Last updated: July 27, 2025
Introduction
Methylsergonovine, commonly known as methylergonovine, is a semi-synthetic ergot alkaloid primarily used to manage postpartum hemorrhage and prevent uterine atony. Its unique pharmacological profile, wide clinical application, and recent shifts in manufacturing and patent landscapes make understanding its market dynamics vital for stakeholders. This report offers an in-depth analysis of the current market environment for methylsergonovine, explores price trajectory forecasts, and discusses factors influencing future valuation.
Market Overview
Indications and Clinical Usage
Methylsergonovine is predominantly prescribed to control postpartum bleeding unresponsive to uterotonics and to manage migraine in some contexts (although less common due to side effects). Its role in obstetrics remains significant, especially in developing countries where access to alternative therapies is limited. The drug's efficacy stems from its vasoconstrictive and smooth muscle constriction effects [1].
Current Market Size
The global uterotonic market, which includes methylsergonovine, is projected to reach approximately USD 1.2 billion by 2025, with ergot derivatives constituting a significant share, especially in low-to-middle-income countries. The demand is driven by high birth rates in emerging markets and expanding access to maternal healthcare services [2].
Manufacturing and Supply Chain Dynamics
Major pharmaceutical players, such as Novartis and Boehringer Ingelheim, historically manufactured methylsergonovine. However, patent expirations, regulatory shifts, and manufacturing consolidations have led to increased generic production, impacting prices and availability. Additionally, recent concerns over ergot alkaloid safety profiles have prompted stricter manufacturing standards, potentially affecting supply stability.
Market Drivers and Barriers
Drivers
- Growing Maternal Healthcare Access: Improving healthcare infrastructure in Africa, Asia, and Latin America propels postpartum hemorrhage management needs [3].
- Patent Expiry and Generic Entry: Increased generic competition generally lowers prices but also increases market penetration.
- Regulatory Approvals: Governments and health agencies endorsing methylsergonovine use bolster market confidence.
Barriers
- Safety and Side Effect Profile: Neurovascular and cardiovascular risks limit broader application [4].
- Availability of Alternatives: Cost-effective and safer alternatives like oxytocin and misoprostol are replacing ergot derivatives in several markets.
- Regulatory Restrictions: Some jurisdictions impose strict controls due to toxicity concerns, impacting marketing and sales.
Regulatory Environment & Patent Landscape
The patent landscape for methylsergonovine has largely expired globally, leading to an influx of generics. Regulatory agencies, including the FDA and EMA, have classified ergot alkaloids with black-box warnings for vasoconstriction and contraindications, influencing market access and pricing strategies. Emerging regulations on manufacturing standards aim to mitigate safety issues but may induce temporary supply chain disruptions [5].
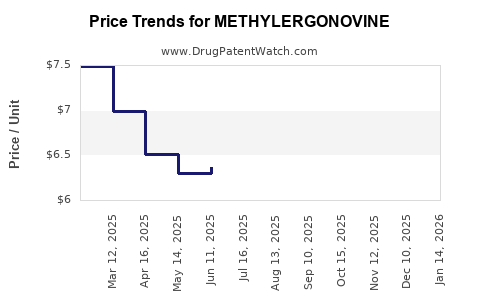
Pricing Trends and Projections
Current Pricing Landscape
- Brand vs. Generic: Branded formulations of methylsergonovine command premium prices; however, generics dominate the market with substantially reduced prices, often 30-50% lower.
- Geographic Variability: Prices in North America and Europe are higher due to regulatory compliance costs, ranging from USD 0.20 to USD 0.50 per unit, compared to USD 0.05 to USD 0.10 in emerging markets.
Pricing Drivers
- Regulatory Costs: Stricter standards increase manufacturing expenses, potentially raising prices temporarily.
- Market Competition: Entry of multiple generics exerts downward pressure.
- Supply Chain Stability: Disruptions—such as shortages caused by manufacturing issues or regulatory crackdowns—can inflate prices temporarily.
Future Price Projections (2023–2030)
- Short-term Outlook (2023–2025): Stabilization followed by modest decreases of 5-10% annually, driven by increased generic penetration and manufacturing efficiencies.
- Medium to Long-term Outlook (2026–2030): Prices may decline further, averaging 10-15% reduction per annum, contingent on the development of safer, more effective alternatives, and regulatory harmonization.
However, certain markets with limited regulatory oversight may see price stabilization or even increases due to supply constraints and demand dynamics.
Market Outlook and Strategic Implications
Regional Market Insights
- Developing Countries: High demand persists due to limited alternatives and ongoing maternal health challenges. Prices remain relatively stable, with some reductions as generics gain favor.
- Developed Countries: Use is declining in favor of safer drugs, exerting downward pressure on prices. Regulatory barriers restrict market expansion.
- Emerging Markets: Rapid adoption and regulatory approvals drive growth, providing opportunities for pricing premiums in localized markets.
Potential for Innovation
New formulations focusing on safety and ease of administration could modify market dynamics, potentially impacting pricing structures by enhancing therapeutic profiles and safety margins.
Key Factors Influencing Price Movement
- Global regulatory changes and safety concerns.
- The pace and scale of generic market penetration.
- Supply chain stability amidst geopolitical and manufacturing considerations.
- Adoption of alternative uterotonics and their influence on demand.
- Developments in drug patent landscape and potential patent extensions or litigation outcomes.
Conclusion
The methylsergonovine market remains vital in obstetric care, especially in regions with limited access to newer therapies. Current pricing is heavily influenced by generic competition, regulatory pressures, and supply chain factors. Forecasts indicate a gradual decline in prices over the next decade, driven by increased competition and manufacturing efficiencies, tempered by safety concerns and market-specific regulatory landscapes. Stakeholders should focus on compliance, safety profile improvements, and strategic positioning within emerging markets to maximize growth potential.
Key Takeaways
- Methylsergonovine’s market sustains strong demand in developing regions, where postpartum hemorrhage remains a leading cause of maternal mortality.
- Generic competition is the dominant pricing driver, leading to a downward trend forecasted at approximately 10-15% annually from 2026.
- Regulatory evolution, especially concerning safety warnings, could temporarily disrupt supply and influence prices.
- Opportunities exist in developing safer, improved formulations to enhance market share and justify premium pricing.
- Companies should monitor regional regulatory landscapes and supply chain stability to optimize market entry and expansion strategies.
FAQs
1. What factors are most influencing methylsergonovine prices today?
Primarily, the entry of generics, regulatory restrictions due to safety concerns, and manufacturing costs are shaping current price levels.
2. Will methylsergonovine remain relevant in obstetric care?
Yes, particularly in low-resource settings, although health authorities increasingly favor safer alternatives like oxytocin and misoprostol.
3. How might safety concerns impact future market potential?
Stricter safety regulations and adverse event reports could restrict use, decreasing demand and impacting prices unless safer formulations are introduced.
4. Are there regional differences in methylsergonovine market strategies?
Yes. Developed markets focus on compliance and safety, leading to premium pricing, whereas emerging markets emphasize cost-effectiveness and accessibility.
5. What are the key opportunities for investment in methylsergonovine?
Developing safer, more tolerable formulations and strengthening market presence in underserved regions offer significant growth prospects.
Sources
[1] World Health Organization. Efficacy and safety profile of ergot alkaloids in postpartum hemorrhage. 2021.
[2] MarketsandMarkets. Uterotonics market forecast. 2022.
[3] WHO Maternal Health Reports. 2020.
[4] FDA. Black-box warning for ergot alkaloids. 2019.
[5] EMA. Regulatory standards for ergot derivatives. 2021.