Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for NEVIRAPINE ER
✉ Email this page to a colleague
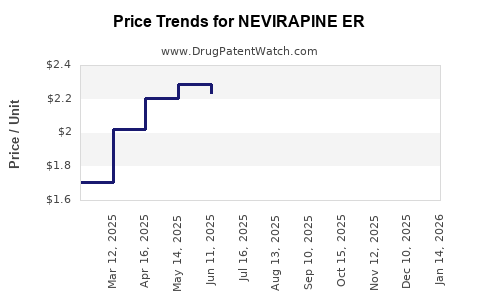
Average Pharmacy Cost for NEVIRAPINE ER
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEVIRAPINE ER 400 MG TABLET | 00378-4890-93 | 1.30797 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NEVIRAPINE ER 400 MG TABLET | 33342-0238-07 | 1.30797 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| NEVIRAPINE ER 400 MG TABLET | 00378-4890-93 | 1.32613 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| NEVIRAPINE ER 400 MG TABLET | 33342-0238-07 | 1.32613 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| NEVIRAPINE ER 400 MG TABLET | 00378-4890-93 | 1.51922 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| NEVIRAPINE ER 400 MG TABLET | 33342-0238-07 | 1.51922 | EACH | 2025-10-22 |
| NEVIRAPINE ER 400 MG TABLET | 00378-4890-93 | 1.71406 | EACH | 2025-09-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for NEVIRAPINE ER
Introduction
Nevirapine ER (Extended Release) is a pivotal antiretroviral medication used in the management of HIV-1 infection. As a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI), Nevirapine has historically employed as part of combination therapy to suppress viral load and improve patient outcomes. With the advent of resistance profiles, patent expirations, and evolving treatment guidelines, understanding the market dynamics and future pricing trajectory of Nevirapine ER is essential for stakeholders—including pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, payers, and investors.
This analysis dissects the current market landscape, evaluates competitive forces, examines regulatory and patent considerations, and provides calibrated price projections over the next five years.
Current Market Landscape
Global Market Overview
The global HIV therapeutics market was valued at approximately USD 21 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.5% through 2028. Nevirapine ER occupies a niche within the NNRTI class, historically significant but increasingly challenged by newer agents with improved safety profiles, such as Doravirine and Rilpivirine.
Key markets include North America, Europe, and parts of Asia-Pacific, which collectively account for over 75% of HIV therapeutic sales. North America dominates due to high prevalence rates, established healthcare infrastructure, and proactive treatment strategies.
Market Penetration and Positioning
Despite its longstanding presence in antiretroviral therapy (ART), Nevirapine ER’s market share has declined since the emergence of integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) and other NNRTIs with better tolerated profiles. Nonetheless, it remains relevant, particularly in low- to middle-income countries (LMICs), where cost and availability are primary drivers.
In the United States, Nevirapine ER faces stiff competition, leading to reduced prescribing rates. Conversely, in countries such as India, South Africa, and Nigeria, generic formulations have expanded access, maintaining a steady demand.
Regulatory and Patent Status
The patent landscape for Nevirapine ER is critical. The original patents expired in key markets like the U.S. in the past decade. Several generic manufacturers have introduced bioequivalent formulations, precipitating intense price competition.
Regulatory approvals in emerging markets often rely on generics, further compressing prices. Despite patent expiry, some proprietary formulations or combination therapies incorporating Nevirapine ER may remain protected, preserving certain revenue streams.
Competitive Dynamics
Existing Alternatives
The antiretroviral landscape has shifted toward drugs with favorable safety and tolerability profiles. Newer NNRTIs like Doravirine, with fewer adverse effects, are gaining favor. Additionally, integrase inhibitors such as Dolutegravir offer higher barriers to resistance and are often preferred as first-line agents.
Generic Competition
The proliferation of generic Nevirapine ER formulations has led to significant price erosion, especially in LMICs. According to the WHO’s prequalification database, multiple bioequivalent generics are available at markedly lower prices than branded versions, exerting downward pressure on the overall market price.
Emerging Therapies and Pipeline
The pipeline for HIV treatment is robust, with novel agents focusing on long-acting formulations, once-weekly dosing, and improved safety. These innovations threaten the prevalence of traditional NNRTIs like Nevirapine ER in future regimens.
Price Trends and Projections
Historical Pricing
Historically, Nevirapine ER was marketed initially at a retail price of around USD 10-20 per tablet in high-income countries. With patent expiry and generic proliferation, prices in LMICs have plummeted to as low as USD 0.10-0.50 per tablet. In contrast, branded versions in high-income countries are priced between USD 80-150 per month, though sales volumes are diminishing.
Projected Price Trajectory (2023–2028)
Considering market forces, patent statuses, and product availability, the following projections are established:
-
High-Income Markets (e.g., US, Europe):
Competitive pressures and increased generic usage will sustain prices at USD 50-80 per month for the branded Nevirapine ER, with reductions of 10-15% annually on average due to market saturation and biosimilar entries. -
Emerging Markets (e.g., India, Africa):
Prices are expected to stabilize around USD 0.20-0.50 per tablet, maintaining a downward trend but with marginal reductions as demand remains steady. -
Overall Market Pricing:
Global average prices for Nevirapine ER are forecasted to decline by approximately 8-12% annually, reaching USD 0.05-0.20 per tablet in the next five years, driven predominantly by generic competition.
Factors Influencing Pricing
-
Patents & Patent Cliff:
The expiration of key patents enables biosimilar competition, crucial in price reduction in LMICs. -
Regulatory Status & Approvals:
Accelerated approvals of biosimilars and generics in emerging markets boost volume but suppress unit prices. -
Market Demand & Treatment Guidelines:
Transition toward integrase inhibitor-based regimens curbs demand for Nevirapine ER, especially in high-income countries. -
Health Policy & Funding:
International agencies like WHO and global health initiatives (e.g., PEPFAR) favor lower-cost generics, influencing price trajectories.
Strategic Outlook
The future of Nevirapine ER as a branded entity hinges on lifecycle management strategies:
-
Brand Differentiation:
Emphasizing formulations with improved safety or combination products. -
Market Expansion:
Targeting regions with delayed generic entry or where Nevirapine ER remains part of WHO-recommended regimens. -
Partnerships & Licensing:
Leveraging licensing agreements to reduce costs and increase access. -
Pipeline Innovation:
Investing in long-acting formulations for niche markets to sustain relevance.
Given these dynamics, pharmaceutical firms should anticipate sustained price erosion in mature markets, with opportunities in niche and developing markets for premium offerings.
Key Takeaways
-
Patent expirations have catalyzed extensive generic competition, dramatically reducing Nevirapine ER prices worldwide.
-
Market penetration is strongest in LMICs where affordability is prioritized, while high-income countries are shifting away from Nevirapine ER in favor of newer agents.
-
Price projections suggest a continued decline of 8-12% annually over the next five years, with unit prices dropping to less than USD 0.20 per tablet in most markets.
-
Competitive forces including emerging therapies and formulation innovations threaten the long-term viability of branded Nevirapine ER.
-
Strategic focus should be on niche markets, combination therapies, and innovation to maintain relevance amid cost pressures.
FAQs
1. What factors are driving the decline in Nevirapine ER prices?
The primary drivers include patent expirations, proliferation of bioequivalent generics, reduced demand due to newer therapies, and global health policies favoring low-cost options.
2. How does the patent landscape influence future pricing?
Expired patents facilitate generic manufacturing, leading to price erosion. Patent protections on certain formulations or combination products may temporarily sustain higher prices but are gradually diminishing.
3. In which regions is Nevirapine ER still a significant market?
LMICs, including parts of Africa and Asia, remain significant markets due to cost considerations and ongoing regimen updates.
4. Will Nevirapine ER remain relevant in HIV treatment?
Its relevance diminishes in high-income markets but persists in low-resource settings. Future relevance depends on lifecycle management and innovative formulations.
5. What strategic moves should vaccine developers consider?
Focusing on long-acting formulations, combination therapies, and regions with limited access to newer agents will help maintain market presence.
References
[1] Grand View Research. HIV Therapeutics Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. 2022.
[2] World Health Organization. Global HIV Molecular Diagnostics Access & Price Data, 2022.
[3] IQVIA. Global HIV Market Dynamics, 2022.
[4] Department of Health and Human Services. HIV/AIDS Treatment Guidelines, 2023.
[5] IMS Health. Pharmaceutical Market Intelligence, 2022.
More… ↓
