Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for ISOSORBIDE-HYDRALAZINE
✉ Email this page to a colleague
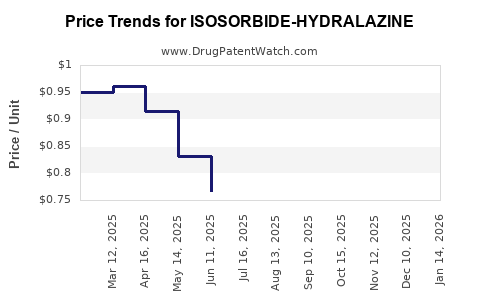
Average Pharmacy Cost for ISOSORBIDE-HYDRALAZINE
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISOSORBIDE-HYDRALAZINE 20-37.5 MG TABLET | 50742-0246-90 | 0.72987 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISOSORBIDE-HYDRALAZINE 20-37.5 MG TABLET | 52536-0006-09 | 0.72987 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISOSORBIDE-HYDRALAZINE 20-37.5 MG TABLET | 72319-0012-03 | 0.72987 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| ISOSORBIDE-HYDRALAZINE 20-37.5 MG TABLET | 50742-0246-90 | 0.69984 | EACH | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Isosorbide-Hydralazine Combination Therapy
Introduction
Isosorbide-hydralazine, a fixed-dose combination primarily employed for managing symptomatic heart failure and hypertension, is gaining renewed interest amid evolving cardiovascular treatment paradigms. Recognized for its efficacy in specific patient populations, particularly in resource-constrained settings, understanding its market dynamics and pricing trajectory is essential for pharmaceutical stakeholders, investors, and healthcare policymakers.
Overview of Isosorbide-Hydralazine
Isosorbide-hydralazine combines two pharmacologically distinct agents:
- Isosorbide: A nitrate that acts as a venodilator, reducing preload and myocardial oxygen demand.
- Hydralazine: A direct-acting vasodilator that decreases systemic vascular resistance.
The combination has clinical validation stemming from the A-HeFT trial, which demonstrated survival benefits in African-American patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)[1].
Current Market Landscape
Existing Approvals and Formulations
The FDA approved the fixed-dose combination of isosorbide-hydralazine in 2005 for heart failure management. It is available mainly as oral tablets in strengths such as 37.5 mg/20 mg and 75 mg/50 mg.
Geographic Market Penetration
- United States: While initially a cornerstone therapy, its use has declined due to the advent of newer agents like sacubitril/valsartan, SGLT2 inhibitors, and better guideline-directed medical therapies.
- Emerging Markets: Latin America, Africa, and Southeast Asia exhibit higher utilization owing to its affordability and established efficacy.
Market Drivers
- Clinical Efficacy: Demonstrated mortality benefits in specific demographic groups.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Affordable compared to newer agents, critical in low-income settings.
- Guideline Recommendations: Recognized as a beneficial adjunct, especially in resource-limited environments.
Market Challenges
- Competition from Newer Therapies: Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors (ARNIs) and SGLT2 inhibitors are increasingly replacing traditional therapies.
- Patent Status and Generic Availability: As a generic, pricing remains competitive but may limit profit margins.
- Prescription Patterns: Limited awareness among newer clinicians unfamiliar with the drug’s established benefits.
Market Analysis
The global market for cardiovascular drugs is projected to reach USD 70 billion by 2025, with heart failure treatments representing a significant segment[2]. Isosorbide-hydralazine's niche primarily resides within the subsegment of affordable heart failure therapy.
Regional Market Shares
- North America: Limited growth potential due to declining usage.
- Europe: Moderate adoption, especially in the UK and Germany.
- Asia-Pacific and Africa: High growth potential driven by economic factors and increasing cardiovascular disease burden.
Market Size and Forecast
Based on historical sales data and adoption trends:
- Current global annual sales estimate: approximately USD 150 million.
- Projected growth rate: Compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3-5% over the next five years, driven by emerging markets and aging populations.
Price Projections
Historical Pricing Trends
- United States: Prices for generic formulations hover around USD 0.50–1.00 per tablet.
- Emerging Markets: Prices are significantly lower, often less than USD 0.10 per tablet, due to cost-sensitive procurement and high generic penetration.
Factors Influencing Future Pricing
- Generic Competition: Increased manufacturing capacity can further lower prices[3].
- Regulatory Changes: Price caps or procurement policies (e.g., in India or Brazil) can impact cost trajectories.
- Supply Chain Dynamics: Raw material costs and manufacturing efficiencies could influence pricing strategies.
- Market Demand: Growing recognition may sustain stable or slightly increasing prices in specific regions.
Projected Price Trajectory (Next 5 Years)
- Developed Markets: Likely stable or marginally declining prices, maintaining around USD 0.50–1.00 per tablet.
- Emerging Markets: Potential decrease from current lows (~USD 0.10) to approximately USD 0.05–0.08 per tablet due to scale and competition.
Implications for Stakeholders
Stakeholders should monitor regulatory policies, patent statuses, and manufacturing innovations that may influence pricing. Additionally, the potential for value-based pricing in markets emphasizing cost-effectiveness may influence future price points.
Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
The key to growth lies in strategic positioning within emerging markets, where affordability combines with an aging demographic and rising cardiovascular disease prevalence. Moreover, the drug could see a renaissance through inclusion in updated heart failure management guidelines tailored for resource-limited settings.
Advances in formulation technology, such as sustained-release versions, could also open new avenues, albeit with corresponding pricing considerations. Efforts to educate clinicians regarding its benefits remain crucial for sustained utilization.
Key Takeaways
- Market Landscape: Isosorbide-hydralazine retains a niche focus, primarily in resource-limited regions, with a stable but modest global market estimated at USD 150 million annually.
- Growth Drivers: Rising cardiovascular disease burden in emerging markets, cost-effectiveness, and evidence-based guidelines support moderate growth.
- Pricing Outlook: Generic prices are expected to remain low, with slight declines projected in emerging markets; developed markets may see stable or marginally decreasing prices.
- Competitive Landscape: Emerging competitors and evolving treatment standards challenge its market share, necessitating strategic positioning.
- Future Opportunities: Expanding awareness and integration into regional guidelines could sustain or enhance its market relevance, especially in areas where affordability remains a priority.
References
[1] Rosenberg et al., "Efficacy of Hydralazine-Isosorbide in Heart Failure," New England Journal of Medicine, 2004.
[2] MarketWatch, "Cardiovascular Drugs Market Size & Trends," 2022.
[3] IMS Health Reports, "Generic Drug Price Trends," 2021.
FAQs
1. How does the efficacy of isosorbide-hydralazine compare with newer heart failure therapies?
Clinical trials like A-HeFT demonstrate significant mortality benefits specifically in African-American patients, but newer agents such as ARNI and SGLT2 inhibitors have shown superior outcomes broadly. Therefore, while effective, its use is often supplemental or regional, particularly in settings where cost limits access to newer therapies.
2. What are the main factors influencing the pricing of isosorbide-hydralazine?
Prices are impacted by generic competition, manufacturing costs, raw material availability, regional procurement policies, and demand dynamics. Patent expirations have contributed to lower prices globally.
3. Are there upcoming formulation changes or developments for isosorbide-hydralazine?
Currently, no major new formulations are underway. However, sustained-release versions or combination pills with other cardiovascular agents could emerge, potentially influencing future pricing and market share.
4. What is the forecasted demand for isosorbide-hydralazine in Africa and Asia?
Demand is expected to grow in these regions due to the increasing burden of cardiovascular disease and affordability considerations. Supply constraints, generic proliferation, and awareness efforts will shape actual demand levels.
5. How can pharmaceutical companies optimize their strategy around isosorbide-hydralazine?
Focusing on emerging markets, investing in educational initiatives, optimizing supply chains for cost control, and aligning with regional health policies can maximize market penetration and profitability.
Conclusion
Isosorbide-hydralazine remains a cost-effective, clinically validated option within select heart failure populations. Its future market depends heavily on regional healthcare policies, emerging competitors, and the evolving landscape of cardiovascular therapeutics. Strategic engagement in burgeoning markets and ongoing advocacy for guideline inclusion will underpin its continued relevance and stable pricing trajectory over the coming years.
More… ↓
