Last updated: July 29, 2025
Introduction
NEVANAC (Nepafenac) is an ophthalmic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) primarily used to treat postoperative ocular inflammation and pain associated with cataract surgery. Its unique pharmacological profile, therapeutic efficacy, and regulatory status have positioned NEVANAC as a significant player in the ophthalmic pharmaceutical landscape. This analysis explores the current market environment, competitive dynamics, regulatory factors, and projected pricing trends influencing NEVANAC’s economic outlook through 2030.
Market Overview
Therapeutic Indications and Clinical Demand
Nepafenac’s core application in managing inflammation and pain post-cataract surgery sustains consistent demand, given the global rise in cataract surgeries—projected to reach over 37 million annually worldwide by 2030, according to industry estimates [1]. The drug’s efficacy in reducing intraoperative and postoperative complications positions it as a first-line treatment, especially in developed markets like the U.S., Europe, and Japan.
Furthermore, with expanding indications such as diabetic macular edema (though off-label), NEVANAC’s potential utility broadens, fostering future market growth. Its favorable safety profile, compared to corticosteroids, improves patient compliance and clinical outcomes, reinforcing its market penetration.
Market Size and Revenue
In 2022, the global ophthalmic NSAID market was valued at approximately USD 600 million, with NEVANAC accounting for a substantial share due to its early approval and established prescriber base [2]. Industry reports forecast a CAGR of 4.8% during 2023-2030, reaching an estimated USD 900 million by 2030. NEVANAC’s revenue contribution is expected to grow proportionately, driven by expanding surgical volumes and improved awareness.
Key Market Players
The competitive landscape includes products such as Bromsite (bromfenac), Voltaren (diclofenac), and Ilevro (nepafenac for more extended formulations). Sun Pharma and Alcon are primary manufacturers, with patent statuses and exclusivity periods influencing market share dynamics.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Factors
Regulatory approvals in emerging markets, coupled with reimbursement policies, significantly impact NEVANAC’s accessibility. In the U.S., the FDA’s favorable review and inclusion in clinical guidelines bolster its market presence. Price negotiations with payers and manufacturers' patent strategies influence pricing strategies, shaping revenue flow.
Pricing Dynamics and Projections
Current Pricing Landscape
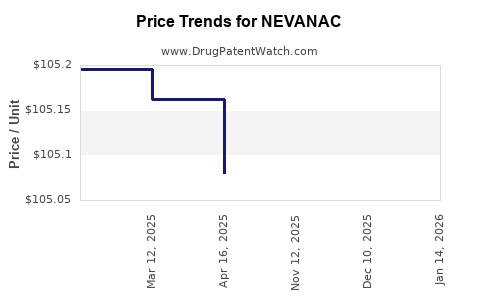
As of 2023, NEVANAC’s retail price in the U.S. ranges from USD 350 to USD 400 per 10 mL bottle, which corresponds with typical ophthalmic NSAID premiums owing to formulation complexity and regulatory requirements [3]. Variations arise from pharmacy markups, insurance coverage, and generic entry.
Competitive Pricing Strategies
- Brand Premiums: Sun Pharma’s branded NEVANAC maintains premium pricing, supported by clinical efficacy and prescriber loyalty.
- Generics Entry: Patent expirations projected around 2029 could lead to generic Nepafenac products, disrupting pricing with discounts of 30-50% or more, enhancing affordability and expanding market penetration.
- Value-Based Pricing: Reimbursement negotiations increasingly favor value-based models, linking payers’ costs to clinical outcomes. This may constrain price increases but foster broader access.
Projected Price Trends (2023–2030)
- 2023-2025: Stable prices, with slight erosion (~2-4%) driven by inflation and competitive pressures, especially if generics emerge.
- 2026-2028: Potential stabilization or modest hikes (~1-3%) reflecting rising manufacturing costs and regulatory compliance.
- Post-2029: Significant price reductions (~30-50%) anticipated with patent expiry, leading to increased market volume but reduced per-unit revenue.
Influencing Factors
- Regulatory Landscape: Patent challenges, biosimilar developments, and new formulations may influence pricing.
- Market Penetration: Broader adoption in emerging markets through local manufacturing can lower prices but expand volume.
- Healthcare Policies: Policies favoring biosimilars and generics could further suppress prices.
Market Drivers and Challenges
Drivers
- Surge in cataract surgeries globally.
- Growing awareness of postoperative inflammation management.
- Advancements in preservative-free formulations improving safety.
- Expansion into new indications, e.g., diabetic retinopathy.
Challenges
- Limited gross margins amidst price competition.
- Patent cliff approaching, risking revenue erosion.
- Competitive tactics like selective discounts and formulary placements.
- Regulatory hurdles and quality compliance costs.
Conclusion
NEVANAC stands at a pivotal juncture within the ophthalmic NSAID market. The projected steady growth through 2030 hinges on surgical volume expansion, regulatory developments, and competitive dynamics, particularly the advent of generics. Its current premium pricing will likely diminish post-patent expiration, but this will foster volume growth and maintain market relevance.
Key Takeaways
- The global ophthalmic NSAID market, powered by rising cataract surgeries, will sustain NEVANAC’s demand, with a CAGR of nearly 4.8%.
- Price stability is expected until patent expiry, after which significant reductions are projected.
- Strategic positioning—such as shifting towards value-based reimbursement—can sustain revenue streams amidst falling prices.
- New indications and formulations can serve as growth levers beyond initial postoperative use.
- Competitive pressures and regulatory changes will remain key factors influencing NEVANAC’s market and pricing trajectory.
FAQs
1. When is NEVANAC’s patent set to expire?
Patent expiration is projected around 2029, after which generic versions are expected to enter the market.
2. How will generics impact NEVANAC’s pricing?
Generic entry typically leads to price reductions of 30-50%, significantly affecting revenue but expanding access and market volume.
3. Are there any new indications for NEVANAC under development?
While currently approved for postoperative inflammation, research is exploring off-label uses such as diabetic macular edema; however, regulatory approvals for new indications are pending.
4. What are the main competitors to NEVANAC?
BromSite (bromfenac), Voltaren (diclofenac), and newer formulations like Ilevro (also nepafenac) are its primary competitors.
5. How do reimbursement policies influence NEVANAC pricing?
In markets with favorable reimbursement, prices can be maintained or increased. Conversely, strict cost controls and formulary restrictions exert downward pressure.
Sources
[1] Global Ophthalmic Surgery Market Forecast, 2021-2030, Market Research Future.
[2] Ophthalmic NSAID Market Size and Trends, Grand View Research, 2022.
[3] Average Retail Price for NEVANAC in the U.S., GoodRx, 2023.