Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Neomycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, is primarily used to treat bacterial infections, notably in gastrointestinal decontamination, ocular infections, and as an ingredient in certain topical formulations. Given its longstanding presence in the healthcare landscape, understanding the current market dynamics and future price trajectories of neomycin is essential for pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and investors aiming to navigate this segment effectively.
Market Overview
Global Demand and Usage Trends
The global demand for neomycin remains steady, driven primarily by its use in ophthalmology, dermatology, and gastrointestinal applications. Market reports reveal that while newer antibiotics have emerged, neomycin retains a niche due to its cost-effectiveness and established efficacy profile. The drug’s utilization is closely linked to infection rates, healthcare infrastructure, and regulatory approvals across markets.
Regional Market Dynamics
- North America: Extensive healthcare infrastructure and widespread use in ophthalmic preparations sustain high demand. Regulatory controls, especially concerning ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity risks, influence formulations and prescribing habits.
- Europe: Similar trends as North America, with a focus on topical formulations. Stringent regulations necessitate precise quality standards.
- Asia-Pacific: Rapidly expanding healthcare systems and a high burden of infectious diseases bolster demand. Cost considerations favor generic formulations.
- Emerging Markets: Increasing access to essential medicines further propels demand, although supply chain and regulatory hurdles may influence market penetration.
Market Drivers
- Ageing Population and Rising Infection Rates: Older populations are more susceptible to bacterial infections that require antibiotic intervention, boosting demand.
- Expanding Ophthalmic and Topical Uses: The growth of eye care and dermatology markets increases utilization.
- Cost-Effectiveness of Generic Neomycin: The availability of affordable generic options sustains its popularity, especially in price-sensitive markets.
- Increasing Healthcare Infrastructure in Developing Countries: Enhanced access encourages broader use of established antibiotics.
Market Restraints and Challenges
- Toxicity Concerns: Neomycin's potential ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity restrict chronic or systemic use, leading to cautious prescribing.
- Regulatory Limitations: Stricter regulations and safety warnings, especially in developed countries, can limit market expansion.
- Competition: Replacement by broader-spectrum or newer antibiotics with improved safety profiles reduces reliance on neomycin.
- Antimicrobial Stewardship Initiatives: Drive towards minimizing antibiotic use to combat resistance may curtail demand for older antibiotics like neomycin.
Pricing Landscape
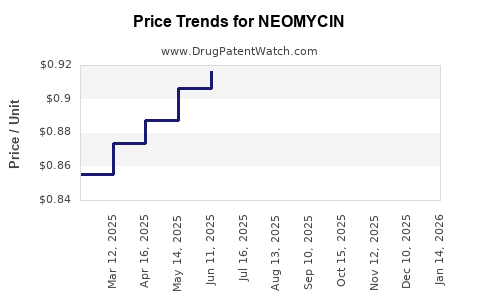
Current Pricing Dynamics
Neomycin's pricing varies significantly based on formulation, concentration, source, and geographic location. Generic forms dominate in price-sensitive markets, with wholesale prices often substantially lower than branded equivalents. In developed nations, government tenders and reimbursement policies influence retail prices.
Factors Influencing Pricing
- Regulatory Standards: Compliance costs impact manufacturing expenses and, consequently, pricing.
- Formulation Type: Topical formulations (ointments, creams) are generally less expensive than injectable forms.
- Market Competition: A higher number of suppliers suppresses prices, boosting affordability.
- Supply Chain Constraints: Raw material costs, especially for specialized amino sugars, impact the final price.
- Patent Status: As a longstanding generic drug, neomycin faces little to no patent restrictions, maintaining competitiveness.
Forecasting Price Trends
Near-term Outlook (Next 3-5 years)
- Stability or Slight Decline in Price: Due to intense generic competition and increased manufacturing efficiencies, prices are likely to remain stable or decline marginally.
- Regional Variations: In high-income markets, prices may stabilize owing to regulatory compliance costs, while developing markets could see further reductions due to increased competition.
Long-term Price Projections (5-10 years)
- Potential Moderation: As newer antibiotics with improved safety profiles gain adoption, demand for neomycin could diminish, exerting downward pressure on prices.
- Impact of Biosimilars or Alternatives: While unlikely for small molecules like neomycin, advancements could influence the availability and pricing landscape.
- Regulatory and Safety Pressures: Heightened safety concerns may restrict usage, impacting volume and pricing power.
Market Opportunities and Strategic Recommendations
- Focus on Biopharmaceutical Formulations: Developing or investing in formulations with improved safety profiles may enable market differentiation.
- Explore New Delivery Systems: Targeted delivery platforms could expand application scopes, particularly in ophthalmic or topical segments.
- Invest in Quality and Compliance: Meeting international standards can open access to regulated markets, commanding premium pricing.
- Monitor Regulatory Changes Closely: Staying ahead of safety warnings and compliance requirements can prevent market disruptions.
Conclusion
Neomycin remains a key component within the broader antibiotic market, especially in topical and ophthalmic formulations. Its mature status and generic prevalence contribute to stable, price-sensitive market conditions, with a gradual trend toward declining prices driven by competition and evolving medical practices. Stakeholders should leverage opportunities in formulation innovation and regulatory compliance to sustain profitability amid a landscape shifting toward newer agents with better safety and efficacy profiles.
Key Takeaways
- Neo mycin's global demand remains stable but faces competitive and safety-related pressures.
- Price projections suggest stability in the short term with gradual declines over the longer term.
- Market growth is primarily driven by demand in ophthalmic, dermatological, and gastrointestinal applications.
- Strategies focusing on formulation innovation and regulatory adherence can create competitive advantages.
- The evolving antimicrobial landscape demands continuous monitoring to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
FAQs
1. What are the primary clinical uses of neomycin today?
Neomycin is predominantly used topically in dermatology, ophthalmology, and gastrointestinal decontamination. Its systemic use is limited due to toxicity risks.
2. How does the safety profile of neomycin influence its market?
Concerns over ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity restrict systemic use, which constrains growth but sustains demand for topical and ophthalmic formulations.
3. What are the main factors impacting neomycin's pricing in the current market?
Factors include competition among generics, formulation types, regulatory compliance costs, and regional economic conditions.
4. Is there potential for new formulations or delivery systems of neomycin?
Yes. Innovations such as sustained-release topical applications or targeted delivery methods might expand its use and improve safety, influencing pricing and market positioning.
5. What future trends could affect the demand for neomycin?
The development of newer antibiotics with enhanced safety profiles, antimicrobial stewardship policies, and regulatory restrictions could reduce demand over time.
Sources
[1] Global Market Insights, “Antibiotics Market Size & Trends,” 2022.
[2] World Health Organization, “Antimicrobial Resistance and Antibiotic Consumption,” 2021.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration, “Guidance on Ototoxic and Nephrotoxic Antibiotics,” 2020.
[4] MarketWatch, “Pharmaceutical Price Trends,” 2022.
[5] Reports and data from leading pharmaceutical market research firms, 2021-2023.