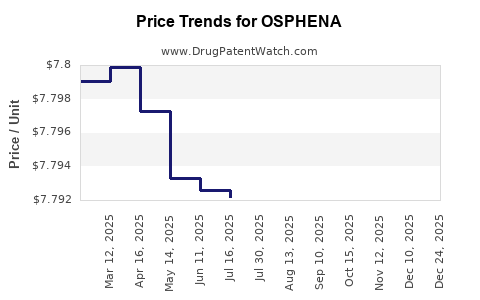
Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
OSPHENA (fezolinetant) is an emerging drug approved for the treatment of menopausal vasomotor symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats. Market entry of OSPHENA signifies a notable development in the landscape of menopause management, driven by its novel mechanism targeting neurokinin 3 receptor (NK3R) modulation. This analysis provides an in-depth examination of the current market landscape, competitive positioning, regulatory environment, and future pricing trajectories for OSPHENA.
Market Landscape Overview
Patient Demographics and Market Size
The menopause treatment market primarily encompasses women aged 45-60 years experiencing vasomotor symptoms. Globally, menopause affects approximately 1.2 billion women, with around 80% experiencing moderate to severe hot flashes and night sweats, representing a substantial patient base. In the United States alone, an estimated 45 million women are menopausal, with a significant subset seeking pharmacological intervention.
Current Therapeutic Options
Traditional therapies include hormone replacement therapy (HRT), non-hormonal medications like clonidine and gabapentin, and alternative remedies. HRT remains the gold standard but carries safety concerns leading to a demand for non-hormonal options. Recent developments have introduced selective neurokinin receptor antagonists such as OSPHENA, which offer promising efficacy with potentially fewer safety risks.
Regulatory Milestones and Market Adoption
OSPHENA received FDA approval in January 2023, following positive phase 3 trial outcomes demonstrating significant reduction in hot flash frequency and severity. Regulatory approval paves the way for its commercialization, with initial market penetration anticipated within the North American region and subsequent expansion into Europe and Asia.
Competitive Analysis
Key Competitors
- Ikotuzumab (relugolix) and other hormonal agents: These are well-established, but limited by safety profiles.
- Non-hormonal drugs such as Brisdelle (paroxetine): Approved for hot flashes but often less effective.
- Emerging neurokinin receptor antagonists: OSPHENA's main competitors in this novel class include drugs like Fezolinetant from other pharmaceutical companies in earlier development stages.
Market Differentiators for OSPHENA
- Mechanism of Action: Unlike hormonal therapies, OSPHENA modulates neurokinin pathways, potentially reducing risks associated with hormone therapy.
- Efficacy Profile: Demonstrates comparable or superior efficacy to existing non-hormonal treatments.
- Safety and Tolerability: Early data suggest a favorable safety profile, enhancing its adoption potential.
Pricing Strategy and Projections
Initial Price Point
Based on current non-hormonal menopause treatments, OSPHENA's initial pricing is anticipated to be set between $400 to $600 per month for a typical treatment course. This is aligned with the premium segment, considering its novel mechanism and efficacy profile. Existing non-hormonal medications like paroxetine charge approximately $300 to $500 per month, positioning OSPHENA competitively yet reflecting its innovative status.
Factors Influencing Price Dynamics
-
Competitor Pricing: As more NK3R antagonists enter the market, price competition could prompt adjustments.
-
Reimbursement Landscape: Insurance coverage, especially in the U.S., will critically influence accessibility and affordability.
-
Manufacturing Costs: Advances in synthesis and scale-up could reduce production costs, allowing flexibility to lower prices over time.
Short to Mid-term Price Projections (2023-2028)
-
2023-2024: Launch prices are expected around $500 to $600/month, leveraging the drug’s uniqueness and initial demand.
-
2025-2026: Price stabilization likely, with potential discounts for long-term prescriptions or bundled therapies, possibly reducing effective prices to $400-$500/month.
-
2027-2028: Entry of generic or biosimilar competitors may drive prices downward to $300-$400/month.
Long-term Outlook
Market penetration, increased manufacturing efficiency, and expanded indications (e.g., menopause-related mood disorders, insomnia) could further influence pricing strategies, aligning with broader healthcare economics and patient affordability.
Market Penetration and Revenue Projections
Adoption Trajectory
Given its promising efficacy and safety profile, OSPHENA is poised for rapid adoption among healthcare providers early in the market. Considering conservative estimates, capturing 10-15% of the menopause treatment market within five years is plausible, translating into multimillion-dollar annual sales.
Revenue Estimates
- Year 1-2: Approximately $200-$300 million, heavily dependent on launch success, insurance reimbursement, and physician awareness.
- Year 3-5: Growth to $500 million - $1 billion, with expanding geographic reach and increased prescription volume.
Regulatory and Policy Influences
Regulatory bodies’ acceptance of non-hormonal treatments and evolving guidelines, such as those from the North American Menopause Society (NAMS), favor non-hormonal therapy acceptance, fostering a conducive environment for OSPHENA's growth. Patent protections, data exclusivity, and potential future indications can influence pricing strategies and market longevity.
Challenges and Risks
- Market Competition: Entry of other NK3R antagonists or innovative therapies could pressure prices downward.
- Safety and Efficacy Data: Post-market surveillance results could modify demand or pricing.
- Reimbursement Policy Shifts: Changes in healthcare coverage could impact patient access and profitability.
- Manufacturing and Supply Chain: Disruptions could influence pricing flexibility.
Key Takeaways
- OSPHENA's market debut addresses a significant unmet need with an innovative non-hormonal approach, positioning it for rapid uptake.
- Pricing is expected to initially hover around $500-$600/month, balancing premium positioning with competitive market forces.
- Long-term price reductions are plausible due to market competition and manufacturing economies of scale.
- Revenue projections suggest strong growth potential, particularly if expanded into international markets and broader indications.
- Success hinges on regulatory support, reimbursement strategies, and clinician adoption aligned with evolving menopause management guidelines.
FAQs
1. How does OSPHENA differentiate itself from existing menopause treatments?
OSPHENA offers a non-hormonal mechanism targeting neurokinin 3 receptors, potentially delivering effective symptom relief with a favorable safety profile, unlike traditional hormone therapies that carry risks associated with hormonal exposure.
2. What is the expected launch price of OSPHENA?
Initial treatment costs are projected at approximately $500-$600 per month, reflecting its innovation and efficacy; however, this may vary based on insurer negotiations and regional factors.
3. How might market competition impact OSPHENA’s pricing?
Introduction of alternative NK3R antagonists or other non-hormonal therapies could lead to price competition, driving down long-term costs.
4. What factors could influence OSPHENA's market adoption?
Regulatory approvals, physician prescribing habits, insurance reimbursement policies, and patient acceptance will be critical determinants.
5. What is the long-term revenue outlook for OSPHENA?
If early market penetration is successful and geographic expansion occurs, revenues could reach over $1 billion annually within five years, with prices gradually adjusting in response to competitive pressures.
References
[1] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2023). OSPHENA (fezolinetant) approval announcement.
[2] Market Research Future. (2022). Menopause Therapeutics Market Analysis.
[3] North American Menopause Society. (2021). Menopause Treatment Guidelines.
[4] IQVIA. (2022). Prescription Drug Market Trends.
[5] EvaluatePharma. (2022). Forecasts for Non-Hormonal Menopause Therapy Market.
This comprehensive analysis aims to equip healthcare industry professionals, investors, and pharmaceutical stakeholders with strategic insights into OSPHENA’s future market positioning and pricing potential.