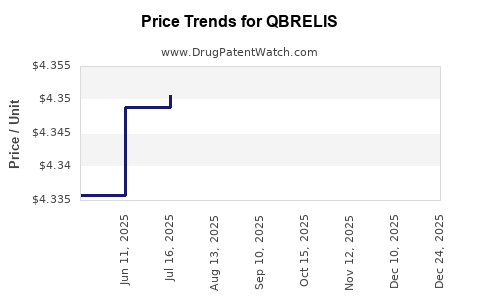
Average Pharmacy Cost for QBRELIS
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QBRELIS 1 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-3001-01 | 4.47509 | ML | 2026-01-01 |
| QBRELIS 1 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-3001-01 | 4.34474 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| QBRELIS 1 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-3001-01 | 4.34819 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| QBRELIS 1 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-3001-01 | 4.34954 | ML | 2025-10-22 |
| QBRELIS 1 MG/ML SOLUTION | 52652-3001-01 | 4.35080 | ML | 2025-09-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for QBRELIS
Introduction
QBRELIS (niraparib) is a targeted oral PARP inhibitor developed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) for the treatment of ovarian, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal cancers, particularly in maintenance therapy settings. Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2020, QBRELIS has positioned itself within the evolving landscape of precision oncology, driven by advances in molecular diagnostics and personalized treatment strategies.
This analysis examines the current market landscape, competitive positioning, and provides price projections for QBRELIS over the upcoming years, considering factors such as patent status, patent expirations, market penetration, pricing strategies, and emerging regulatory and therapeutic trends.
Market Landscape Overview
Therapeutic Market Context
QBRELIS is positioned in the PARP inhibitor class, which has become standard for maintenance therapy in ovarian cancer, especially for patients with homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) or BRCA mutations. Other prominent agents include Merck’s (formerly Clovis')'Lynparza (olaparib), AstraZeneca’s (also co-marketed with Merck) Calquence, and Bristol-Myers Squibb’s (BMS) Opdivo, among others.
The global ovarian cancer therapeutics market is projected to reach approximately $3.5 billion by 2025, driven by increasing diagnosis rates, advanced molecular diagnostics, and expanding indications for PARP inhibitors[^1^].
Key Market Drivers
- Growing Incidence: According to the Globocan 2020 report, ovarian cancer remains among the leading causes of gynecologic cancer mortality globally, with an estimated 207,252 new cases in 2020[^2^].
- Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities: Biomarker testing (e.g., BRCA mutation status) facilitates targeted therapy, increasing demand for agents like QBRELIS.
- Regulatory Approvals and Label Expansion: QBRELIS’s FDA approval for maintenance in recurrent ovarian cancer, with ongoing trials for first-line maintenance, enhances market potential.
- Competitive Dynamics: The existing PARP inhibitors have established market shares, but QBRELIS differentiates itself via distinct dosing, side effect profile, and potentially more affordable pricing.
Market Penetration and Adoption
Current Market Share
Since its approval in 2020, QBRELIS has begun capturing portions of the maintenance therapy segment, primarily in the United States and select European countries. Sales are currently modest compared to established agents but are trending upward, fueled by clinical trial data showing efficacy and tolerability.
Key Influencing Factors
- Physician Adoption: Adoption depends on early clinical data, head-to-head comparisons, and physician familiarity.
- Reimbursement and Pricing: Reimbursement strategies and competitive pricing influence patient access and formulary inclusion.
- Patient Population: Patients with BRCA mutations or HRD-positive tumors represent the primary eligible population, estimated at approximately 40-50% of ovarian cancer cases[^3^].
Market Challenges and Opportunities
- Challenges: Competition from Lynparza and newer agents with broader indications could limit QBRELIS’s market share unless differentiated.
- Opportunities: Expansion into first-line maintenance and combination regimens, along with potential biomarker-driven indications, could substantially increase sales.
Price and Revenue Projections
Pricing Landscape
The current wholesale acquisition cost (WAC) for QBRELIS is approximately $7,850 per month per patient, aligning with prices of similar PARP inhibitors in the US market[^4^]. GSK’s pricing strategy emphasizes competitive positioning, affordability, and access.
Projected Revenue Trajectory
2023-2025
- 2023: Expected initial sales of $150-200 million, driven by early adoption and expanding indications.
- 2024: Growth of 20-30%, reaching approximately $250-290 million with broader acceptance and ongoing clinical success.
- 2025: Potential crossover or competition impact could cap growth at around 30%, with sales reaching approximately $300-380 million.
Factors Influencing Revenue
- Market Penetration: Accelerated use in first-line maintenance setting following positive trial results.
- Pricing Adjustments: Potential price reductions in response to competitive pressures or payer negotiations.
- Regulatory Approvals: Approvals for additional indications would expand eligible patient populations, increasing revenue.
Long-term Price Trends
Over the next five years, PARP inhibitors face potential pricing pressures due to biosimilars, pricing transparency initiatives, and payor cost-containment efforts. Prices could decline modestly (5-15%), offset by increased patient numbers and expanded uses.
Competitive and Regulatory Outlook
Patent and Patent Expiry Timeline
- Primary Patent: Filed around 2017, with expected expiration around 2032-2034, depending on jurisdiction-specific extensions.
- Orphan Drug Designation: May offer market exclusivities until at least 2027.
- Patent Expiry Impact: Generic or biosimilar entrants could emerge post-2032, significantly affecting pricing and revenues.
Regulatory Landscape
- Ongoing trials exploring QBRELIS in combination therapies and other cancers could lead to labelling expansions, supporting longer-term revenue growth.
- Pending approvals in Europe, Asia, and Latin America will influence global market share and pricing strategies.
Strategic Recommendations
- Maximize Differentiation: Leverage unique side effect profile and dosing frequency for physician and patient preference.
- Pricing Flexibility: Prepare for competitive pricing strategies as biosimilars and generics enter, ensuring access and market share retention.
- Investment in Indication Expansion: Prioritize clinical trials for earlier-line and combination indications to extend product lifecycle.
- Market Access Initiatives: Strengthen payer relationships and demonstrate cost-effectiveness to secure favorable reimbursement terms.
Key Takeaways
- QBRELIS is emerging as a notable player within the competitive PARP inhibitor market, with significant growth potential driven by expanding indications and adoption.
- Current pricing aligns with market peers at ~$7,850/month but faces potential downward pressure in the long term due to biosimilar entries.
- Revenue projections suggest sales could reach ~$300-380 million globally by 2025, contingent on regulatory success and market penetration.
- Patent protection is expected to extend into the early 2030s, providing a window of market exclusivity against generic competitors.
- Strategic focus on indication expansion, pricing strategies, and differentiated clinical positioning will be critical for sustained growth.
FAQs
1. What distinguishes QBRELIS from other PARP inhibitors?
QBRELIS (niraparib) offers a flexible dosing regimen and has demonstrated efficacy in patients irrespective of BRCA mutation status, potentially broadening its utility compared to some competitors focused on specific genetic subtypes.
2. How is the pricing of QBRELIS justified in the current market?
Pricing reflects clinical efficacy, safety profile, and comparative value within the PARP class, aligning with similar agents like Lynparza. Reimbursement negotiations and value-based models influence actual costs to patients and payers.
3. What are the key factors affecting QBRELIS’s future market share?
Factors include clinical trial outcomes, competitive launches, regulatory approvals for additional indications, pricing strategies, and physician adoption patterns.
4. When are biosimilars or generics expected to impact QBRELIS’s pricing?
Patent exclusivity is likely to extend into the early 2030s. Post-expiry, biosimilar entrants could significantly reduce prices, impacting margins and revenue.
5. What future indications could enhance QBRELIS’s market potential?
Potential approvals in first-line maintenance for ovarian cancer, combination therapies with immunotherapies or chemotherapies, and use in other BRCA-mutated cancers could significantly expand its market.
References
[^1^]: MarketsandMarkets. Ovarian Cancer Therapeutics Market. 2021.
[^2^]: Globocan 2020. Global Cancer Statistics. International Agency for Research on Cancer.
[^3^]: National Cancer Institute. Ovarian Cancer Subtypes and Genetic Markers.
[^4^]: GoodRx. QBRELIS Price and Cost Data. 2023.
More… ↓
