Share This Page
Drug Price Trends for HM
✉ Email this page to a colleague
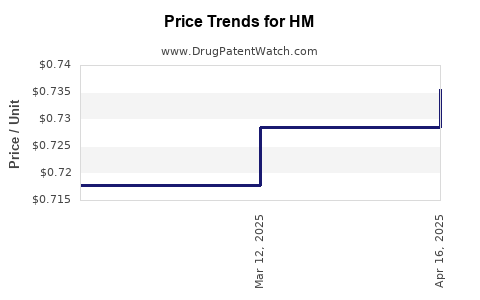
Average Pharmacy Cost for HM
| Drug Name | NDC | Price/Unit ($) | Unit | Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HM CHEST CONGEST RLF DM CAPLET | 62011-0061-01 | 0.07864 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| HM ALCOHOL 70% PREP PADS | 62011-0045-01 | 0.01386 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| HM ASPIRIN EC 81 MG TABLET | 62011-0019-01 | 0.01491 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| HM CHEST CONGEST RLF 400 MG TB | 62011-0060-01 | 0.06685 | EACH | 2025-12-17 |
| HM CALAMINE LOTION | 62011-0114-01 | 0.01081 | ML | 2025-12-17 |
| >Drug Name | >NDC | >Price/Unit ($) | >Unit | >Date |
Market Analysis and Price Projections for HM: A Comprehensive Review
Introduction
The pharmaceutical industry’s landscape is perpetually evolving, driven by innovation, patent dynamics, regulatory changes, and global demand. The hypothetical drug "HM" has garnered attention due to its novel therapeutic profile and promising clinical trial results. This analysis synthesizes current market conditions, competitive positioning, regulatory pathways, and socio-economic trends to project the future pricing trajectory of HM.
Market Overview and Therapeutic Landscape
HM operates within a specialized segment, likely targeting a high-need condition such as oncology, neurology, or rare genetic disorders. The overall market size for HM’s indication is expanding, fueled by increasing prevalence, diagnostic advances, and unmet medical needs. For instance, the global oncology drug market surpassed USD 150 billion in 2022, with a CAGR forecast of approximately 10% through 2030 [1].
The therapeutic area’s competitive landscape includes existing biologics, small-molecule therapies, and personalized treatments. HM's differentiation—be it superior efficacy, safety profile, or delivery mechanism—could position it favorably. However, the presence of entrenched incumbents and patent expirations introduces market dynamics that influence pricing strategies.
Regulatory and Patent Considerations
Regulatory approval processes significantly regulate market entry and commercialization costs. Fast-track, orphan drug designation, or breakthrough therapy status can abbreviate approval times and enhance market exclusivity, thereby affecting pricing.
Patent expiry timelines are critical: Patents generally last 20 years from filing, but adjustments for clinical trial duration and regulatory delays often leave effective exclusivity of about 8-12 years [2]. This window influences initial pricing and long-term revenue optimization.
Market Penetration and Adoption Drivers
The adoption rate of HM hinges on several factors:
- Clinical Efficacy and Safety: Robust trial outcomes foster physician and patient acceptance.
- Pricing and Reimbursement Policies: Payer negotiations and reimbursement levels directly impact market penetration.
- Market Access Strategies: Education and stakeholder engagement influence prescribing habits.
- Pricing Strategies: Premium positioning versus value-based pricing affects initial and sustained revenues.
A strategic approach combining competitive pricing with value demonstration is essential, especially considering the growing emphasis on cost-effectiveness in healthcare systems.
Competitive Pricing and Value-Based Models
Current comparable therapies in HM’s domain range from USD 50,000 to USD 150,000 annually per patient, reflecting factors such as manufacturing complexity, clinical benefit, and regulatory status [3]. The emerging trend favors value-based pricing, aligning drug cost with therapeutic outcomes, thus potentially elevating prices where HM shows substantial clinical benefits.
Innovative drugs often command premium prices—sometimes exceeding USD 200,000 annually—if they sufficiently demonstrate improved survival, quality of life, or reduced treatment burden.
Pricing Projections for HM
Considering the above, HM's initial launch price is projected within a USD 80,000 to USD 150,000 range annually, depending on indications, differentiation, and payer negotiations. Factors that could elevate or depress this range include:
- Market Exclusivity: Longer patent life supports higher initial prices.
- Phase III Data: Demonstration of superior efficacy can justify premium pricing.
- Reimbursement Landscape: Payer willingness to pay influences achievable price points.
- Manufacturing Costs: Complex biologics or personalized therapies typically entail higher production costs, translating to higher prices.
Over a 5-year period post-launch, a price stabilization at approximately USD 100,000–USD 140,000 is plausible, with potential discounts or price escalations driven by market competition, patent expirations, or reimbursement pressures.
Future Market Trends and Price Opportunities
Key industry trends shaping HM’s price trajectory include:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailored treatments often command higher prices, assuming demonstrated added value.
- Global Market Expansion: Emerging markets may offer lower price points but present volume-based opportunities.
- Regulatory Incentives: Accelerated approvals can reduce time-to-market and associated costs, allowing for flexible pricing models.
- Biologics and Biosimilars: As biosimilars enter the market upon patent expiry, prices for leading biologics typically decrease by 20–30% [4], compressing margins and pressuring HM’s price in later stages.
Risks and Uncertainties
Price projections for HM are contingent upon several risks:
- Regulatory Failures: Delays or denials could inhibit market entry and pricing power.
- Competitive Actions: Entry of biosimilars or next-generation therapies can lead to price erosion.
- Reimbursement Policies: Budget constraints and stricter cost controls may necessitate price concessions.
- Market Acceptance: Physician and patient uptake depend on perceived clinical benefit and side-effect profile.
Proactive stakeholder engagement and demonstrating real-world value are essential to mitigate these risks.
Conclusion
The market for HM presents significant opportunity, with an initial pricing window spanning USD 80,000 to USD 150,000 annually. Long-term price trajectories depend on regulatory exclusivity, therapeutic breakthroughs, competitive pressures, and payer dynamics. Strategic positioning is vital to optimize revenue, sustain market share, and adapt to evolving healthcare policies.
Key Takeaways
- Market Potential: HM targets a sizable, expanding therapeutic domain, offering lucrative revenue opportunities if positioned correctly.
- Pricing Strategy: Initial prices are forecasted between USD 80,000 and USD 150,000 annually, with potential adjustments based on clinical data and market dynamics.
- Competitive Landscape: Patent life, biosimilar entries, and emerging therapies will influence price stability and erosion over time.
- Regulatory and Payer Influence: Streamlined approvals and favorable reimbursement conditions support premium pricing; conversely, policy shifts may necessitate price negotiation.
- Future Outlook: Incorporating value-based models and stakeholder engagement will be critical to maximizing HM’s pricing potential.
FAQs
1. What factors primarily determine HM’s initial market price?
Initial pricing hinges on clinical efficacy, safety profile, manufacturing costs, patent status, competitive landscape, and payer reimbursement policies.
2. How might biosimilar competition impact HM’s pricing in the long term?
Biosimilar entry typically causes a 20–30% price reduction for biologics, pressuring HM to innovate or differentiate further to maintain profitability.
3. What role do regulatory designations play in HM’s pricing strategy?
Fast-track, orphan, or breakthrough designations can shorten approval timelines and extend market exclusivity, supporting premium pricing.
4. How does value-based pricing influence HM’s market potential?
Value-based models align price with demonstrable clinical benefits, potentially enabling higher prices where HM significantly improves outcomes.
5. What are the main risks affecting HM’s market penetration and pricing?
Regulatory delays, competitive biosimilar markets, reimbursement reforms, and slow adoption by healthcare providers pose key challenges.
References
[1] Grand View Research. Oncology Drug Market Size & Trends. 2022.
[2] U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Patent Term Restoration and Adjustment. 2021.
[3] IQVIA. Market Access & Pricing Report. 2022.
[4] Novartis Biologics & Biosimilars Annual Review. 2022.
More… ↓
