Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for NOVOLIN N
✉ Email this page to a colleague
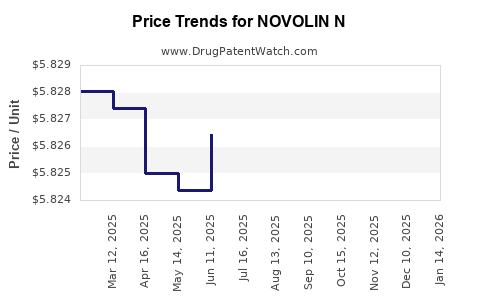
Average Pharmacy Cost for NOVOLIN N
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOVOLIN N 100 UNIT/ML FLEXPEN | 00169-3004-15 | 5.82947 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| NOVOLIN N 100 UNIT/ML VIAL | 00169-1834-11 | 4.62564 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| NOVOLIN N 100 UNIT/ML FLEXPEN | 00169-3004-15 | 5.82671 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| NOVOLIN N 100 UNIT/ML VIAL | 00169-1834-11 | 4.62768 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| NOVOLIN N 100 UNIT/ML FLEXPEN | 00169-3004-15 | 5.82655 | ML | 2025-10-22 |
| NOVOLIN N 100 UNIT/ML VIAL | 00169-1834-11 | 4.62955 | ML | 2025-10-22 |
| NOVOLIN N 100 UNIT/ML FLEXPEN | 00169-3004-15 | 5.82557 | ML | 2025-09-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for NOVOLIN N
Introduction
NOVOLIN N (insulin isophane suspension) is a long-acting insulin marketed primarily for the management of diabetes mellitus. As a biosimilar or generic insulin product, its market dynamics are influenced by factors including regulatory approvals, patent statuses, competitive landscape, technological innovations, and economic considerations. This analysis explores current market conditions, competitive positioning, regulatory environment, global demand, and future price trajectories for NOVOLIN N.
Market Landscape and Key Drivers
Diabetes Epidemic and Insulin Market Growth
The global prevalence of diabetes has surged, with the International Diabetes Federation estimating 537 million adults affected in 2021, projected to rise to 643 million by 2030 [1]. The increasing burden of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes propels global insulin demand, underpinning steady growth in insulin markets.
Role of Biosimilar Insulins
Biosimilar insulins, including NOVOLIN N, have gained prominence as cost-effective alternatives to originator biologics. Regulatory pathways in regions like the U.S., EU, and Asia have facilitated biosimilar approval, resulting in increased market access and competitive pressures. Cost reductions stimulated by biosimilars have expanded patient access, influencing demand dynamics.
Patent Expiry and Market Entry
NOVOLIN N, marketed by Sanofi as a biosimilar or via licensing agreements in some regions, has faced patent expirations and regulatory approvals in various jurisdictions, enabling generic competition. The availability of biosimilars reduces prices and heightens market competition, especially in price-sensitive markets.
Competitive Environment
Major Competitors
The insulin market is dominated by key players including Novo Nordisk (with products like Tresiba and Basaglar), Eli Lilly (Basaglar, Humalog), and Sanofi (Lantus, Toujeo). Biosimilar insulins by companies such as Biocon, Wockhardt, and Momenta Pharmaceuticals also operate in this space [2].
Market Penetration and Brand Preference
Although originator brands maintain high market share, biosimilars like NOVOLIN N are gaining traction due to pricing and expanding healthcare provider acceptance. Regional variations influence brand loyalty, reimbursement policies, and prescribing behaviors.
Regulatory Environment
Regulatory agencies, including the FDA, EMA, and health authorities in emerging markets, have established frameworks for biosimilar approval, emphasizing biosimilarity, safety, and efficacy. Such regulatory clarity accelerates market entry and influences pricing strategies.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Price Trends
Insulin prices have generally trended downward in markets with robust biosimilar competition. In the U.S., the introduction of biosimilars and increased competition contributed to an approximate 16% decrease in insulin prices between 2019 and 2021 [3].
Globally, price reductions vary by region. The UK’s NHS has seen significant savings due to biosimilar adoption, with some biosimilars priced 20-30% below originator brands [4].
Future Price Projections
-
North America: The availability of multiple biosimilars is expected to continue driving prices downward, with projections indicating an average price decrease of 10-15% annually over the next five years, contingent on regulatory approvals and market penetration.
-
Europe: Similar trends are anticipated, with potential stabilization as biosimilar market share reaches saturation [5].
-
Emerging Markets: Price reductions may be less aggressive due to market fragmentation, reimbursement barriers, and limited biosimilar penetration, but overall, biosimilar entry is expected to exert downward pressure.
Factors Influencing Price Trajectory
- Regulatory approvals: Expansion into new markets and accelerated approvals enhance competition, reducing prices.
- Reimbursement policies: Favorable reimbursement promotes biosimilar adoption, pressuring prices.
- Manufacturing costs: Advances in biotechnology decrease production costs, fostering further price reductions.
- Patient and provider acceptance: Growing trust in biosimilars accelerates uptake, influencing market prices.
- Patent landscape: Ongoing patent litigations and expirations may unlock new market segments, affecting pricing.
Strategic Considerations
Market players aiming to position NOVOLIN N effectively should monitor regulatory developments, payer policies, and competitor strategies. Emphasizing cost-effectiveness and demonstrating bioequivalence can support favorable reimbursement and wider market access.
Key Price Projection Summary
| Region | Price Trend (Next 5 Years) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 10-15% annual decrease | Biosimilar competition, healthcare cost pressures |
| Europe | Stabilization or moderate decline | Regulatory approval, market saturation |
| Emerging Markets | Variable, modest declines | Market fragmentation, reimbursement challenges |
Conclusion
NOVOLIN N is positioned amid a robust, growing insulin market driven by rising diabetes prevalence and increased biosimilar acceptance. While prices have declined historically, future projections suggest continued downward trends, particularly in competitive regions with multiple biosimilars. Market dynamics will hinge on regulatory environments, reimbursement policies, and the pace of biosimilar adoption.
Key Takeaways
- The global insulin market is expanding, with biosimilar targets like NOVOLIN N playing an integral role in cost containment strategies.
- Price reductions are expected to persist, driven by biosimilar competition and technological advancements in manufacturing.
- Regulatory pathways and payer policies significantly influence regional pricing trajectories and market access.
- Market saturation and acceptance levels will moderate price declines over time.
- Strategic positioning focusing on bioequivalence, safety, and cost-efficiency will enable stakeholders to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
FAQs
1. How does the biosimilar status of NOVOLIN N impact its market price?
Biosimilar status enables NOVOLIN N to compete with originator insulins, generally resulting in lower prices due to increased competition and cost-based pricing strategies, especially in regions with favorable regulatory frameworks.
2. What factors could hinder price declines for NOVOLIN N?
Limited market penetration, regulatory barriers, supply chain constraints, and slow adoption by healthcare providers can limit price reductions, maintaining higher prices especially in emerging markets.
3. How does regional regulatory approval affect NOVOLIN N’s pricing?
Regulatory approvals facilitate market access, impacting supply and competition levels. Faster approvals may lead to earlier market entry and strengthening of price competition, thereby reducing prices.
4. What are the main drivers of demand for NOVOLIN N in the coming years?
Increasing global diabetes prevalence, acceptance of biosimilar insulins, healthcare cost containment policies, and expanding healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets are primary drivers.
5. How might technological innovations influence NOVOLIN N’s future pricing?
Advancements such as improved insulin delivery devices, digital health integrations, and biosimilar manufacturing efficiencies will likely reduce production costs and support further price declines.
Sources
- International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th Edition.
- IQVIA. (2022). The Global Biosimilar Market Report.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. (2022). Drug Price Trends in Insulin Market.
- NHS Digital. (2021). Biosimilar Insulin Adoption and Cost Savings.
- European Medicines Agency. (2022). Biosimilar Medicines in Europe: Market Impact.
More… ↓
