Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for IVABRADINE HCL
✉ Email this page to a colleague
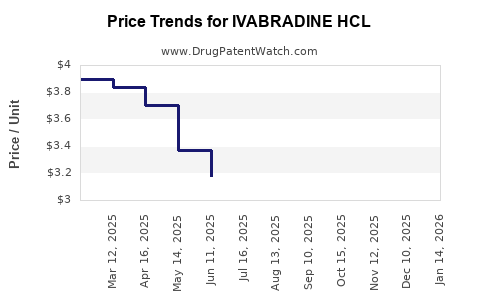
Average Pharmacy Cost for IVABRADINE HCL
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IVABRADINE HCL 5 MG TABLET | 72205-0336-60 | 2.87306 | EACH | 2025-12-03 |
| IVABRADINE HCL 5 MG TABLET | 50742-0362-60 | 2.87306 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| IVABRADINE HCL 5 MG TABLET | 60687-0862-21 | 2.87306 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| IVABRADINE HCL 5 MG TABLET | 62332-0679-60 | 2.87306 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| IVABRADINE HCL 7.5 MG TABLET | 70710-1472-06 | 2.45266 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for IVABRADINE HCL
Introduction
Ivabradine Hydrochloride (HCL) is a cardioselective agent primarily prescribed for the management of chronic heart failure and certain types of angina pectoris. Its unique mechanism of action involves selectively inhibiting the If current in the sinoatrial node, leading to a reduction in heart rate without affecting myocardial contractility or blood pressure. Since its approval by regulatory agencies such as the FDA in 2015, ivabradine has gained traction as a vital adjunct in cardiovascular therapy, with expanding market potential driven by increasing prevalence of heart failure and related cardiovascular conditions.
This analysis explores the current market landscape of ivabradine HCL, evaluates key drivers and barriers, and projects pricing trends over the coming five years. The insights aim to aid pharmaceutical companies, investors, and healthcare policymakers in strategic decision-making.
Market Landscape and Competitive Position
Existing Market Conditions
The global cardiology drug market is forecasted to grow at a CAGR of approximately 6.3% through 2027, driven by rising cardiovascular disease incidence, aging populations, and increased healthcare access [1]. Ivabradine's role in heart failure management, especially following its inclusion in treatment guidelines, positions it favorably within this expanding sector.
Approved Indications and Market Penetration
Originally approved for chronic stable angina, its expanded indication for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)—particularly after the SHIFT trial demonstrated mortality benefits—has broadened its patient pool [2]. The drug’s primary competitors include beta-blockers and other heart rate-lowering agents, but ivabradine’s selective mechanism offers a distinct niche.
Market Share and Key Players
Major manufacturers such as Amgen (marketed as Corlanor in the U.S.) and Servier (marketed as Procoralan in Europe) dominate supply channels. Patent exclusivity and regulatory approvals influence market share dynamics; notably, the patent exclusivity for Corlanor in the U.S. extends until 2032, shaping pricing strategies and market competition.
Geographic Market Dynamics
North America remains the largest market, driven predominantly by high healthcare spending and prevalence of heart failure. Europe follows, supported by mature healthcare systems and clinical adoption. Emerging markets in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East present significant growth opportunities due to increasing cardiovascular disease burden and improving healthcare infrastructure.
Price Analysis and Projection
Current Pricing Landscape
In the United States, the average wholesale price (AWP) for a 30-day supply of ivabradine HCL is approximately $300–$350, variable based on dosage and formulation. Insurance coverage, patient assistance programs, and generic availability influence actual out-of-pocket expenses.
Europe’s pricing varies widely among countries, often regulated by national health authorities, with prices ranging from €150–€250 per month. In markets where patents have lapsed or are nearing expiration, generic versions have driven prices downward.
Pricing Trends and Future Projections
Short-term (1–2 years):
Patent exclusivity and high clinical demand sustain premium pricing. With initial market penetration plateauing in mature markets, prices are expected to remain relatively stable but may marginally decline due to increased generic competition.
Medium to Long-term (3–5 years):
Approaching patent expiration around 2032 in key markets [3], generic ivabradine HCL is anticipated to enter the market. This will likely lead to substantial price reductions—potentially 40–60%—reflecting typical generic price erosion patterns.
Impact of Generic Entry and Market Competition
As generics gain approval, price competition intensifies. Studies indicate that generic drug prices often reach 20–50% of brand-name costs within five years of market entry [4]. Payers and healthcare systems may push for accelerated generic uptake, further compressing prices.
Pricing Influence of Regulatory and Economic Factors
Price modulation will also depend on regulatory negotiations, price caps, and reimbursement policies, especially in countries with active price control mechanisms like the UK’s National Health Service or Germany’s statutory health insurances.
Strategic Considerations for Stakeholders
-
For Pharma Companies:
Investment in lifecycle management, including seeking new indications, formulation improvements, or combination therapies, will be essential to sustain revenues amid impending patent cliffs. -
For Policymakers and Payers:
Balancing cost containment with access to innovative treatments necessitates transparent negotiations and incentivizing biosimilar development. -
For Investors:
Monitoring patent expiration timelines, pipeline developments, and regional regulatory approvals is critical for valuation assessments.
Conclusion
The ivabradine HCL market is poised for steady growth with a substantial downside risk from upcoming generic competition. Current pricing levels will likely remain stable in the near term, followed by notable decreases over the next five years, driven by patent expirations and market entry of generics. Strategic planning must focus on differentiation through additional indications, formulation innovation, and regional expansion.
Key Takeaways
- Market growth is supported by increasing cardiovascular disease prevalence and expanding indications for ivabradine HCL.
- Pricing in developed markets remains premium due to patent exclusivity, with prices ranging between $300–$350 monthly.
- Time to generic entry around 2032 is expected to cause significant price reductions, potentially by up to 60%.
- Regional disparities influence pricing and market penetration, especially in emerging economies.
- Strategic focus on lifecycle extensions and pipeline diversification is essential to mitigate revenue erosion from generics.
FAQs
1. When does ivabradine HCL patent protection expire in major markets?
Patent protections generally extend until 2032 in key markets like the U.S. and Europe, after which generic versions are expected to enter.
2. What are the primary factors influencing ivabradine pricing?
Patent status, clinical demand, regulatory policies, competition from generics, and regional reimbursement schemes are the main influences.
3. How will generic entrants affect the market in the next five years?
Generic entry is projected to significantly reduce prices (by approximately 40–60%) and increase market accessibility, especially in countries with robust generic acceptance.
4. Are there ongoing clinical trials that could extend ivabradine’s indications?
Yes, ongoing trials are exploring additional uses, including potential benefits in other cardiovascular conditions, which could sustain market interest.
5. What strategies can manufacturers adopt to maintain revenue post-patent expiration?
Investing in new formulations, expanding indications, pursuing biosimilar development, and geographic expansion can help sustain revenues.
References
[1] Grand View Research. Cardiovascular Drugs Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. 2022.
[2] Swedberg K, et al. "Ivabradine in Chronic Heart Failure (SHIFT): a randomized placebocontrolled trial." Lancet. 2010.
[3] U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Patent expiration data for Corlanor. 2022.
[4] IMS Health. Historical Price Erosion Trends for Generic Drugs. 2021.
More… ↓
