Share This Page
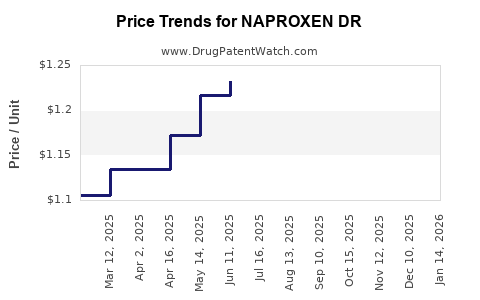
Drug Price Trends for NAPROXEN DR
✉ Email this page to a colleague
Average Pharmacy Cost for NAPROXEN DR
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAPROXEN DR 500 MG TABLET | 90096-0161-01 | 2.08378 | EACH | 2025-12-03 |
| NAPROXEN DR 500 MG TABLET | 42494-0454-10 | 2.08378 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| NAPROXEN DR 375 MG TABLET | 42494-0453-10 | 1.26796 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| NAPROXEN DR 375 MG TABLET | 70954-0925-10 | 1.26796 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for NAPROXEN DR
Introduction
Naproxen DR (Extended Release) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) primarily indicated for the treatment of pain, inflammation, and arthritis. As a high-demand medication in the chronic pain management segment, its market dynamics are influenced by factors such as clinical efficacy, competition, patent status, pricing strategies, and regulatory landscapes. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the current market landscape and forecasts future pricing trends for Naproxen DR.
Market Landscape of NAPROXEN DR
Market Overview
Naproxen, marketed under various brand names, is a well-established NSAID, with Naproxen DR formulations designed to improve patient adherence through once-daily dosing, thus enhancing compliance in chronic conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. The global NSAID market is projected to reach approximately USD 13 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 4% driven by rising prevalence of chronic inflammatory diseases and an aging population [1].
Naproxen DR holds a significant share within this landscape, especially in North America and Europe, where prescription volumes for long-acting NSAID formulations are high. The rise of generic formulations post-patent expiry has intensified competition, pressuring brand premiums.
Regulatory and Patent Environment
Current market dynamics are heavily influenced by patent protections and exclusivity rights. Naproxen's original patents have expired in major markets, leading to an influx of generic options, which significantly impact pricing strategies. The market entry of generics pressures branded Naproxen DR to innovate, often via formulation enhancements or drug delivery patents.
Competitive Landscape
Major competitors include both branded drugmakers and generic manufacturers:
- Brand Name: Aleve® (Bayer), Naprosyn® (Bayer)
- Generic Versions: Multiple manufacturers producing standardized Naproxen, including extended-release versions.
Competition has led to pricing erosion, compelling manufacturers to differentiate through formulation, delivery systems, or added value propositions such as combination therapies.
Price Analysis and Trends
Current Pricing Landscape
The price of Naproxen DR varies considerably by region and patent status:
- United States: The average retail price for a 30-day supply of brand-name Naproxen DR ranges from USD 50 to USD 100, depending on pharmacy and insurance coverage. Generics are priced approximately 70% lower, often around USD 15–25 per month.
- Europe: Prices tend to be lower, with a 30-day supply costing approximately EUR 20–40 in most countries.
The price differential underscores the impact of patent protection and market competition. Brand-name formulations typically command a premium during patent exclusivity, with significant discounts emerging once generics dominate the market.
Pricing Dynamics Post-Patent Expiry
Post-patent expiry, a rapid decline in prices is observed—generics can reduce costs by 60-80%. Anti-trust and market entry strategies also influence pricing; for instance, pay-for-delay deals or patent litigations can temporarily sustain higher prices.
Predicted Pricing Trends
Based on historical data and competitive analysis, the following projections are envisaged:
- Short-term (1–2 years): Prices are expected to remain relatively stable, especially in regions with delayed generic entry or limited competition. Brand-name Naproxen DR could sustain premiums of 20-30% over generics.
- Medium-term (3–5 years): As patent exclusivity diminishes further and more generics penetrate the market, prices are forecasted to decline by an additional 50%, aligning with typical generic price erosion patterns.
- Long-term (>5 years): Price stabilization at low generic levels, potentially around 20-25% of original branded prices, unless innovative delivery systems or combination drugs create new market segments.
Factors Influencing Future Price Projections
- Patent and Regulatory Changes: Patent extensions through new formulations or delivery mechanisms can preserve premium pricing. Conversely, patent expirations accelerate price reductions.
- Market Penetration of Generics: Increased availability and aggressive pricing strategies by generic manufacturers will continue to drive down costs.
- Emergence of Biosimilars and Alternatives: The advent of biosimilar NSAIDs or novel analgesics could further pressurize Naproxen DR prices.
- Insurance and Reimbursement Policies: Favorable coverage for generics will encourage substitution and suppress branded pricing.
- Research and Innovation: Incorporation of nanotechnology or other advanced delivery systems could justify premium pricing due to enhanced efficacy or convenience.
Strategic Recommendations for Stakeholders
- Pharmaceutical Innovators: Invest in formulation patents or unique delivery systems to sustain premium pricing.
- Manufacturers of Generics: Focus on cost-efficient production to capture large market shares fueled by price sensitivity.
- Healthcare Providers: Promote generics where clinically appropriate to optimize patient access and reduce healthcare costs.
- Policy Makers: Monitor patent law enforcement and promote competition to foster affordable medication access.
Key Takeaways
- The global Naproxen DR market is characterized by high initial brand premiums during patent exclusivity, with prices expected to decline significantly post-generic entry.
- In the US, current branded Naproxen DR prices range from USD 50–100 per month, while generics cost around USD 15–25.
- Price erosion trends indicate a potential reduction of 50-70% over 3–5 years, aligning with typical NSAID market patterns.
- Innovations such as new formulations or combination therapies could sustain higher price points, even amidst generic competition.
- Stakeholder strategies should center on patent management, market differentiation, and cost competitiveness to optimize market position.
FAQs
1. How does patent expiry affect the price of Naproxen DR?
Patent expiry typically leads to increased generic competition, which drives prices down. Branded formulations often see a 60-80% reduction in price within a few years of patent expiration.
2. Are there any upcoming patent extensions or formulations that could impact Naproxen DR prices?
While patent extensions through formulation innovations are possible, they are limited and subject to regulatory approval. Such innovations can temporarily preserve premium pricing.
3. How does the pricing of Naproxen DR compare to other NSAIDs?
Naproxen DR’s pricing is generally comparable to other extended-release NSAIDs, though variations depend on manufacturing costs, brand premiums, and country-specific healthcare policies.
4. What influences the adoption rate of generic Naproxen in clinical practice?
Factors include physician prescribing habits, insurance coverage favoring generics, patient affordability, and regulatory approvals.
5. Will emerging therapies threaten Naproxen DR’s market share?
Yes; novel analgesics, biologics, or alternative pain management options could reduce demand. Continuous innovation is vital for maintaining market relevance.
References
[1] MarketWatch. "NSAID Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis," 2022.
[2] IMS Health. "Global NSAID Market Forecast," 2021.
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. "Patent and Exclusivity Information," 2022.
[4] IQVIA. "Prescription Drug Price Trends," 2022.
Disclaimer: This market analysis is for informational purposes and reflects current trends and projections based on available data. Changes in regulatory, competitive, or scientific landscapes may alter market dynamics.
More… ↓
