Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for OXYBUTYNIN CL ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
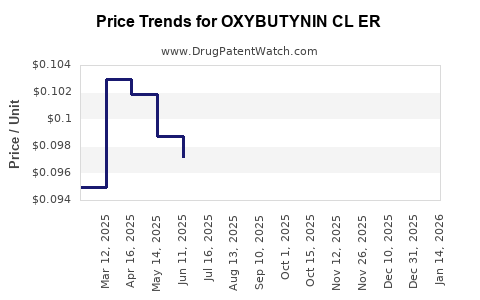
Average Pharmacy Cost for OXYBUTYNIN CL ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OXYBUTYNIN CL ER 10 MG TABLET | 27241-0156-08 | 0.10696 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| OXYBUTYNIN CL ER 10 MG TABLET | 50268-0628-11 | 0.10696 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| OXYBUTYNIN CL ER 10 MG TABLET | 27241-0156-04 | 0.10696 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| OXYBUTYNIN CL ER 10 MG TABLET | 50268-0628-15 | 0.10696 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| OXYBUTYNIN CL ER 10 MG TABLET | 16729-0318-01 | 0.10696 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| OXYBUTYNIN CL ER 5 MG TABLET | 72888-0030-05 | 0.09281 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Oxybutynin CL ER
Introduction
Oxybutynin Cl ER (extended-release) is a blockbuster pharmaceutical used primarily for the management of overactive bladder (OAB). As a first-line treatment, it blocks muscarinic receptors in the bladder, reducing incontinence and urinary urgency. With the global rise of OAB and increasing aging populations, the drug's market remains robust. This analysis explores current market dynamics, competitive landscape, pricing strategies, and future price projections to guide stakeholders and investors.
Market Overview
Global Market Size and Growth
The demand for oxybutynin extends across North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, regions witnessing amplified prevalence of OAB, driven by aging demographics, lifestyle factors, and increased awareness. The global overactive bladder therapeutics market was valued at approximately USD 5.4 billion in 2022, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.3% projected through 2030 [1].
Oxybutynin ER forms a significant segment of this market, comprising roughly 30-35% of the total OAB pharmacotherapy, mostly favored due to its once-daily dosing and improved tolerability over immediate-release forms.
Key Drivers
-
Aging Population: The global population aged 65+ is expanding, fostering higher OAB prevalence. Approximately 17% of individuals over 65 report symptoms [2].
-
Product Advancements: Development of enhanced formulations like oxybutynin ER, which feature sustained release and fewer side effects, bolsters market acceptance.
-
Healthcare Awareness: Increased awareness and destigmatization encourage treatment initiation, expanding market penetration.
Challenges
-
Generic Competition: The patent expiry for branded oxybutynin ER formulations, such as Ditropan XL, has led to increased generic competition, exerting downward pressure on prices.
-
Pricing and Insurance Dynamics: Variability in reimbursement policies and patient copay burdens influence consumer uptake.
-
Alternative Therapies: The rise of non-pharmacologic treatments and newer drugs (e.g., mirabegron) influence market share dynamics.
Competitive Landscape
Major Players
-
Watson Pharmaceuticals (Actavis/Teva): Leader in generics, accounting for over 60% of oxybutynin ER sales worldwide due to extensive manufacturing capacity.
-
Pfizer: Historically marketed Ditropan XL, with ongoing pipeline developments.
-
Allergan (AbbVie): Offers competing formulations; however, focused more on other OAB drugs.
Patent and Regulatory Environment
The original patent for oxybutynin ER expired in key markets (e.g., US in 2014), catalyzing generic entry [3]. Subsequent patent cliffs for formulations drive price adjustments and market shifts towards generics, which typically retail at 50-70% lower prices than branded counterparts.
Pricing Analysis
Current Pricing Trends
-
Branded Oxybutynin ER (e.g., Ditropan XL): Average retail price of a 30-day supply ranges from USD 300-350 in the US.
-
Generics: Prices range from USD 50-100 for the same duration, representing substantial savings for consumers.
-
Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs) and insurance plans significantly influence net prices through rebates and negotiations, often reducing patient out-of-pocket contributions.
Factors Influencing Price
-
Manufacturing Costs: Generics benefit from lower R&D and regulatory costs, translating into lower prices.
-
Market Competition: Higher entry of generics causes price erosion, further accelerated by strategic bulk manufacturing.
-
Reimbursement Policies: Strict formulary inclusion criteria and tiering modify inpatient and outpatient costs.
Future Price Projections
Near-Term Outlook (2023-2025)
-
Price Stabilization: With intense generic competition, retail prices for oxybutynin ER are expected to decline further by 10-15% annually in mature markets like North America and Europe.
-
Reimbursement Influence: Payer negotiations will continue to suppress net prices, favoring generics over branded products.
Long-Term Outlook (2026-2030)
-
Market Maturation: Price declines may plateau as the market reaches a saturation point for generics, but new formulations offering improved delivery or reduced side effects could command premium pricing.
-
Emergence of Biosimilars and Alternatives: Although biosimilars are not applicable to oxybutynin, newer drugs like mirabegron might influence market share and pricing dynamics.
-
Regional Variations: Emerging markets may see slower price declines due to less aggressive generic penetration and slower regulatory changes.
Factors Driving Price Trends
-
Regulatory Policies: Stricter price controls and reference pricing in countries like Germany and France could further downscale prices.
-
Major Payer Strategies: Larger insurers leveraging formulary management will continue to favor lowest-cost generics, limiting premium price opportunities.
-
Innovation Incentives: Companies investing in extended-release or combination formulations could justify higher prices if significant clinical benefits or improved adherence are demonstrated.
Implications for Stakeholders
-
Manufacturers: Focus on cost-efficient manufacturing and strategic marketing of value-added formulations to sustain margins.
-
Healthcare Providers: Preference might shift toward generics unless new formulations with clear clinical advantages are introduced.
-
Patients and Payers: Cost containment policies will favor generic utilization, incentivizing pharmaceutical companies to optimize pricing strategies.
-
Investors: Expect continued price erosion in mature markets with growth potential in emerging regions if price controls remain stringent.
Key Takeaways
-
Market Growth Continues: Driven by demographic shifts and increased awareness, the oxybutynin ER market maintains robust growth, despite challenges posed by generic competition.
-
Price Declines Are Inevitable: Generic entry has already reduced prices significantly, with further declines expected in the short to medium term.
-
Pricing Is Region-Dependent: North America and Europe will experience steeper price declines, whereas emerging markets may sustain relatively higher prices.
-
Innovation Is Paramount: The future profitability hinges on the development of formulations with tangible clinical benefits that justify higher prices.
-
Regulatory Environment Shapes Pricing: Policies fostering price controls and reimbursement reforms will influence the trajectory of product pricing.
FAQs
1. How has patent expiration impacted oxybutynin ER prices?
Patent expiration in key markets has led to a surge of generic entries, significantly reducing prices and margins for branded formulations.
2. What factors could reverse or slow down price declines?
Introduction of innovative formulations with improved efficacy or tolerability, or regulatory changes favoring branded products, could stabilize or increase prices.
3. Are biosimilars relevant for oxybutynin ER?
No, as oxybutynin is a small-molecule drug, biosimilar development is not applicable; however, new chemical entities (NCEs) in the OAB space may influence the market.
4. How do regional policies influence pricing?
Countries with strict price controls or reference pricing tend to suppress prices more aggressively than those with free-market mechanisms.
5. What are the outlooks for branded oxybutynin ER in the coming years?
While branded prices will decline due to generics, niche branded formulations with unique benefits could maintain premium pricing under specific patient segments.
References
- Market Research Future, "Overactive Bladder Therapeutics Market Outlook," 2022.
- Britannica, "Overactive Bladder," 2023.
- U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, "Patent Expiry Dates," 2014.
- IQVIA, "Pharmaceutical Market Insights," 2022.
- WHO Articles on Aging and OAB prevalence, 2021.
More… ↓
