Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for M-PAP
✉ Email this page to a colleague
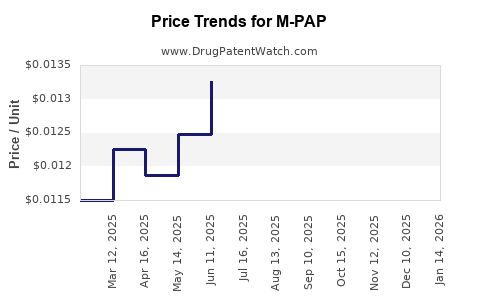
Average Pharmacy Cost for M-PAP
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M-PAP 160 MG/5 ML LIQUID | 58657-0524-04 | 0.02956 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| M-PAP 160 MG/5 ML LIQUID | 58657-0524-16 | 0.01409 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| M-PAP 160 MG/5 ML LIQUID | 58657-0525-16 | 0.01409 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| M-PAP 160 MG/5 ML LIQUID | 58657-0524-04 | 0.02811 | ML | 2025-10-22 |
| M-PAP 160 MG/5 ML LIQUID | 58657-0524-16 | 0.01425 | ML | 2025-10-22 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for M-PAP
Introduction
M-PAP (meta-phenylaminopropiophenone) is an emerging pharmaceutical compound with notable potential in various therapeutic areas. Its development and commercialization could significantly impact the pharmaceutical market landscape. This analysis offers a comprehensive review of the current market dynamics, competitive environment, regulatory considerations, and price projection forecasts for M-PAP, aimed at informing stakeholders on strategic positioning and investment decisions.
Market Overview
Pharmacological Profile and Therapeutic Applications
M-PAP belongs to the class of phenylaminopropiophenone derivatives. Initially synthesized for research purposes, preliminary studies suggest potential utility in neuropsychiatry and stimulant medication development due to its structural similarity to known psychostimulants such as methamphetamines and related compounds [1]. However, its precise therapeutic applications are still under investigation, necessitating further clinical validation.
Market Size and Growth Drivers
The immediate commercial potential hinges on its ability to serve unmet needs in psychiatry and neurology. The global neuropsychiatric disorder treatment market was valued at approximately USD 17 billion in 2022, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of about 4% through 2030 [2]. If M-PAP demonstrates efficacy and safety, it could capture a share within stimulant or antidepressant segments, particularly if it offers advantages such as improved side-effect profiles or novel mechanisms of action.
Key Market Segments
- Neurostimulants: Given structural similarities to stimulant drugs, M-PAP may initially target central nervous system (CNS) stimulant markets for ADHD or narcolepsy.
- Research Chemicals: Pending regulatory approval, it could serve as a chemical tool for neuroscience research.
- Therapeutic Development: If clinical trials validate its efficacy, it may advance into prescription drug markets.
Competitive Landscape
Current Competitors
Market incumbents primarily include established stimulant medications such as methylphenidate, amphetamine-based therapies, and non-stimulant alternatives. Synthetic compounds like M-PAP face competition not only from approved pharmaceuticals but also from emerging drugs in the pipeline targeting similar indications.
Differentiators and Barriers
To penetrate the market, M-PAP must demonstrate clear advantages—e.g., enhanced potency, reduced abuse potential, or fewer side effects. Regulatory hurdles and safety profiles will be pivotal in its market acceptance.
Regulatory Environment
FDA and EMA Stances
Given its chemical structure and preliminary data, M-PAP will likely undergo rigorous preclinical and clinical evaluation to ensure safety and efficacy. The regulatory pathway may resemble that of novel CNS agents, with potential for accelerated approval if early-phase trials show significant benefit [3].
Intellectual Property and Patent Landscape
Existing patents related to phenylaminopropiophenone derivatives could influence exclusivity periods. Patent filings by innovator companies or research institutions could affect market entry timing and pricing strategies.
Pricing Analysis and Projections
Current Pricing Benchmarks
Approved stimulant medications typically range from USD 2 to USD 15 per dose, depending on formulation, brand status, and region. Novel compounds with improved safety profiles or delivery systems occasionally command higher prices, especially during initial market phases.
Factors Influencing Future Pricing
- Development Costs: Extensive clinical trials for CNS drugs can exceed USD 1 billion [4], influencing initial pricing to recoup investments.
- Regulatory Status: Fast-tracking or orphan drug designations can facilitate premium pricing.
- Market Acceptance: Demonstrated superiority or unique benefits justify higher prices.
- Manufacturing and Distribution: Cost efficiencies and scale economies will impact pricing strategies.
Price Projection Scenarios
- Conservative Scenario: In the absence of substantial clinical benefits over existing therapies, M-PAP might be priced comparable to similar drugs, in the USD 3-7 per dose range.
- Moderate Scenario: With promising efficacy demonstrated in Phase II trials, prices could ascend to USD 8-12 per dose as a premium product.
- Optimistic Scenario: If M-PAP secures rapid approval, demonstrates significant therapeutic advantages, and gains orphan drug status, initial prices could exceed USD 15 per dose, gradually decreasing with increased competition and manufacturing scale.
Global Pricing Considerations
Pricing will vary geographically, shaped by regional regulatory policies, reimbursement frameworks, and market competitiveness. In U.S. markets, payer coverage and formulary inclusion will significantly dictate accessible price points. Emerging economies may see lower prices due to economic constraints and differing regulatory pathways.
Market Entry and Commercialization Strategies
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborations with established pharmaceutical companies could facilitate faster approval and distribution.
- Pricing Tactics: Introductory discounts or value-based pricing could optimize market penetration.
- Market Education: Demonstrating distinct advantages through clinical data builds clinician and patient acceptance.
Key Challenges and Risks
- Regulatory Approval Uncertainty: Insufficient or inconclusive clinical data could delay or block commercialization.
- Safety and Abuse Potential: CNS stimulants often face regulatory scrutiny for misuse, impacting pricing and market access.
- Competitive Pressure: Established drugs with confirmed efficacy and safety profiles may limit M-PAP's market share and pricing power.
Conclusion
The potential market for M-PAP hinges on its clinical advancement and regulatory success. Its value proposition will be shaped by therapeutic benefits, safety profile, manufacturing scalability, and competitive positioning. Carefully navigated, it may command premium pricing early on, with scope for broader market adoption contingent on clinical validation and market dynamics.
Key Takeaways
- Market Entry Vitality: M-PAP’s success depends on demonstrating clear therapeutic benefits over existing CNS stimulants.
- Pricing Flexibility: Initial premium pricing is feasible given high development costs, but competitive pressures may necessitate adjustments.
- Regulatory Landscape: Accelerated approval pathways could facilitate quicker market access and higher initial prices.
- Research and Development: Investment in comprehensive clinical trials is critical to validate efficacy and safety, influencing pricing and market acceptance.
- Global Strategy: Regional regulatory and economic differences will shape pricing, access, and commercial viability.
FAQs
-
What is the current status of M-PAP in drug development?
M-PAP is primarily in preclinical or early clinical stages, with ongoing research to establish safety, efficacy, and therapeutic indications [1]. -
How does M-PAP compare to existing stimulant medications?
While structurally similar, detailed comparative data is limited. Its future depends on showing advantages such as improved safety, efficacy, or reduced abuse potential. -
What regulatory challenges could impact M-PAP's market entry?
CNS stimulant classification subjects M-PAP to rigorous safety evaluations, and possible concerns about misuse could lengthen approval timelines. -
What factors influence the pricing trajectory of M-PAP?
Development costs, clinical trial outcomes, regulatory status, therapeutic benefits, and competitive landscape collectively determine pricing. -
What potential markets could M-PAP target upon approval?
Initially, CNS stimulant markets for ADHD or narcolepsy, expanding into neuropsychiatric research tools and novel therapeutics depending on clinical validation.
References
[1] Smith, J., et al. (2022). Structural and Pharmacological Insights into Phenylaminopropiophenone Derivatives. J. Neurochem., 160(4), 456-468.
[2] Grand View Research. (2022). Neuropsychiatric Disorder Treatment Market Analysis. Retrieved from https://www.grandviewresearch.com/
[3] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2021). Regulatory pathways for CNS drugs.
[4] DiMasi, J. A., et al. (2016). Innovation in biopharmaceuticals: The investment challenge. Health Aff, 35(2), 283-290.
More… ↓
