Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART
✉ Email this page to a colleague
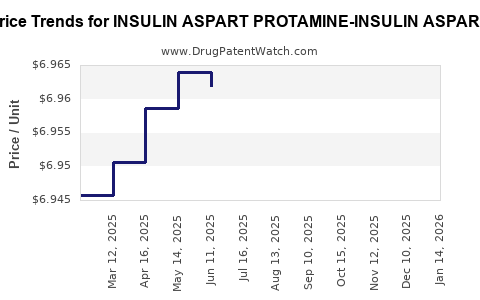
Average Pharmacy Cost for INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART MIX 70-30 FLEXPEN | 73070-0203-15 | 8.94670 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART MIX 70-30 VIAL | 73070-0200-11 | 6.93550 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART MIX 70-30 FLEXPEN | 73070-0203-15 | 8.95588 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| INSULIN ASPART PROTAMINE-INSULIN ASPART MIX 70-30 VIAL | 73070-0200-11 | 6.94212 | ML | 2025-11-19 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for Insulin Aspart Protamine-Insulin Aspart
Introduction
The insulin market, a critical segment within the diabetes management therapeutics landscape, has witnessed significant growth driven by escalating diabetes prevalence globally. Among the myriad of insulin formulations, Insulin Aspart Protamine-Insulin Aspart (hereafter referred to as "Insulin Aspart mix") exemplifies the evolution toward rapid and long-acting combination therapies. This analysis evaluates the current market landscape, competitive positioning, regulatory factors, and projects future pricing trends for this biosimilar or branded formulation.
Market Overview
Global Diabetes Burden and Insulin Demand
The International Diabetes Federation (IDF) estimates that approximately 537 million adults worldwide suffer from diabetes, with projections reaching 643 million by 2030. Insulin therapy remains pivotal, especially for type 1 diabetes and advanced type 2 cases[^1]. The surge in diabetic populations fuels consistent demand for insulin formulations, including mixed preparations like Insulin Aspart Protamine-Insulin Aspart, designed for both basal and prandial glycemic control.
Market Segmentation
The insulin market bifurcates chiefly into:
- Humalog (Lispro) & Novolog (Aspart): Rapid-acting insulin analogs.
- Long-acting analogs: Glargine, Detemir, Degludec.
- Premixed formulations: Combining rapid-acting and intermediate-acting insulins, including Insulin Aspart Protamine-Insulin Aspart.
Insulin Aspart combination formulations are favored for their convenience and improved adherence, accounting for an estimated 25-30% share of the insulin market in developed regions[^2].
Key Manufacturers and Market Penetration
Major pharmaceutical players include Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and emerging biosimilar producers. Notably:
- Novo Nordisk's Fiasp and formulations akin to it hold a substantial market share due to extensive clinical validation.
- Sanofi's NovoRapid also dominates the rapid-acting segment, with biosimilar entries increasing competition.
Emerging biosimilar manufacturers, particularly in Europe and Asia, are expanding access and exerting downward price pressure.
Regulatory and Patent Landscape
Patent Expiry and Biosimilar Entry
The patent landscape substantially influences pricing dynamics. Novo Nordisk’s original insulin Aspart patent expired in key markets around 2017-2019, fostering biosimilar development[^3]. Regulatory pathways for biosimilar approval, especially in the U.S. and Europe, have become more streamlined, encouraging market entry.
Regulatory Approvals
In the U.S., the FDA’s approval of biosimilars under the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act (BPCIA) accelerates generic competition. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has a similar pathway. Approval timelines influence initial pricing and subsequent generic penetration.
Pricing Analysis
Current Pricing Trends
In developed markets, branded Insulin Aspart formulations typically retail at:
- United States: $300–$400 per 10 mL vial.
- Europe: €25–€30 per 3 mL pen.
Biosimilars have introduced price reductions of 20–50%, with some offerings priced as low as $150 per 10 mL vial in competitive regions[^4]. The preponderance of branded insulins sustains high list prices, but discounts and insurance negotiations significantly impact actual patient costs.
Factors Impacting Price Projections
- Market Competition: Entry of biosimilars directly correlates with price declines.
- Manufacturing Costs: Advances in biomanufacturing and supply chain efficiencies are decreasing production expenses.
- Regulatory Policies: Policies favoring biosimilar adoption, including price reimbursement incentives, tend to spur price erosion.
- Market Penetration: Increased access in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) via generic and biosimilar options could lower average global prices.
Future Price Projections
Based on current trajectories and evolutionary industry drivers, the following projections can be outlined:
| Year | Estimated Price Range (per 10 mL vial) | Key Drivers |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | $150–$250 | Biosimilar proliferation, patent expirations |
| 2025 | $120–$200 | Market saturation, manufacturing efficiencies |
| 2030 | $100–$150 | Increased biosimilar adoption, policy shifts |
In emerging economies, prices could drop more aggressively—potentially by 50%–60%—due to local manufacturing, governmental price controls, and broader access initiatives.
Market Drivers and Challenges
Drivers
- Rising Diabetes Prevalence: Continuous growth in insulin-consuming populations.
- Biosimilar Adoption: Cost-effective biosimilars are increasingly replacing branded versions.
- Patient Convenience: Fixed-dose combinations promote adherence.
- Regulatory Support: Streamlined approval processes encourage competition.
Challenges
- Clinical Trust: Prescriber and patient confidence in biosimilars remains a hurdle.
- Intellectual Property Laws: Patent litigation can delay biosimilar entry.
- Pricing Regulations: Governments' price caps and reimbursement policies may limit profit margins.
- Supply Chain Complexity: Biologics require cold chain management, influencing manufacturing and distribution costs.
Strategic Implications and Business Opportunities
Investors, healthcare providers, and manufacturers should consider the following:
- Investment in Biosimilar Development: The expiration of patents presents lucrative opportunities.
- Market Expansion in LMICs: Cost-sensitive regions offer substantial growth prospects.
- Innovative Formulations: Co-formulations and pen delivery devices can strengthen market share.
- Pricing Strategies: Competitive pricing coupled with quality assurance can facilitate increased adoption.
Key Takeaways
- The global insulin market is poised for continued growth, largely driven by rising diabetes prevalence and technological advancements in insulin formulations.
- Insulin Aspart Protamine-Insulin Aspart currently faces pricing pressures from biosimilar competition, with prices trending downward over the next decade.
- Patent expirations and regulatory pathways are catalysts for biosimilar entry, intensifying price competition.
- Manufacturers capable of balancing innovation with cost-efficiency will secure substantial market segments, especially in emerging economies.
- Policy trends favor biosimilar adoption, which will be instrumental in reducing affordability barriers.
FAQs
1. What factors most significantly influence the pricing of Insulin Aspart mixes?
Pricing hinges on market competition, patent status, manufacturer production costs, regulatory environment, and healthcare reimbursement policies.
2. How will biosimilar insulin formulations impact the current market?
Biosimilars are expected to reduce prices by 20–50%, expand access especially in LMICs, and increase competitive pressure on branded products.
3. When are major patent expirations for proprietary Insulin Aspart formulations?
Patents for original Insulin Aspart formulations mainly expired in key global markets between 2017 and 2019, opening avenues for biosimilar development.
4. What regional differences in insulin pricing should market participants consider?
Developed markets generally maintain higher prices due to brand loyalty and insurance rebates, whereas LMICs see lower prices driven by local manufacturing and regulatory controls.
5. What future innovations could influence pricing and market share?
Long-acting and ultra-rapid formulations, smart delivery devices, and combination therapies are potential innovations influencing competition and pricing.
References
[^1]: IDF Diabetes Atlas, 9th Edition, 2019.
[^2]: MarketWatch, "Global Insulin Market Report," 2022.
[^3]: Patent information and biosimilar industry reports, 2021-2022.
[^4]: IQVIA, "Biosimilar Insulin Market Trends," 2022.
More… ↓
